DOPAMINE, after dilution, is administered intravenously through a suitable intravenous catheter or needle. An i.v. drip chamber or other suitable metering device is essential for controlling the rate of flow in drops/minute. Each patient must be individually titrated to the desired hemodynamic and/or renal response with DOPAMINE.
What herbs boost dopamine?
Top 7 Herbs to Increase Dopamine and Serotonin
- Kava Scientific name:Piper methysticum Kava ( get it here) or kava-kava, as it is also known is a tropical shrub from the Pacific Islands. ...
- St. John’s Wort Scientific name:Hypericum perforatum St. ...
- Ginseng Scientific name:Panax ginseng Ginseng has been used in traditional Chinese medicine since ancient times. ...
How does marijuana interfere with dopamine?
Summary. The link between marijuana and dopamine is complicated, but researchers have uncovered some basic facts. In the short term, marijuana use tends to cause an increase in dopamine activity in the brain’s reward pathway. After long term use, dopamine levels may drop as the body downregulates these receptors.
What does dopamine do, and how does it influence behavior?
Dopamine is an excitatory neurotransmitter. Dopamine communicates with brain cells and encourages them to act in a pleasurable, excitable, euphoric way. The excitatory nature of dopamine is also one of the reasons why the chemical messenger motivates us. By encouraging our brain cells to take certain actions, dopamine influences our behavior.
What is dopamine used for as a medication?
Dopamine is used to treat hypotension (low blood pressure), low cardiac output, and reduced perfusion of body organs due to shock, trauma, and sepsis. Dopamine is available in only the generic form.
How do you get a dopamine infusion?
VIII. Dosing: Adult InfusionPreparation. Start with 1-2 ampules Dopamine (400 mg each) Dissolve 400-800 mg Dopamine in 250 ml D5W. Final Concentration: 1600-3200 ug/ml.Start Dose: 1-5 ug/kg/min.Titrate: 5-20 ug/kg/min to clinical response. Perfusion. Urine Output. Blood Pressure.
Is dopamine taken orally?
Background: Docarpamine (DOC) is a dopamine prodrug which can be orally administered. It has been found that oral docarpamine transforms into dopamine in vivo, and increases cardiac output and renal blood flow as effectively as intravenous dopamine.
How is dopamine administered IV?
Rate of Administration – Dopamine Hydrochloride Injection, USP after dilution, is administered intravenously by infusion via a suitable intravenous catheter or needle.
When should dopamine be administered?
Dopamine injection (Intropin) is used to treat certain conditions that occur when you are in shock, which may be caused by heart attack, trauma, surgery, heart failure, kidney failure, and other serious medical conditions.
Why do we not use oral dopamine?
Peripherally administered (outside of the central nervous system) dopamine is not effective because it cannot cross the blood brain barrier. 4 The reason for its inability to cross the blood brain barrier has to do with at least two influencing factors.
Is there a dopamine pill?
Pramipexole (Mirapex). This is a prescription medication available in tablet form in brand and generic versions. The short and long acting forms are used to treat symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD), a chronic degenerative condition in which dopamine cells slowly die causing movement and mood related disorders.
What happens when you inject dopamine?
It works by improving the pumping strength of the heart and improves blood flow to the kidneys. Dopamine is used to treat certain conditions that occur when you are in shock, which may be caused by heart attack, trauma, surgery, heart failure, kidney failure, and other serious medical conditions.
What does IV dopamine feel like?
fast, slow, or pounding heartbeats; shortness of breath; cold feeling, numbness, or blue-colored appearance in your hands or feet; or.
Why is dopamine given with dextrose?
Dopamine Hydrochloride in Dextrose Injection is indicated to improve hemodynamic status in patients in distributive shock, or shock due to reduced cardiac output.
What are 4 functions controlled by dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter made in your brain. It plays a role as a “reward center” and in many body functions, including memory, movement, motivation, mood, attention and more.
What are the side effects of taking dopamine?
Side effects of Dopamine include:Irregular heartbeats.Nausea.Vomiting.Anxiety.Headache.Chills.Goosebumps.Shortness of breath.
What is a lethal amount of dopamine?
The LD50, or dose which is expected to prove lethal in 50% of the population, has been found to be: 59 mg/kg (mouse; administered intravenously); 950 mg/kg (mouse; administered intraperitoneally); 163 mg/kg (rat; administered intraperitoneally); 79 mg/kg (dog; administered intravenously).
Can dopamine be injected?
Dopamine is injected into a vein through an IV. A healthcare provider will give you this injection. Tell your caregivers if you feel any burning, pain, or swelling around the IV needle when dopamine injection is injected.
How do you get dopamine with ADHD?
You can also do the following to increase your dopamine levels:Try something new.Make a list of small tasks and complete them.Listen to music you enjoy.Exercise regularly.Try meditation or yoga.
How can I get dopamine naturally?
How can I increase dopamine levels in a natural way?Eat a diet that's high in magnesium and tyrosine-rich foods. These are the building blocks of dopamine production. Tyrosine is an amino acid. ... Engage in activities that make you happy or feel relaxed. This is thought to increase dopamine levels.
How does dopamine make you feel?
Dopamine is known as the “feel-good” hormone. It gives you a sense of pleasure. It also gives you the motivation to do something when you're feeling pleasure. Dopamine is part of your reward system.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not be treated with dopamine if you have pheochromocytoma (tumor of the adrenal gland).If possible before you receive dopamine, tell you...
How Is Dopamine Injection given?
Dopamine is injected into a vein through an IV. A healthcare provider will give you this injection.Tell your caregivers if you feel any burning, pa...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Since dopamine injection is given by a healthcare professional in a medical setting, you are not likely to miss a dose.
What Happens If I Overdose?
Since this medicine is given by a healthcare professional in a medical setting, an overdose is unlikely to occur.
Dopamine Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose of Dopamine for Nonobstructive Oliguria:Initial dose: 1 to 5 mcg/kg/min by continuous IV infusion.Titrate to desired response. Adm...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Dopamine?
Other drugs may interact with dopamine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell your doctor abou...
Dopamine Injection Description
Dopamine Hydrochloride, USP a sympathomimetic amine vasopressor, is the naturally occurring immediate precursor of norepinephrine. Dopamine Hydroch...
Dopamine Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
Dopamine is a natural catecholamine formed by the decarboxylation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). It is a precursor to norepinephrine in nora...
Indications and Usage For Dopamine Injection
Dopamine Hydrochloride, USP is indicated for the correction of hemodynamic imbalances present in the shock syndrome due to myocardial infarction, t...
Dopamine Injection Dosage and Administration
WARNING: This is a potent drug; it must be diluted before administration to the patient.Dopamine hydrochloride injection is administered (only afte...
How Is Dopamine Injection Supplied
Dopamine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution supplied as follows:Avoid contact with alkalies (in...
How is dopamine hydrochloride administered?
Dopamine hydrochloride injection is administered (only after dilution) by intravenous infusion.
What is dopamine injection?
Dopamine Injection Description. Dopamine Hydrochloride, USP a sympathomimetic amine vasopressor, is the naturally occurring immediate precursor of norepinephrine. Dopamine Hydrochloride, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder, which may have a slight odor of hydrochloric acid.
Why is dopamine HCl a MAO inhibitor?
1. Because dopamine is metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO), inhibition of this enzyme prolongs and potentiates the effect of dopamine. Patients who have been treated with MAO inhibitors within two to three weeks prior to the administration of dopamine HCl should receive initial doses of dopamine HCl no greater than one-tenth (1/10) of the usual dose.
How much dopamine is in 80 mg/ml?
Each milliliter of the 80 mg/mL preparation contains 80 mg of Dopamine Hydrochloride, USP (equivalent to 64.62 mg of dopamine base). Each milliliter of both preparations contains the following: Sodium metabisulfite 9 mg added as an antioxidant; citric acid, anhydrous 10 mg; and sodium citrate, dihydrate 5 mg added as a buffer.
What is the effect of dopamine on the heart?
Cardiac effects of dopamine are antagonized by beta-adrenergic blocking agents, such as propranolol and metoprolol. The peripheral vasoconstriction caused by high doses of dopamine HCl is antagonized by alpha-adrenergic blocking agents.
What is the name of the neurotransmitter that is produced by the decarboxylation of 3,4-?
Dopamine is a natural catecholamine formed by the decarboxylation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). It is a precursor to norepinephrine in noradrenergic nerves and is also a neurotransmitter in certain areas of the central nervous system, especially in the nigrostriatal tract, and in a few peripheral sympathetic nerves.
What are the conditions that affect dopamine?
Hypoxia, Hypercapnia, Acidosis – These conditions, which may also reduce the effectiveness and/or increase the incidence of adverse effects of dopamine, must be identified and corrected prior to, or concurrently with, administration of dopamine HCl. 4.
How is dopamine hydrochloride administered?
Dopamine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is administered (only after dilution) by intravenous infusion.
What is dopamine used for?
Dopamine is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of low blood pressure, low cardiac output and improves blood flow to the kidneys. Dopamine may be used alone or with other medications. Dopamine belongs to a class of drugs called Inotropic Agents.
What is the effect of dopamine on the heart?
Cardiac effects of dopamine are antagonized by beta-adrenergic blocking agents, such as propranolol and metroprolol. The peripheral vasoconstriction caused by high doses of dopamine HCl is antagonized by alpha-adrenergic blocking agents.
How long does dopamine stay in the body?
Dopamine Hydrochloride Injection, USP has been found to be stable for a minimum of 24 hours after dilution in the sterile intravenous solutions listed above. However, as with all intravenous admixtures, dilution should be made just prior to administration.
How much dopamine is in a ml of dopamine?
Each mL contains either 40 mg, 80 mg, or 160 mg of dopamine hydrochloride (equivalent to 32.3 mg, 64.6 mg and 129.2 mg of dopamine base respectively) in water for injection, q.s.
What are the conditions that affect dopamine?
Hypoxia, Hypercapnia, Acidosis- These conditions which may also reduce the effectiveness and/or increase the incidence of adverse effects of dopamine, must be identified and corrected prior to, or concurrently with administration of dopamine HCl.
What are the side effects of Dopamine?
The most common side effects of Dopamine include: headache, anxiety, nausea, vomiting, chills and. goose bumps.
What is dopamine used for?
Dopamine is a peripheral vasostimulant used to treat low blood pressure, low heart rate, and cardiac arrest. Low infusion rates (0.5 to 2 micrograms/kg per minute) act on the visceral vasculature to produce vasodilation, including the kidneys, resulting in increased urinary flow. Intermediate infusion rates (from 2 to 10 micrograms/kg/min) stimulate myocardial contractility and increase electrical conductivity in the heart leading to increased cardiac output. Higher doses cause vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure via the adrenergic receptors alpha-1, beta-1, and beta-2, potentially leading to poor peripheral circulation. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse event profile, pharmacology, monitoring, and relevant interactions of doxorubicin, pertinent for members of the interprofessional team in the treatment of patients with indicated conditions.
Where does dopamine release occur?
Given this complex sequence, the modulation of dopamine can occur at various levels, such as the entire neuron, its projections, or the neuronal circuitry across the nervous system. Also, during the synthesis of DA (transcriptional, translational, and post-translational regulation), synaptosomal packaging (regulation of VMAT, transport of vesicle to synapse), DA release (neuronal depolarization, calcium signaling, vesicle fusion), and via reuptake and metabolism through regulation of the respective enzymes and their spatial localization relative to their substrate. [18][19]
What are the two substances that are synthesized in the biosynthesis of adrenaline and noradrenaline?
Biosynthesis of catecholamines adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine), intermediates DOPA and dopamine. Contribtued by NEUROtiker, CC-BY-SA 2.5 ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5/ )
What is the role of DA in the brain?
As previously stated, the neurotransmitter DA also acts centrally within the mesocorticolimbic pathway and has roles in processing reward and fear, as well as focusing attention and executive functioning, including complex planning. [31][32] While systemic dopamine does not cross the blood-brain barrier, central dopamine carries implications in somnolence, schizophrenia, addiction, and impulse control disorders. [13][27][41]Patients with neurologic conditions using high doses of L-DOPA for Parkinson disease may experience such physiological alterations from the dysregulation of DA within the CNS pathways.
What happens to the DA receptors after release?
After DA release into the synaptic space, it interacts with various receptors on the pre and post-synaptic terminals, causing neuronal excitation or inhibition at the target neuron. There are two entire families of DA receptors composed of five different isoforms, each affecting different intracellular signaling pathways.[14] Both families of dopamine receptors, D1 and D2, are, by definition, G-protein-coupled receptors, but the D1 receptor class results in the neuron's depolarization, whereas the D2 receptors inhibit neuronal firing. [15]
What is the precursor of dopamine?
Dopamine biosynthesis occurs following the same enzymatic sequence as norepinephrine (NE). In fact, DA is a precursor in the synthesis of NE (see Figure). [5][6]The first step of DA synthesis is rate-limiting and involves converting L-tyrosine to L-DOPA by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) enzyme. [7][8][9]This conversion requires oxygen, an iron co-factor, and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4 or THB) and results in adding a hydroxyl group to the aromatic ring to form L-DOPA. This molecule subsequently converts to DA by the aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, involving removing the carboxyl group. Once synthesized, DA is transported into synaptic vesicles via the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) to the synaptic terminals. [10][11][12]
How long does dopamine stay in the system?
Dopamine half-life in the systemic circulation is between 1 to 5 minutes; thus, slower forms of administration, such as oral administration, are typically ineffective. [37]
How is dopamine made?
It’s made in the brain through a two-step process. First, it changes the amino acid tyrosine to a substance called dopa, and then into dopamine.
What Is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a type of neurotransmitter. Your body makes it, and your nervous system uses it to send messages between nerve cells. That's why it's sometimes called a chemical messenger.
What is the drug that helps with ADHD?
Some research shows it may be due to a shortage of dopamine. This problem may be due to your genes. The ADHD drug methylphenidate (Ritalin) works by boosting dopamine.
What is the role of dopamine in our lives?
Dopamine plays a role in how we feel pleasure. It's a big part of our unique human ability to think and plan. It helps us strive, focus, and find things interesting.
Why is dopamine a chemical messenger?
Your body makes it, and your nervous systemuses it to send messages between nerve cells. That's why it's sometimes called a chemical messenger. Dopamine plays a role in how we feel pleasure. It's a big part of our unique human ability to think and plan. It helps us strive, focus, and find things interesting.
Why is it important that your doctor knows all the medications you take?
Because many drugs interact with it , it’s important that your doctor knows all the medications you take.
What is dopamine? What is its function?
Dopamine: What It Is & What It Does. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in pleasure, motivation, and learning. It’s also linked to some major diseases. Here’s what you should know. Skip to main content .
Does dopamine help with renal function?
electrolytes. NOTE: although the use of dopamine has not been shown to improve renal function when it is administered for the sole purpose of stimulating dopaminergic receptors (low dose infusions), dopamine may indirectly improve renal function if it is administered at doses that improve cardiac ouptut.
Can dopamine be infused through a peripheral vasuclar?
Must be administered via central venous access device; in emergency situations dopamine may be temporarily infused through a peripheral vasuclar access device until a central venous line can be established. Patient requires placement of an arterial line to monitor BP.
Can you inject a catheter through a pulmonary artery catheter?
Should not be infused via the proximal injectate port (blue) of a pulmonary artery catheter. If this is the only available central venous line, it may be administered through the proximal injectate port but thermodilution cardiac output measurements must not be measured during infusion).
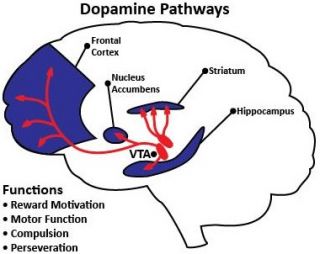
What are the pathways that dopamine is transported through?
Dopamine is transported through your brain along specific pathways. These are called dopaminergic pathways or dopamine pathways. In people with Parkinson’s disease, two significant dopamine pathways — the mesolimbic pathway and the nigrostriatal pathway — stop communicating with other neurons and parts of the brain.
What happens when dopamine falls?
As the dopamine starts to fall, signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease will begin to reveal themselves. That means the smooth, controlled body movements may be replaced by symptoms like tremor or stiffness in limbs. Fluid motions may become slow, shaky, and halted.
Why does dopamine drop in Parkinson's?
It’s not clear why dopamine levels drop off in people with Parkinson’s disease, but the lower the level of dopamine, the more likely you are to experience symptoms of the disorder.
What is the chemical that helps move electrical signals through the brain?
Dopamine is a type of brain chemical known as a neurotransmitter. This means dopamine is responsible for helping move electrical signals through the brain. It’s produced in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra.
How does deep brain stimulation work?
Deep brain stimulation is a type of treatment that includes placing electrodes on specific parts of the brain and using a generator to send electrical impulses through the brain. In people with Parkinson’s disease, these electrical signals can help reduce symptoms like tremor, rigidity, and muscle spasms.
What happens when you don't have dopamine?
With no dopamine to move, levels of the neurotransmitter begin to fall. A blood test can be used to measure the level of dopamine transporters in the body. Research suggests a lower level of the dopamine transporter density is implicated in Parkinson’s disease development.
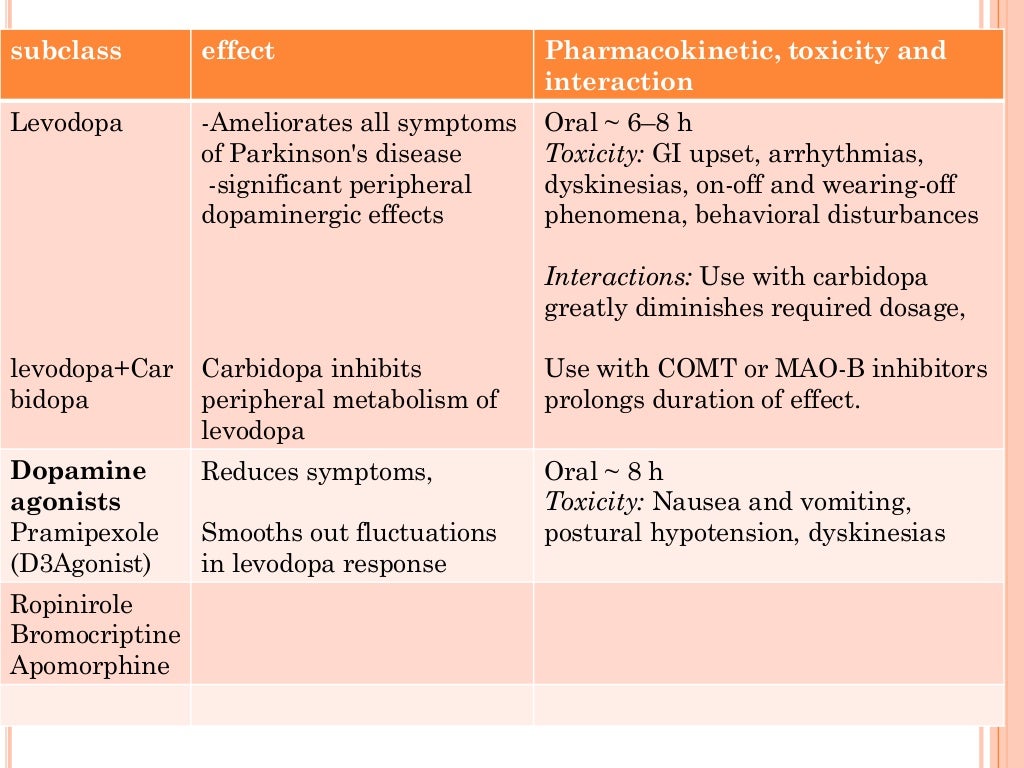
Does levodopa help Parkinson's?
An amino acid called levodopa can help increase levels of dopamine in the brain. If given as a medication, it can cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, levodopa is converted to dopamine. Levodopa won’t replace all of the lost dopamine, but it can help to reduce symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.