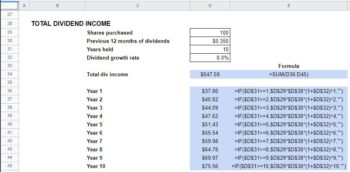
To calculate dividends for a given year, do the following:
- Take the retained earnings at the beginning of the year and subtract it from the the end-of-year number. That will tell you the net change in retained earnings for the year.
- Next, take the net change in retained earnings, and subtract it from the net earnings for the year. ...
How do you calculate dividends?
Article SummaryX. To calculate dividends, find out the company's dividend per share (DPS), which is the amount paid to every investor for each share of stock they hold. Next, multiply the DPS by the number of shares you hold in the company's stock to determine approximately what you're total payout will be.
Are dividends an expense on the income statement?
Key Takeaways Cash or stock dividends distributed to shareholders are not recorded as an expense on a company's income statement. Cash dividends are cash outflows to a company's shareholders and are recorded as a reduction in the cash and retained earnings accounts.
How do you calculate dividends from DPS?
Finding Total Dividends from DPS Determine how many shares of stock you hold. If you're not already aware of how many shares of company stock you own, find out. Determine the dividends paid per share of company stock. Find your company's dividends per share (or "DPS") value. Multiply the DPS by the number of shares.
How do you convert dividends to per share?
Once you have the total dividends, converting that to per-share is a matter of dividing it by shares outstanding, also found in the annual report. Here is the formula for dividends per share: Total dividends ÷ shares outstanding = dividends per share.
How is a dividend payment calculated?
The dividend payment for a stock is stated on a per share basis and expressed by the dividends per share (DPS) ratio. This ratio is calculated by taking the total dividends paid out by a company over a period of time and dividing it by the total number of common stock shares held by its stockholders.
Where is dividend expense on the income statement?
Dividends on common stock are not reported on the income statement since they are not expenses. However, dividends on preferred stock will appear on the income statement as a subtraction from net income in order to report the earnings available for common stock.
How do you calculate dividends per shareholder?
Dividends per share is calculated by dividing the total number of dividends paid out by a company (including interim dividends) over a period of time, by the number of shares outstanding.
What is a dividend expense?
Dividend Expenses means, to the extent not included in Net Income (Loss), any dividends paid in cash, Capital Stock, in kind or otherwise, in respect of any Capital Stock issued at any time by the Corporation or any of its Consolidated Entities.
Why can dividends be an expense?
Dividends are not considered an expense, because they are a distribution of a firm's accumulated earnings. For this reason, dividends never appear on an issuing entity's income statement as an expense. Instead, dividends are treated as a distribution of the equity of a business.
What is a good dividend per share?
A good dividend yield varies depending on market conditions, but a yield between 2% and 6% is considered ideal.
What is dividend per share with example?
For example, assume ABC company paid a total of $237,000 in dividends over the last year, during which there was a special one-time dividend totaling $59,250. ABC has 2 million shares outstanding, so its DPS is ($237,000-$59,250)/2,000,000 = $0.09 per share.
Are dividends paid per share?
A dividend is paid per share of stock — if you own 30 shares in a company and that company pays $2 in annual cash dividends, you will receive $60 per year.
Is dividends an asset or expense?
For shareholders, dividends are an asset because they increase the shareholders' net worth by the amount of the dividend. For companies, dividends are a liability because they reduce the company's assets by the total amount of dividend payments.
Are dividends a company expense?
A dividend is a payment a company can make to shareholders if it has made a profit. You cannot count dividends as business costs when you work out your Corporation Tax. Your company must not pay out more in dividends than its available profits from current and previous financial years.
Where does a dividend go on a balance sheet?
If a company pays stock dividends, the dividends reduce the company's retained earnings and increase the common stock account. Stock dividends do not result in asset changes to the balance sheet but rather affect only the equity side by reallocating part of the retained earnings to the common stock account.
Where are dividends reported?
If you receive over $1,500 of taxable ordinary dividends, you must report these dividends on Schedule B (Form 1040), Interest and Ordinary Dividends. If you receive dividends in significant amounts, you may be subject to the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) and may have to pay estimated tax to avoid a penalty.
How to calculate dividends per share?
This represents the amount of dividend money that investors are awarded for each share of company stock they own. For a given time period, DPS can be calculated using the formula DPS = (D - SD)/S where D = the amount of money paid in regular dividends, SD = the amount paid in special, one-time dividends, and S = the total number of shares of company stock owned by investors.
What is total dividend?
Total dividends are regular dividends plus "special" (one-time) dividends.
How do companies make money?
On one hand, it can reinvest this money in the company by expanding its own operations, buying new equipment, and so on. (Money spent this way is called "retained earnings.") Alternatively, it can use its profits to pay its investors. Money paid to investors in this way is called a "dividend". Calculating the dividend that a shareholder is owed by a company is generally fairly easy; simply multiply the dividend paid per share (or "DPS") by the number of shares you own. It's also possible to determine the "dividend yield" (the percentage of your investment that your stock holdings will pay you in dividends) by dividing the DPS by the price per share.
How much do you make on 7.5% stock?
Simple math will tell you that you will make approximately $.09 for each share in a year on the 7.5% stock, and $1.90 on the 6.8% stock. The % stated typically does not include special dividend payments. Dividends are not guaranteed and can be adjusted or taken away altogether at anytime with the approval of the board of directors.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield is the percentage of your investment that a stock will pay you back in the form of dividends. Dividend yield can be thought of as an "interest rate" on a stock. To get started, you'll need to find the current price per share of the stock you're analyzing.
What does it mean when a stock price falls?
Price movements reflect supply and demand. If a stock's price falls, that indicates the buying public is simply not as interested in acquiring shares of that stock as it used to be, or the drop may occur after the company has issued more shares.
How to find out how many shares of stock you own?
If you're not already aware of how many shares of company stock you own, find out. You can usually get this information by contacting your broker or investment agency or checking the regular statements that are usually sent to a company's investors via mail or email.
What is a Stock?
A stock allows ordinary individuals to own a small fraction of a corporation. One unit of a stock is referred to as a “share”. Those who purchase shares of a corporation’s stock are referred to as shareholders.
What are Dividends?
Dividends are cash payments to the shareholders of a stock. Each shareholder receives a dividend for every share they own of the stock. The amount of the dividend is determined by the company’s Board of Directors.
Why do companies pay dividends?
Dividends are paid by companies as a mechanism to share part of their profits. They can also be used as a way to entice investors to purchase the company’s stock and hold onto it.
Are dividends guaranteed?
No, dividends are not guaranteed. The company’s Board of Directors will decide each quarter what dividend amount to pay, based on business conditions.
Do all companies pay dividends?
No, only a subset of stocks pay dividends to shareholders. The ones that do tend to be relatively mature organizations, with stable businesses, and stable profits.
How often are dividends paid?
Usually, dividends are paid quarterly to shareholders, though there are some stocks where dividends are paid monthly, annually, or twice per year.
What is dividend yield?
Dividend yield is a percentage that measures the annual dividend payment of a stock compared with the current stock price.
Why is Dividend Expense?
The dividends are regarded as the residual profits that are distributed by the business from the residual earnings that it had earned from the previous financial year. These profits are distributed in the hand of the investors of the business to make investors retain with the business as stakeholders, and in better terms, this is regarded as a practice to boost investor confidence towards the business as a whole. Therefore, for the purpose of both taxes and reporting, the dividends are never classified as expenses.
Why can't dividends be classified as dividend expense?
Therefore, another reason why dividends can never be classified as dividend expense is that such entries happen at the balance sheet level, and no journal is created on the income statement level. In dividend accounting, normally, dividend declaration date, dividend date, payment date, and record date are regarded as critical dates. The dividend declaration date is regarded as the date when the board of directors officially declare the net profit value to be declared as dividends. Similarly, the record date is defined as the date where the shareholders are recorded in the book of accounts of the business. Finally, the in-dividend date is basically the trading day which is the final day where the shareholders being the part of the business on this specific day are entitled to receive the dividends.
What happens when a company declares dividends?
Whenever the business declares the dividends, they reduce the balance in the shareholder equity. When declared at the declaration date, the dividends would be a creation of a journal entry. The journal entry would create a debit to the equity account and credit to the dividend payable account. When the dividends are paid out officially on the pay-out date, the dividends will get debited from the dividend payable account. The corresponding journal entry would be a credit to the cash account in the balance sheet.
Can dividends be classified as an expense?
Dividends are basically residual profits that are distributed to the shareholders from the retained earnings that the business generates round the year and, therefore, cannot be classified as an expense. If classified as an expense, the dividends would give the business a handle to write them off and report out profits equivalent to zero, thereby evading taxes. The business has to report dividends under the cash flow statement of the balance sheet under the column of the financing activities. The amount reported under the financing activities then reduces the ending cash balance of the business. Whenever the business declares the dividends, they reduce the balance in the shareholder equity. Therefore, another reason why dividends can never be classified as dividend expense is that such entries happen at the balance sheet level, and no journal is created on the income statement level.
Is dividend an operational expense?
Moreover, the operational expenses are defined as expenses that are borne by the business on a day to day business. Similarly, the cost of goods sold is regarded as the cost that comes in building the finished goods. Therefore, dividends can never be classified as operational expense or cost of goods sold since the dividends are generally distributed once or twice a year. Therefore, they have no relevance in building products or are not borne on a daily basis. Moreover, the business always has the capability to modify or cancel out the dividend policy, and thus such values may then go un-reported in the financial statements of the business. The dividends, however, influence the cash flow statement of the business. The dividends, therefore, influence the financing activities of the cash flow statement wherein it reduces the cash balance of the business, and although they cannot be classified as an expense, they basically reduce the ending balance of the cash.
Can retained earnings be used to make dividends?
To avoid such a case, the business has to retain some profits in their savings account, and that could be regarded as retained earnings. They have to maintain and keep accumulating the profits in such an account, which would help them make a surplus. From the surplus, they can start the dividend distribution. The retained earnings account has to be presented in the balance sheet account.
Does dividends affect cash flow?
Whenever it declares the dividends to the shareholders, the business generally has an impact on the cash flow statement. This is because the business has to report dividends under the cash flow statement of the balance sheet under the column of the financing activities. The amount reported under the financing activities then reduces the ending cash balance of the business.
How are dividends paid?
How Dividends Are Paid. Whether paid in cash or in stock, dividends generally are announced, or "declared," by a company and are then paid out on a quarterly basis at a specified date. Investors are paid in proportion to their holdings. For example, a company might pay a dividend of .25 cents per share, payable 60 days from the date ...
What is a cash dividend?
Cash dividends are cash outflows to a company's shareholders and are recorded as a reduction in the cash and retained earnings accounts. Stock dividends reallocate part of a company's retained earnings to its common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts.
Why do dividends show up in cash flow?
Because cash dividends are not a company's expense, they show up as a reduction in the company's statement of changes in shareholders' equity. Cash dividends reduce the size of a company's balance sheet and its value since the company no longer retains part of its liquid assets . However, cash dividends also impact a company's cash flow statement.
How do dividends affect shareholders?
Instead, dividends impact the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet. Dividends, whether cash or stock, represent a reward to investors for their investment in the company. While cash dividends reduce the overall shareholders' equity balance, stock dividends represent a reallocation of part of a company's retained earnings to ...
What is cash flow?
Cash flow refers to the inflows or increases as well as the outflows or reductions in cash. Cash dividends impact the financing activities section of the cash flow statement by showing a reduction in cash for the period. In other words, although cash dividends are not an expense, they reduce a company's cash position.
Why are dividends not included in income statement?
The cost of dividends is not included in the company's income statement because they're not an operating expense, which are the costs to run the day-to-day business. A company's dividend policy can be reversed at any time and that, too, will not show up on its financial statements .
Why is dividends important?
A company's history of dividends is an important factor in many investors' decision-making process. Dividends tend to be most prized by relatively conservative investors who buy stocks for the long term, and by investors who value the regular income they provide.
How to calculate dividends?from wikihow.com
To calculate dividends for a given year, do the following: 1 Take the retained earnings at the beginning of the year and subtract it from the the end-of-year number. That will tell you the net change in retained earnings for the year. 2 Next, take the net change in retained earnings, and subtract it from the net earnings for the year. If retained earnings has gone up, then the result will be less than the year's net earnings. If retained earnings have fallen, then the result will be greater than the net earnings for the year.
How to find dividend yield?from wikihow.com
Divide the DPS by the share price. Finally, divide your DPS value by the price per share for the stock you own to find your dividend yield (or, in other words, use the formula DY = DPS/SP ). This simple ratio compares the amount of money you are paid in dividends to the amount of money you had to pay for the stock to begin with. The greater the dividend yield, the more money you'll earn on your initial investment.
How to find the DPS of a stock?from wikihow.com
Again, the formula is DPS = (D - SD)/S where D = the amount of money paid in regular dividends, SD = the amount paid in special, one-time dividends, and S = the total number of shares of company stock owned by all investors.
How to find retention ratio of dividends?from wallstreetmojo.com
This dividend can also be used to find out the retention ratio of the company. When you subtract the dividend payout ratio from 1, you will get the retention ratio Retention Ratio Retention ratio indicates the percentage of a company’s earnings which is not paid out as dividends but credited back as retained earnings. This ratio highlights how much of the profit is being retained as profits towards the development of the firm. read more, which depicts how much the company is confident for its future and how much they want to invest.
What happens when you subtract dividend payout ratio from 1?from wallstreetmojo.com
When you subtract the dividend payout ratio from 1, you will get the retention ratio, which depicts how much the company is confident for its future and how much they want to invest. This kind of ratios are mostly used by the stock analyst, investors to ascertain the confidence of the company.
What is dividend payout ratio?from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Dividend Payout Ratio Dividend Payout Ratio is the amount of dividends paid to shareholders in relation to the total amount of net income generated by a company. Formula, example
How do companies make money?from wikihow.com
On one hand, it can reinvest this money in the company by expanding its own operations, buying new equipment, and so on. (Money spent this way is called "retained earnings.") Alternatively, it can use its profits to pay its investors. Money paid to investors in this way is called a "dividend". Calculating the dividend that a shareholder is owed by a company is generally fairly easy; simply multiply the dividend paid per share (or "DPS") by the number of shares you own. It's also possible to determine the "dividend yield" (the percentage of your investment that your stock holdings will pay you in dividends) by dividing the DPS by the price per share.
How to calculate dividend payout ratio?
We can use the below formula to calculate dividends and come out with dividend payout Dividend Payout The dividend payout ratio is the ratio between the total amount of dividends paid (preferred and normal dividend) to the company's net income. Formula = Dividends/Net Income read more.
What happens when you subtract dividend payout ratio from 1?
When you subtract the dividend payout ratio from 1, you will get the retention ratio, which depicts how much the company is confident for its future and how much they want to invest. This kind of ratios are mostly used by the stock analyst, investors to ascertain the confidence of the company.
How to find retention ratio of dividends?
This dividend can also be used to find out the retention ratio of the company. When you subtract the dividend payout ratio from 1, you will get the retention ratio Retention Ratio Retention ratio indicates the percentage of a company’s earnings which is not paid out as dividends but credited back as retained earnings. This ratio highlights how much of the profit is being retained as profits towards the development of the firm. read more, which depicts how much the company is confident for its future and how much they want to invest.
Why is dividend important?
Furthermore, it tells one about how much is the firm or the organization is rewarding or, in order words, paying the dividend to its stockholders. And further again, how much the firm or the organization is reinvesting into itself, which can be called the retained earnings.
What is the dividend of an organization?
Dividend Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed ...
What is reinvestment in investing?
Reinvest Reinvestment is the process of investing the returns received from investment in dividends, interests, or cash rewards to purchase additional shares and reinvesting the gains. Investors do not opt for cash benefits as they are reinvesting their profits in their portfolio. read more.
Does Patel Limited pay dividends?
Patel limited last paid dividend for 150,000 when it made a net profit for 450,000. This year also, the company is looking to pay a dividend as they have done spectacular business, and shareholders are pleased about it. The company has decided to increase its dividend by 2% than last year. Compute the dividend payout ratio for this year.
How to calculate dividends?
To calculate dividends for a given year, do the following: 1 Take the retained earnings at the beginning of the year and subtract it from the the end-of-year number. That will tell you the net change in retained earnings for the year. 2 Next, take the net change in retained earnings, and subtract it from the net earnings for the year. If retained earnings has gone up, then the result will be less than the year's net earnings. If retained earnings have fallen, then the result will be greater than the net earnings for the year.
How to calculate dividends from balance sheet?
To calculate dividends for a given year, do the following: Take the retained earnings at the beginning of the year and subtract it from the the end-of-year number. That will tell you the net change in retained earnings for the year . Next, take the net change in retained ...
What happens if retained earnings fall?
If retained earnings have fallen, then the result will be greater than the net earnings for the year. The answer represents the total amount of dividends paid. For example, say a company earned $100 million in a given year. It started with $50 million in retained earnings and ended the year with $70 million.
Why do companies calculate dividends?
One of the most useful reasons to calculate a company's total dividend is to then determine the dividend payout ratio, or DPR. This measures the percentage of a company's net income that is paid out in dividends. This is useful in measuring a company's ability to keep paying or even increasing a dividend.
What is the income statement in an annual report?
Second, the income statement in the annual report -- which measures a company's financial performance over a certain period of time -- will show you how much in net earnings a company has brought in during a given year. That figure helps to establish what the change in retained earnings would have been if the company had chosen not to pay any dividends during a given year.
What is retained earnings?
Retained earnings are the total earnings a company has earned in its history that hasn't been returned to shareholders through dividends.
How to convert dividends to per share?
Once you have the total dividends, converting that to per-share is a matter of dividing it by shares outstanding, also found in the annual report.
How to calculate dividend payout ratio?
So, the dividend payout ratio is calculated by dividing the total dividend distribution by the company's net income. Another way to calculate a dividend payment is to utilize the retention ratio where you first subtract the dividends per share from the earnings per share, and then divide the difference by the earnings per share. Then, subtracting the retention ratio from one leaves the payout ratio.
Who decides the size of a dividend?
As mentioned earlier, the directors of a company decide on the size of a dividend and whether any will be paid out at all. More often than not, directors will look at the number of shares eligible for dividend payment rather than any value calculation when considering the size of the dividend.
Is dividend a holding period?
In fact, some dividend conveyances are conditioned on a holding period, which is a span of time that must elapse before any sale can be conducted. The value of this dividend is clearer when measured against the cash retained by the company. Dividends are subtracted on the income statement as a business expense.
Do new companies pay dividends?
This ratio, of course, varies from company to company. Relatively new corporations, for example, may pay no dividends at all as they roll all their income back into expansion, development and marketing.
Do Dividends Have a Downside?
Younger business concerns should be conservative in any decision to issue dividends, and in fact, many growing companies don’t offer a high ratio of dividends per share, if any.
What does dividend interest rate tell us?
The dividend interest rate simply tells us the input value the insurer is using when it calculates the actual dividend payable on a whole life insurance policy. It's one variable of…at least…three (see above for the other two).
What is dividend in life insurance?
Technically speaking, dividends officially operate as a refund of premiums paid by the policy owner . This is a unique tax classification that gives life insurers ...
What is a Dividend on a Whole Life Policy?
A dividend paid on a whole life policy is the mechanism life insurers use to share the profitability of their business operations with policyholders. This teases an obvious question.
What happens if the product of this calculation is greater than the payable dividend?
If the product of this calculation is a number greater than the payable dividend we know the insurer either had higher expenses under the other two variables that caused a negative adjustment to the dividend or some other costing allowance is at play that permits the insurer to take a loss on the policy in this policy year.
What is 6% dividend rate?
So a 6% dividend interest rate implies that the insurer's dividends payable by investment income generated by the assets held by the insurer are 200 basis points above the guaranteed accumulation rate–assuming the whole life contract has a 4% guaranteed accumulation rate.
What is investment return in life insurance?
Investment returns drive the cash value accumulation component of a life insurance contract. Insurers seek to generate investment income at least sufficient to cover the guaranteed provisions of the contract. The majority of life insurers successfully generate investment income well in excess of guaranteed contract features. Income created in excess of these contractual obligations is profit that feed into the dividend payment. This variable generally plays the biggest role in the overall dividend payment and it's the focus of the often talked about dividend interest rate.
What are administrative expenses for life insurance?
This includes things like office supplies, rent on office space, utility bills, wages, etc. When the life insurers operates under budget for these expenses, that surplus can go towards the dividend payment.
