Formula for Calculating Dividend Discount Model
Dividend discount model
The dividend discount model (DDM) is a method of valuing a company's stock price based on the theory that its stock is worth the sum of all of its future dividend payments, discounted back to their present value. In other words, it is used to value stocks based on the net present value of the future dividends. The equation most widely used is called the Gordon growth model.
Is the dividend discount model accurate?
While the two-stage dividend discount model can provide a more accurate valuation than simpler formulas, it does inherit some disadvantages from its single-rate predecessor, the Gordon Growth Model. Firstly, both models assume constant rates of growth, which is rarely an accurate representation of dividend growth.
What is the formula for common stock dividends?
Dividends per Share Formula = Annual Dividend / No. of Shares Outstanding; Dividend per share = $2,02,500/2,00,000; Dividend per share = $1.01 dividend per share; Example #3. Anand Group of Company has paid annual dividends of $5,000. Outstanding Stock at the beginning was 4000 and Outstanding stock at the end it was 6000.
What is a dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model (DDM) or discounted dividend model is a model used to project the fair value of a stock based on the premise that the stock’s current price should be equal to the present value of all future expected dividends for the stock.
What is the best dividend investment?
- The Dogs of the Dow is a strategy that focuses the 10 Dow Jones Industrial Average stocks with the highest dividend yields.
- The strategy entails building a portfolio of these stocks and reallocating it once a year.
- While it has had some measure of success, investors should be cautious around their level of risk and diversification.

How do you calculate dividend discount in Excel?
1:579:23Implementing the DDM in Excel - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd you see here that our value comes out to $25. Per share.MoreAnd you see here that our value comes out to $25. Per share.
What are the 3 types of dividend discount model DDM?
Three Stage DDM Model to determine the value of equity of a business with three growth stage. The first one will be a fast initial phase, then a slower transition phase and finally ends with a lower rate for the finite period.
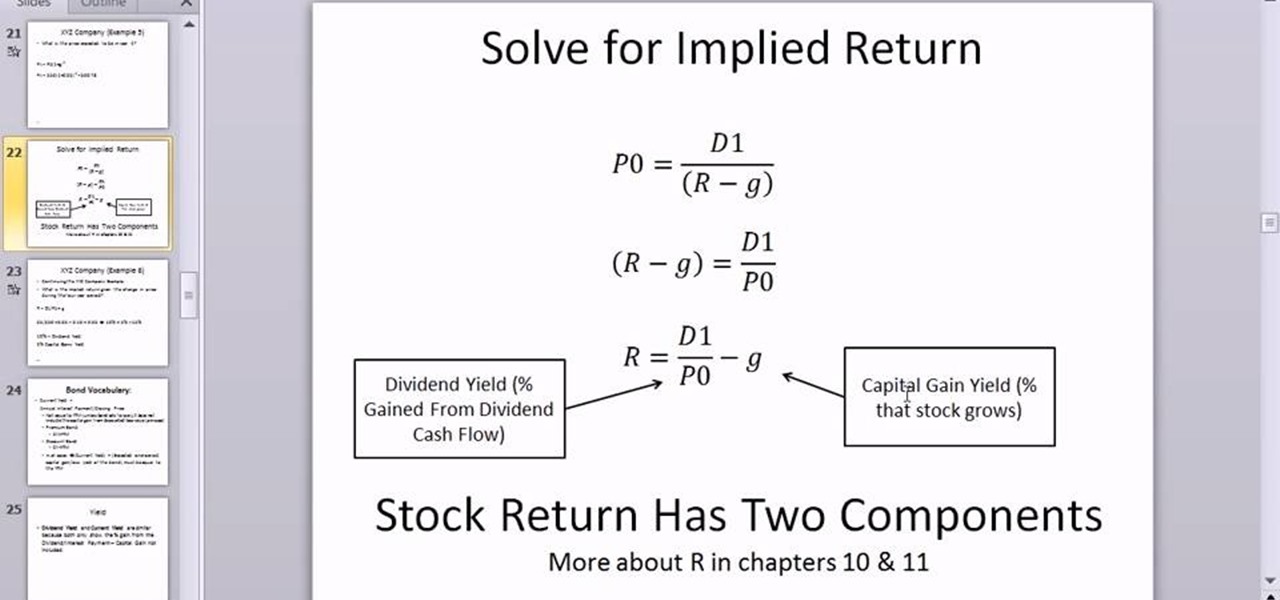
How is D1 DDM calculated?
D1 is dividend per share expected to be received at the end of first year. It may be estimated based on current dividend per share projected for 1 year at the prevailing dividend growth rate (i.e. D1 = D * (1 + g)).
Is dividend discount model the same as dividend valuation model?
The dividend discount model (DDM) is used by investors to measure the value of a stock. It is similar to the discounted cash flow (DFC) valuation method; the difference is that DDM focuses on dividends while the DCF focuses on cash flow. For the DCF, an investment is valued based on its future cash flows.
How is DDM terminal value calculated?
Terminal value is calculated by dividing the last cash flow forecast by the difference between the discount rate and terminal growth rate. The terminal value calculation estimates the value of the company after the forecast period.
How do you calculate K in DDM?
This DDM price is the intrinsic value of the stock....Constant-Growth Rate DDM (aka Gordon Growth Model)D1Intrinsic Value=(k - g)D1 = Next Year's Dividend k = Capitalization Rate g = Dividend Growth Rate
Is WACC used in dividend discount model?
It assumes that the stock's current price contains all the information necessary to discount and extrapolate its future earnings and dividends. The rate of discount for these future cash flows is known as the Weighted Average Cost of Capital or WACC.
Why investors use dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model allows the investor to determine a reasonable price for a stock based on an estimate of the amount of cash it will return in current and future dividends. DDM is one way of estimating the intrinsic value of a stock.
What is the discount rate formula?
How to calculate discount rate. There are two primary discount rate formulas - the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) and adjusted present value (APV). The WACC discount formula is: WACC = E/V x Ce + D/V x Cd x (1-T), and the APV discount formula is: APV = NPV + PV of the impact of financing.
When should you not use DDM?
There are a few key downsides to the dividend discount model (DDM), including its lack of accuracy. A key limiting factor of the DDM is that it can only be used with companies that pay dividends at a rising rate. The DDM is also considered too conservative by not taking into account stock buybacks.
What is a two-stage DDM?
Two-Stage DDM: Considered a “multi-stage” DDM, the two-stage DDM determines the value of a company's share price with the model split between an initial forecast period of increased divident growth and then a period of stable dividend growth.
What are the assumptions of dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model was developed under the assumption that the intrinsic value of a stock reflects the present value of all future cash flows generated by a security. At the same time, dividends are essentially the positive cash flows generated by a company and distributed to the shareholders.
What is a two-stage DDM?
Two-Stage DDM: Considered a “multi-stage” DDM, the two-stage DDM determines the value of a company's share price with the model split between an initial forecast period of increased divident growth and then a period of stable dividend growth.
What is two-stage dividend discount model?
The two-stage dividend discount model comprises two parts and assumes that dividends will go through two stages of growth. In the first stage, the dividend grows by a constant rate for a set amount of time. In the second, the dividend is assumed to grow at a different rate for the remainder of the company's life.
What are the assumptions of the dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model was developed under the assumption that the intrinsic value of a stock reflects the present value of all future cash flows generated by a security. At the same time, dividends are essentially the positive cash flows generated by a company and distributed to the shareholders.
What is the H model?
The H-model is a quantitative method of valuing a company's stock price. The model is very similar to the two-stage dividend discount model. However, it differs in that it attempts to smooth out the growth rate over time, rather than abruptly changing from the high growth period to the stable growth period.
What is dividend discount?
The dividend discount model was developed under the assumption that the intrinsic value#N#Intrinsic Value The intrinsic value of a business (or any investment security) is the present value of all expected future cash flows, discounted at the appropriate discount rate. Unlike relative forms of valuation that look at comparable companies, intrinsic valuation looks only at the inherent value of a business on its own.#N#of a stock reflects the present value of all future cash flows generated by a security. At the same time, dividends are essentially the positive cash flows generated by a company and distributed to the shareholders.
What is a one period discount dividend?
The former is applied when an investor wants to determine the intrinsic price of a stock that he or she will sell in one period (usually one year) from now.
What is multi-period dividend discount?
The multi-period dividend discount model is an extension of the one-period dividend discount model wherein an investor expects to hold a stock for multiple periods. The main challenge of the multi-period model variation is that forecasting dividend payments for different periods is required.
How to find intrinsic value of a stock?
The intrinsic value of a stock (via the Multiple-Period DDM) is found by estimating the sum value of the expected dividend payments and the selling price, discounted to find their present values.
What are the shortcomings of the DDM model?
A shortcoming of the DDM is that the model follows a perpetual constant dividend growth rate assumption. This assumption is not ideal for companies with fluctuating dividend growth rates or irregular dividend payments, as it increases the chances of imprecision.
What is a DDM multiple period?
In the multiple-period DDM, an investor expects to hold the stock he or she purchased for multiple time periods. Therefore, the expected future cash flows will consist of numerous dividend payments, and the estimated selling price of the stock at the end of the holding period.
What is a one year DDM?
The one-period DDM generally assumes that an investor is prepared to hold the stock for only one year. Because of the short holding period, the cash flows expected to be generated by the stock are the single dividend payment and the selling price of the respective stock.
What is dividend discount model?
Dividend Discount Model, also known as DDM, in which stock price is calculated based on the probable dividends that will be paid and they will be discounted at the expected yearly rate. In simple words, it is a way of valuing a company based on the theory that a stock is worth the discounted sum of all of its future dividend payments. In other words, it is used to evaluate stocks based on the net present value of future dividends.
What is a variable growth rate dividend discount model?
This model solves the problems related to unsteady dividends by assuming that the company will experience different growth phases.
Why do companies keep their dividends in sync?
Consistency – Since dividends in most cases are paid by cash, companies tend to keep their dividend payments in sync with the business fundamentals. This implies that companies may not want to manipulate dividend payments as they can directly lead to stock price volatility.
What are some examples of dividend paying companies?
Some examples of regular dividend-paying companies are McDonald’s, Procter & Gamble, Kimberly Clark, PepsiCo, 3M, CocaCola, Johnson & Johnson, AT&T, Walmart, etc. We can use the Dividend Discount Model to value these companies.
What is the value of a stock?
The financial theory states that the value of a stock is worth all of the future cash flows expected to be generated by the firm discounted by an appropriate risk-adjusted rate. We can use dividends as a measure of the cash flows returned to the shareholder.
What can we do to improve the two stage DDM model?
One improvement that we can make to the two-stage DDM Model is to allow the growth rate to change slowly rather than instantaneously.
What happens if a stock pays no dividends?
If the stock pays no dividends, then the expected future cash flow will be the sale price of the stock. Let us take an example.
What is dividend discount model?
Dividend Discount Model (DDM) is a method valuation of a company’s stock which is driven by the theory that the value of its stock is the cumulative sum of all its payments given in the form of dividends which we discount in this case to its present value. In simpler words, this method is used to derive the value of the stocks based on the net present value of dividends to be distributed in the future.
Why is dividend growth rate model important?
The dividend growth rate model is a very effective way of valuing matured companies. It is advantageous because it is much more reliable and proven. Since it doesn’t depend on mathematical assumptions and techniques it is much more realistic.
What is a DDM?
A DDM is a valuation model where the dividend to be distributed related to a stock for a company is discounted back to the cumulative net present value and calculated accordingly. It is a quantitative method to determine or predict the price of a stock pertaining to a company. It majorly excludes all the external market conditions and only considers the fair value of the stock. The two factors which it takes into consideration is dividend pay-out factors and expected market returns. If the value obtained from the calculation of DDM for a particular stock is higher than the current trading price of the stock in the market we term the stock as undervalued and similarly if the value obtained from the calculation of DDM for a particular stock is lower than the current trading price of the stock in the market we term the stock as overvalued. In this method the base which the dividend discount model relies upon is the concept of the time value of money.
What is Gordon growth model?
This is also known as the Gordon Growth Model and assumes that dividends are growing by a fixed specific percentage each year. Constant growth models are specific to the valuation of matured companies only whose dividends have been growing steadily over time.
How many phases does a growth model take?
The model takes into the assumption that the growth will be divided into three or four phases. The first one will be fast initial phase, then a slower transition phase and finally ends with a lower rate for the finite period. This is more realistic when compared to the other two methods. The model solves the problem of a company giving unsteady dividends which is a true picture during the variable growth phases of a company.
Does dividend discount have dividend growth?
The traditional model for dividend discount is shown below with no dividend growth
Is the dividend model a trusted one?
Thus the company will never try to manipula te this number as it can ham per their stock price volatility which means this model is a trusted one.
What is the value of a share under the dividend discount model?
Under the dividend discount model (DDM), the value per share of a company under is equal to the sum of the present value of all expected dividends to be issued to shareholders.
What is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM)?
The Dividend Discount Model (DDM) states that the intrinsic value of a company is a function of the sum of all the expected dividends, with each payment discounted to the present date.
What is the difference between a DDM and a DCF?
The dividend discount model (DDM) states that a company is worth the sum of the present value (PV) of all its future dividends, whereas the discounted cash flow model (DCF) states that a company is worth the sum of its discounted future free cash flows (FCFs).
How to discount dividend payments?
The formula for discounting each dividend payment consists of dividing the DPS by (1 + Cost of Equity) ^ Period Number.
What is Gordon growth DDM?
Gordon Growth DDM: Frequently called the constant growth DDM, as implied by the name, the Gordon Growth variation attaches a perpetual dividend growth rate with no percentage change throughout the entirety of the forecast.
What is discount rate?
The discount rate used must represent the required rate of return ( i.e. the minimum hurdle rate) for the group of capital provider (s) who receive or have a claim to the cash flows being discounted.
What is a two stage DDM?
Two-Stage DDM: Considered a “multi-stage” DDM, the two-s tage DDM determines the value of a company’s share price with the model split between an initial forecast period of increased growth and then a period of stable growth.
How to calculate dividend discount?
It is next year’s expected dividend divided by an appropriate discount rate, less the expected dividend growth rate.
Who created the dividend discount model?
Myron Gordon and Eli Shapiro created the dividend discount model at the University of Toronto in 1956.
Why is dividend growth important?
The dividend growth rate is critically important in determining the fair value of a stock with the dividend discount model.
What is dividend discount?
Updated on April 18th, 2019 by Bob Ciura. The Dividend Discount Model is a valuation formula used to find the fair value of a dividend stock. “Everything should be as simple as it can be, but not simpler”. – Attributed to Albert Einstein. The elegance of the dividend discount model is its simplicity.
How many inputs are needed to find the fair value of a dividend paying stock?
The elegance of the dividend discount model is its simplicity. The dividend discount model requires only 3 inputs to find the fair value of a dividend paying stock.
What is the long term inflation adjusted return of the market not accounting for dividends?
The long-term inflation adjusted return of the market not accounting for dividends is 2.5%. Inflation is expected to be at 1.6% over the next decade. The current dividend yield on the S&P 500 is 1.3%. A fair estimate of market return to use in the CAPM formula is 5.4% (2.5% + 1.6% + 1.3%).
What happens when there is a gap between the discount rate and the growth rate?
There is a hidden advantage here. You don’t have to be right for as long.
Dividend Discount Model Definition
Our online Dividend Discount Model Calculator is a free financial calculator that makes it a snap to learn how to calculate the worth of a stock based on the dividend discount model.
How to Calculate Dividend Discount Model
Let's be honest - sometimes the best dividend discount model calculator is the one that is easy to use and doesn't require us to even know what the dividend discount model formula is in the first place! But if you want to know the exact formula for calculating dividend discount model then please check out the "Formula" box above.
Add a Free Dividend Discount Model Calculator Widget to Your Site!
You can get a free online dividend discount model calculator for your website and you don't even have to download the dividend discount model calculator - you can just copy and paste! The dividend discount model calculator exactly as you see it above is 100% free for you to use.
Breaking Down The Dividend Discount Model
- The dividend discount model was developed under the assumption that the intrinsic valueof a stock reflects the present value of all future cash flows generated by a security. At the same time, dividends are essentially the positive cash flows generated by a company and distributed to the shareholders. Generally, the dividend discount model provides...
Formula For The Dividend Discount Model
- The dividend discount model can take several variations depending on the stated assumptions. The variations include the following:
Notable Shortcomings of The DDM
- A shortcoming of the DDM is that the model follows a perpetual constant dividend growth rate assumption. This assumption is not ideal for companies with fluctuating dividend growth rates or irregular dividend payments, as it increases the chances of imprecision. Another drawback is the sensitivity of the outputs to the inputs. Furthermore, the model is not fit for companies with rate…
Related Readings
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to the Dividend Discount Model. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: 1. Capital Gains Yield 2. Dividend Per Share 3. Ex-Dividend Date 4. Stock Option
Explained in Detail
Formula
- Dividend Discount Model = Intrinsic Value = Sum of Present Value of Dividends + Present Value of Stock Sale Price. This dividend discount model or DDM model price is the stock’sintrinsic value. If the stock pays no dividends, then the expected future cash flow will be the sale price of the stock. Again, let us take an example.
Dividend Discount Model Example
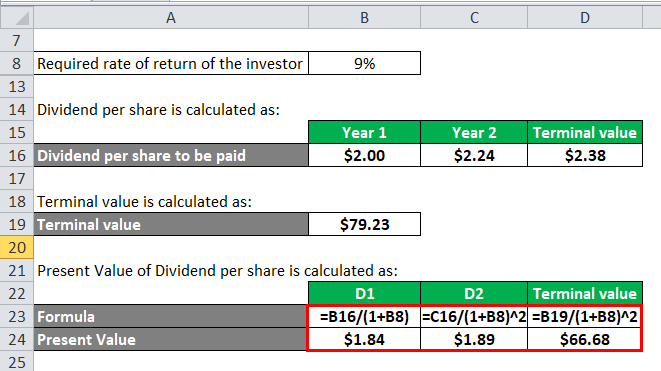
- In this dividend discount model example, assume that you are considering the purchase of a stock which will pay dividends of $20 (Dividend 1) next year and $21.6 (Dividend 2) the following year. After receiving the second dividend, you plan on selling the stock for $333.3. What is the intrinsic value of this stock if your required return is 15%? Solution: One can solve this dividend discount …
Types of Dividend Discount Models
- Now that we have understood the very foundation of the dividend discount model let us move forward and learn about three types of dividend discount models. You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked For eg: Source: Dividend Discount Model (DDM)(wallst…
Advantages
- Sound Logic –The dividend discount model tries to value the stock based on the future cash flow profile. Here, the future cash flows are nothing but dividends. In addition, there is very little sub...
- Mature Business –The regular payment of dividends does imply that the company has matured, and there may not be much volatility associated with the growth rates and earnings…
- Sound Logic –The dividend discount model tries to value the stock based on the future cash flow profile. Here, the future cash flows are nothing but dividends. In addition, there is very little sub...
- Mature Business –The regular payment of dividends does imply that the company has matured, and there may not be much volatility associated with the growth rates and earnings. That is important for...
- Consistency –Since dividends are paid by cash in most cases, companies tend to keep their dividend payments in sync with the business fundamentals. It implies that companies may not want to manipul...
Limitations
- For understanding the limitations of the dividend discount model, let us take the example of Berkshire Hathaway. Amazon, Google, Biogen are other examples that don’t pay dividendsand have given some amazing returns to the shareholders. 1. One can only use it to value mature companies –This model efficiently values mature companies and cannot value high-growth com…
What Next?
- Please comment below if you learned something new or enjoyed this dividend discount model post. Let me know what you think. Many thanks, and take care. Happy learning!
Recommended Articles
- This article has been a guide to what is the Dividend Discount Model. Here, we discuss dividend discount model types (zero-growth, constant-growth, and variable-growth – 2 stages and 3 stages), dividend model formula with practical examples, and case studies. 1. Gordon Growth Model Calculation 2. CAPM Beta 3. Alibaba Valuation Guide 4. Terminal Value Formula