
Difference Between Homology and Convergent Evolution
- Definition. Homology refers to the existence of shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa while convergent evolution refers to the independent evolution of similar features ...
- Ancestry. ...
- Type of Evolution. ...
- Types of Structures. ...
- Significance. ...
- Genetic Similarities. ...
- Occurrence. ...
- Examples. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What are 2 examples of convergent evolution?
What Is Convergent Evolution?
- Characteristics. Species that are linked through convergent evolution oftentimes look very similar. However, they are not closely related on the tree of life.
- Examples. One example of convergent evolution is the Australian sugar glider and the North American flying squirrel.
- Plants. Plants can also undergo convergent evolution to become more similar. ...
What is convergent and divergent evolution?
Divergent and convergent evolution both explain how specific traits develop in an environment that help a species survive and reproduce. However, divergent evolution leads to speciation, while convergent evolution explains how species that are not closely related can end up with similar traits.
What does convergent evolution mean?
In evolutionary biology, convergent evolution is the process whereby organisms not closely related (not monophyletic), independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. It is the opposite of divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits.
Do homoplasies arise via convergent evolution?
Often, a homoplasy will occur when two very different groups of animals evolve to do the same thing. This is known as convergent evolution, or convergence. Sometimes, a homoplasy trait is called an analogous trait.
How is convergent evolution different from homology quizlet?
How are traits produced by convergent evolution different from homologies? -Traits produced by convergent evolution have not evolved from a common ancestral trait, while homologies have.
Is convergent evolution the result of homology?
Convergent evolution occurs when species occupy similar ecological niches and adapt in similar ways in response to similar selective pressures. Traits that arise through convergent evolution are referred to as 'analogous structures'. They are contrasted with 'homologous structures', which have a common origin.
What is the difference between convergent evolution and evolution?
Convergent Evolution vs. Whereas convergent evolution involves unrelated species that develop similar characteristics over time, divergent evolution involves species with a common ancestor that change to become increasingly different over time.
What is convergent evolution and what is the difference between analogous and homologous structures?
Homologous vs Analogous StructuresHomologous StructureAnalogous StructureA result of divergent evolutionA result of convergent evolutionDeveloped as a result of the adaptation to a different environmentDeveloped as a result of the adaptation to a similar environment5 more rows
What is homology in evolution?
Homology is a central concept of comparative and evolutionary biology, referring to the presence of the same bodily parts (e.g., morphological structures) in different species.
What's the meaning of homology?
Homology definition A homologous relationship or correspondence. noun. The definition of homology is two or more things having the same position or structure. An example of homology in biology is the human arm and the wing of a bird.
What is the relationship between divergent evolution and homologous structures?
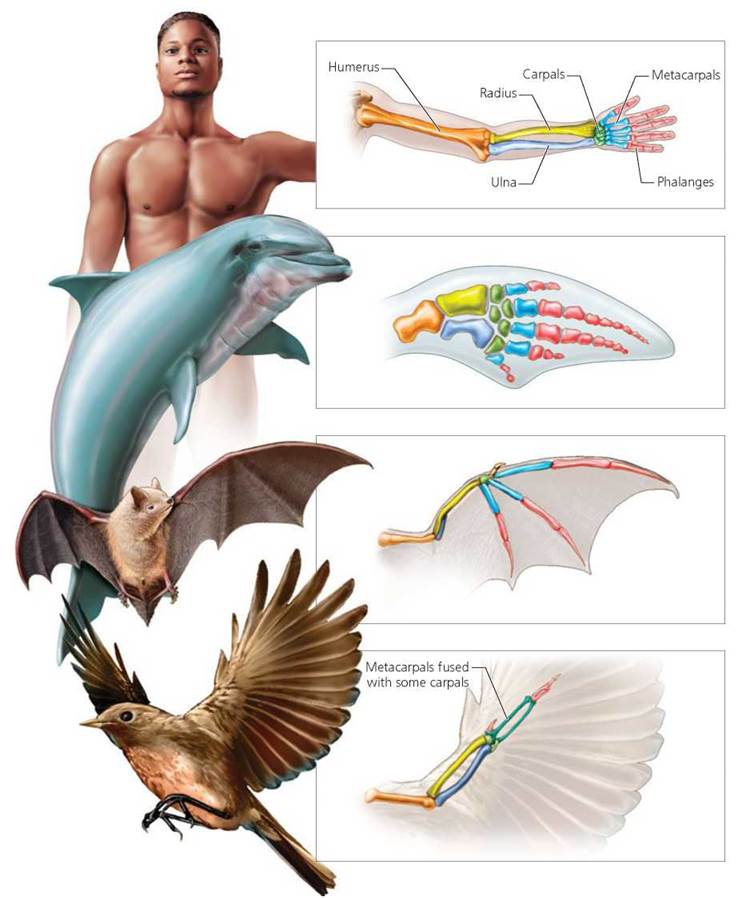
In divergent evolution, homologous structures are structures indicating a species is diverging from its ancestor. These structures need not have the same function as those of the species' ancestors. For example, the forelimbs of humans and bats are homologous structures.
What is convergent evolution explain?
In evolutionary biology, convergent evolution is defined as the process whereby distantly related organisms independently evolve similar traits to adapt to similar necessities.
What is meant by convergent evolution?
It is the independent evolution of features that are similar in species spanning over different eras. This evolution produces analogous structures having similar functions or forms. However, they are not seen in the last common ancestor of those units.
Does convergent evolution produce homologous or analogous structures?
analogous structuresConvergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy.
How would you distinguish between a homologous and an analogous convergent trait on a phylogenetic tree?
The key difference between homologous and analogous structures is that homologous structures are derived from a common ancestral structure while analogous structures are derived from different evolutionary ancestries.
What is the difference between homologous and analogous traits in your answer describe convergent evolution using any two organisms or traits as an example?
Homologous structures share a similar embryonic origin. Analogous organs have a similar function. For example, the bones in a whale's front flipper are homologous to the bones in the human arm. These structures are not analogous.
Is divergent evolution homologous or analogous?
In divergent evolution, species from a common ancestral origin evolve similar anatomical parts (called homologous structures) but with dissimilar functions. One possible cause of divergent evolution is migration.
Does convergent evolution produce homologous or analogous structures?
analogous structuresConvergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy.
How does homology provide evidence for evolution?
Homologous structures provide evidence for common ancestry, while analogous structures show that similar selective pressures can produce similar adaptations (beneficial features). Similarities and differences among biological molecules (e.g., in the DNA sequence of genes) can be used to determine species' relatedness.
What is the difference between homology and homoplasy?
Homology is similarity that reflects common descent and ancestry. Homoplasy is similarity (some might say superficial similarity) arrived at via independent evolution.
What is the difference between convergent and homology?
Generally, homology refers to traits in different species that are descended from a single trait in a common ancestor (and presumably are based on similar, shared genetic mechanisms), while convergent evolution refers to similar traits with very different origins at the gene level. Bats’ and birds’ both evolved similar forelimbs for flight, but that ‘flight’ appears to have occurred independently. Insects fly, too, but this evolved entirely independently. So one can say that flight in insects and bats is a form of convergent evolution, but flight in birds and bats involves homologous structure
What is convergence evolution?
Convergent evolution is the way different animals evolve similar solutions to a problem in life. A clear example is the spindle shape shared by fish, dolphins, ichthyosaurs, and squid. “Fusiform,” it’s called. Half of the squid’s
Why is homology different from analogy?
Rather, it is because of convergent evolution and the fact that each species' environment put similar evolutionary pressures upon it. An example would be the wings of pterodactyls, birds, and bats. They have a somewhat similar structure, but each of these things evolved the trait of wings entirely separately.
Why are parallelism and convergence the same?
The reason for parallelism as well as convergence is the same. The organisms, in order to survive in similar environment, must develop similar biological structures. Parallelism, like convergence, is a matter of adaptation under the control of natural selection. The lack of a tail in gibbons, on the one hand, and the great apes and humans, on the other, is probably a case of parallelism, since their common ancestors probably had tails that were lost in a parallel fashion in the separate evolutionary lines after they diverged. All the monkeys, however, have tails. The Cercopithecidae, the monkeys most closely related to humans and apes, are quite varied in tail length and those species with similar tail lengths are not the most closely related to each other. The tail is a functionally important member used for balance, and very diverse species of Cercopithecidae (the Colobus monkeys and the vervets, for instance) are both arboreal and have long tails, probably as a parallel evolutionary adaptation to arboreal quadrupedal locomotion. Similarly, the reduction of the tail in the brachiating gibbons and the terrestrial Hominoidea is, probably a parallel response to locomotor requirements.
What is the homology of the human body?
Homology is the way parts of organisms match up, even if they don’t look alike or do the same things. There is homology between your arm and a bat’s wing; there’s a bone in the wing that matches each bone in your arm. There’s somewhat less homology between your arm and a horse’s foreleg; the foot matches to your middle finger but none of the other fingers have matches.
Why did we need persistence hunting?
Why? Because we lost sprinting speed by getting upright, so we needed to specialize in persistence hunting
Why are humans considered primates?
Humans are primates and were originally suited for arboreal motion (jumping between tree branches). A couple of million years ago we came down from the trees and adopted bipedal motion (walking and running) - a unique feature in our order. Horses and dogs on the other hand have long specialized in speed and also endurance over long distances - that's probably why we domesticated them in the first place.
What is convergent evolution?
Convergent Evolution Definition. Convergent evolution is the process in which organisms that are not closely related independently evolve similar features. Adaptions may take the form of similar body forms, colors, organs and other adaptions which make up the organism ’s phenotype. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures or ’homoplasies’, ...
What is the term for the evolution of different traits between groups?
Divergent Evolution – The evolution and accumulation of different traits between groups, which results in the formation of new species. Vestigial Structures – A structure or attribute, which is present within an organism but has lost its ancestral function.
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Convergent evolution creates analogous structures or ’homoplasies’, those which have similar forms or functions between diverged species , but were not present in the common ancestor of the two. On the other hand, homologous structures, i.e., a specific organ or bone which appears throughout many different organisms, albeit often in a slightly different form or shape , can indicate a divergence from a common ancestor.
What are the long structures that evolved for collecting nectar?
The long structures (tongues and beaks) evolved for collecting nectar in hummingbirds, bees, moths and butterflies. The evolution of eyespots on the wings of butterflies and the tails of fish. Spines on the bodies of echidnas (monotremes), hedgehogs (mammals) and porcupines (rodents).
Where did mammals evolve?
Separated by the split of continents, mammals evolved to occupy niches in Europe, Africa and America, while marsupials occupied similar niches in Australia and the surrounding islands; this history has produced many examples of convergent evolution.
Is analogous structure convergent?
C is correct. Analogous structures are independently evolved features present in two different species as a product of convergent evolution.
How does divergent evolution work?
As the name implies, divergent evolution shows how species can change slightly over time and separate (diverge) into new forms. For example, in vertebrates like pigs, birds, monkeys and whales, the forelimbs have the same general sets of bones, but they have been modified over time so the animals can use their forelimbs in very different ways. Divergent evolution is studied on a larger scale such as how the current diversity of life on Earth evolved from the first living cells, to a smaller scale where natural selection caused humans and apes to evolve from a common ancestor.
What are the two patterns of evolution?
Over the eons of evolutionary time, organisms have differentiated themselves in recognizable patterns. Two of these patterns are known as convergent and divergent evolution . Both show the ways that organisms have responded to natural selection and provide evidence for the theory of evolution.
Which type of evolution has the same basic structural plan?
The relationship between the analogous structures in different species that evolved through convergent evolution can be less distinct compared to the homologous structures seen in divergent evolution which have the same basic structural plan.
What is the opposite of convergence?
The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution , where related species evolve different traits. Convergent evolution is similar to parallel evolution, which occurs when two independent species evolve in the same direction and thus independently acquire similar characteristics; for instance, gliding frogs have evolved in parallel from multiple types of tree frog .
When two species are similar in a particular character, evolution is defined as: "same as"?
When two species are similar in a particular character, evolution is defined as parallel if the ancestors were also similar, and convergent if they were not. Some scientists have argued that there is a continuum between parallel and convergent evolution, while others maintain that despite some overlap, there are still important distinctions between the two.
What is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time?
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy.
How does phylogenetic reconstruction work?
Phylogenetic reconstruction and ancestral state reconstruction proceed by assuming that evolution has occurred without convergence. Convergent patterns may, however, appear at higher levels in a phylogenetic reconstruction, and are sometimes explicitly sought by investigators.
What did Stephen Jay Gould argue about evolution?
In his 1989 book Wonderful Life, Stephen Jay Gould argued that if one could "rewind the tape of life [and] the same conditions were encountered again, evolution could take a very different course." Simon Conway Morris disputes this conclusion, arguing that convergence is a dominant force in evolution, and given that the same environmental and physical constraints are at work, life will inevitably evolve toward an "optimum" body plan, and at some point, evolution is bound to stumble upon intelligence, a trait presently identified with at least primates, corvids, and cetaceans.
How to measure convergence?
Earlier methods for measuring convergence incorporate ratios of phenotypic and phylogenetic distance by simulating evolution with a Brownian motion model of trait evolution along a phylogeny. More recent methods also quantify the strength of convergence. One drawback to keep in mind is that these methods can confuse long-term stasis with convergence due to phenotypic similarities. Stasis occurs when there is little evolutionary change among taxa.
What is the term for the same phenomenon?
The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight.

What Is Homology
What Is Convergent Evolution
- Convergent evolution is the opposite pattern of evolution to divergent evolution. significantly, the main difference between convergent and divergent evolution is that convergent evolution is the development of similar anatomical structures in several species that live in the same environment. Therefore, their function of that particular structure is similar. However, it may have different phe…
Similarities Between Homology and Convergent Evolution
- Homology and convergent evolution are two mechanisms, which develop similar anatomical structures either structure-wise or function-wise.
- Both are evidence of evolution.
- They derive as adaptations to the changes in the environment.