Energy comes from the three main nutrients carbohydrates, protein, and fats, with carbohydrates being the most important energy source. In cases where carbohydrates have been depleted, the body can utilise protein and fats for energy. Your metabolism is the chemical reactions in the body’s cells that change this food into energy.
What produces energy in the human body and where?
5 ways you can use the human body to generate electricity
- Blood flow. A team of Swiss researchers led by biomedical engineer Alois Pfenniger are showing the world a promising glimpse of the future: microturbines implanted in human arteries.
- Footsteps. Humans walk a lot, so why not capture that effort and use it to generate electricity? ...
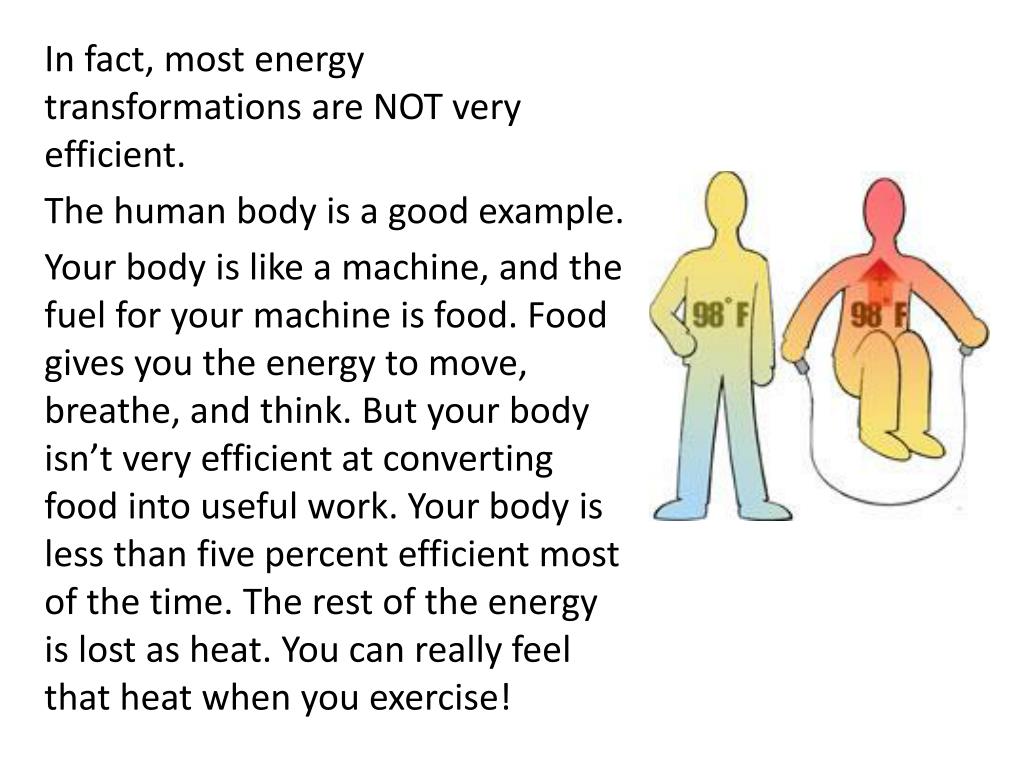
- Exercise. ...
- Body heat. ...
- Urine and feces. ...
How does the human body release and use energy?
- Sex – males release energy from their food 5–7% faster than females.
- Size – the more surface area 4 4 4 4 a person has, the greater is the RMR.
- Body composition – the higher the ratio of lean tissue to fat tissue, the higher is the RMR.
- Thyroid hormone 5 5 5 5 – this hormone 6 6 6 6 stimulates resting metabolism 7 7 7 7 . ...
How to create energy in our body?
Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Treating Your Body and Mind Right Download Article
- Sit up straight to stay alert and avoid muscle soreness. ...
- Practice square breathing to relieve stress and boost energy. How you breathe impacts how your body processes oxygen, which influences your energy levels and overall alertness.
- Integrative Internist Expert Interview. ...
- Integrative Internist Expert Interview. ...
How to fuel your body for energy?
How to Fuel Your Body for Energy
- Turkey
- Chicken breast (without skin)
- Seafood and fish
- Veal
- Pork
- Tenderloin
- Lean ham
- Lean beef
- Eggs
- Yogurt (fat-free or low-fat)

Energy Metabolism – I: Energy Production in the Body
There are two sides of energy metabolism. While the first covers energy production activities from foods; The second includes all activities that consume energy in the body. This article describes the production of power from food in the body.
1. Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration releases the energy they contain by burning carbohydrates, fat, and protein building blocks with oxygen. The reaction takes place in 3 stages, and as a result water, carbon dioxide, and ATP are formed. These stages are;
2. Anaerobic Respiration
Energy production by anaerobic respiration occurs in the muscles during intense physical activity. The energy efficiency is relatively low; however, it is essential to meet urgent energy needs. Glucose is burned by anaerobic respiration, and as a result, 2 moles of ATP and 2 moles of lactic acid are released.
Amount of Energy Produced
As a result of aerobic respiration, a total of 32 moles of ATP is produced from 1 mole of glucose (180 grams). The table regarding the production is given below. Essentially, there is the potential to produce about 85 moles of ATP from 1 mole of glucose; however, the amount produced is 32 moles, and the remaining energy is released as heat.
What is the energy that the body uses?
Image Credit: lzf/iStock/Getty Images. The human body uses energy from food to fuel movement and essential body functions, but the body cells don't get energy directly from food. After food is digested, the carbohydrates, protein and fat break down into simple compounds -- glucose, amino acids and fatty acids -- which are absorbed into ...
How many energy systems does the body use?
The body uses 3 different systems to supply cells with the necessary ATP to fuel energy needs. Most of the body's activities use a continuum of all three energy systems, working together to ensure a constant supply of energy.
What happens when ATP is depleted?
When the body's supply of ATP is depleted, which occurs in a matter of seconds, additional ATP is formed from the breakdown of phosphocreatine (PC) -- an energy compound found in muscle. Advertisement.
What is the aerobic system?
The aerobic system supplies energy for body movement lasting more than just a few minutes, such as long periods of work or endurance activities. This system is also the pathway that provides ATP to fuel most of the body's energy needs not related to physical activity, such as building and repairing body tissues, digesting food, ...
Why is ATP important?
While these systems are well known for their role in fueling athletic performance, ATP is essential for every energy need in the body -- including all the automatic body processes of growth, development and maintaining vital body functions. These energy systems do not work independently and do not function in isolation.
Which energy system produces the most ATP?
The most complex energy system is the aerobic or oxygen energy system, which provides most of the body's ATP. This system produces ATP as energy is released from the breakdown of nutrients such as glucose and fatty acids. In the presence of oxygen, ATP can be formed through glycolysis. This system also involves the Krebs or tricarboxylic acid cycle ...
What is the body's energy source for short movements?
For short and intense movement lasting less than 10 seconds, the body mainly uses the ATP-PC, or creatine phosphate system. This system is anaerobic, which means it does not use oxygen. The ATP-PC system utilizes the relatively small amount of ATP already stored in the muscle for this immediate energy source.
What is the energy source for muscle firing?
The actual creation of energy for muscle firing involves the ATP-adenosine diphosphate (ADP) system , generating “energy” sources for fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscle fibers.
What is the process of ATP?
During prolonged physical activity, which is often intense, muscle glycogen particles are metabolized into glucose molecules that lead to the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process of oxidation.
How does intensity affect glycogen?
The intensity of exercise is directly related to the rate of muscle glycogen degradation. 2 Likewise, the duration of the exercise changes the mathematical equation of glycogen metabolism (e.g., a sprinter has different needs than a long-distance runner) and training programs are modified to not overload the system of one versus another. Consequently, recommended intake of carbohydrates, the primary dietary driver of glucose production, varies to reflect the system load from daily or periodic training. 3
How does glycogen help athletes?
The ability for athletes to train consistently depends largely on consuming adequate levels of nutrients associated with glycogen maintenance and restoration. Most high-expenditure exertion requires sufficient stores of glycogen—which the body places in striated muscle—to allow rapid muscle contraction and release during exertion. During prolonged physical activity, which is often intense, muscle glycogen particles are metabolized into glucose molecules that lead to the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process of oxidation.
How does athlete training depend on nutrition?
The ability for athletes to train consistently depends largely on consuming sufficient levels of nutrients associated with glycogen maintenance and restoration.
How did demands for nourishment and energy change dramatically as society transitioned from hunter-gatherer to?
Historically, demands for nourishment and energy changed dramatically as society transitioned from hunter-gatherer to agrarian base and then to urban collections of masses of people attracted by the industrial age.
Why is it important to give the body the proper nutrients?
In summary, giving the human body the proper nutrients on a consistent basis plays a vital role in helping achieve maximum potential, especially as individuals learn how energy works for them, no matter the level of their athletic pursuits.
ATP Yield
As seen in the above process, one glucose molecule yields between 30 or 32 ATPs.
Respiration in Summary
We can summarize the entire respiration process using the following simple reaction in terms of inputs and outputs.
ATP and Energy Regulation
The amount of ATP varies at different times driven by the amount of energy available.
Conclusion
Ever since life evolved reportedly some 3.5 billion years ago, ATP has faithfully served as power storage units for life’s processes.
What is the energy field of the human body?
When applied to the human body, every atom, molecule, cell, tissue and body system is composed of energy that when superimposed on each other create what is known as the human energy field.
What is the definition of energy?
Energy is defined as the capacity to perform work. According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, the total amount of energy in the universe is constant — incapable of being created or destroyed — and can only change from one form to another.
What is Energetic Balancing Total Body?
EBTBis a supportive treatment approach that addresses the body as a total unit while supporting the innate ability of the body to heal. This concept of holism refers to the physical representation of the sum of the structural, physiological, energetic, mental, emotional, behavioral, spiritual, consciousness, and environmental influences.
What are the effects of stress on the body?
As the body accumulates acute and chronic stress patterns, tension from unre solved mental, emotional, behavioral, and spiritual/consciousness issues can lead to pain, poor posture, restricted range of motion, and altered function. This technique includes an evaluation, principle-based treatment, and re-evaluation.
What are the four types of tissues in the human body?
In particle form, the solid mass of the human body is composed of four types of tissues:epithelial, connective, muscle, and nerve tissue. A closer examination of the epithelial tissue (skin), however, shows how the tissue is actually created by these superimposed energy fields.
Where does the observation that collapses that potential into physical form come from?
The observation that collapses that potential into physical form comes from our experiences, conditioning, expectations, thoughts, and beliefs. The physical body is therefore a manifested form of potential in particle form.
Is the physical body a manifestation or representation of an energy field?
Since all matter and psychological processes — thought, beliefs, emotions, and consciousness — are composed of energy, the physical body is therefore the manifestation or representation of an energy field made of superimposed dynamic segments of vibration. Nothing rests.
Where is ATP produced?
ATP is produced by the oxidative reactions in the cytoplasm and mitochondrion of the cell, where carbohydrates, proteins, and fats undergo a series of metabolic reactions collectively called cellular respiration. For example, glycolysis is a series of reactions in which glucose is converted to pyruvic acid and some of its chemical potential energy is transferred to NADH and ATP.
Where is glycogen stored?
Excess glycogen can be converted to fats, which are stored in the lower layer of the skin of mammals for insulation and energy storage.
Why are fats important in the diet?
Fats are required in the diet to aid the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of fat-soluble hormones.
What are the organic molecules that make up cellular material?
The organic molecules required for building cellular material and tissues must come from food. Carbohydrates or sugars are the primary source of organic carbons in the animal body. During digestion, digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy through metabolic pathways. Complex carbohydrates , including polysaccharides, can be broken down into glucose through biochemical modification; however, humans do not produce the enzyme cellulase and lack the ability to derive glucose from the polysaccharide cellulose. In humans, these molecules provide the fiber required for moving waste through the large intestine and a healthy colon. The intestinal flora in the human gut are able to extract some nutrition from these plant fibers. The excess sugars in the body are converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles for later use. Glycogen stores are used to fuel prolonged exertions, such as long-distance running, and to provide energy during food shortage. Excess glycogen can be converted to fats, which are stored in the lower layer of the skin of mammals for insulation and energy storage. Excess digestible carbohydrates are stored by mammals in order to survive famine and aid in mobility.
What is the source of nitrogen in a protein?
Protein catabolism provides a source of organic nitrogen. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and protein breakdown provides amino acids that are used for cellular function. The carbon and nitrogen derived from these become the building block for nucleotides, nucleic acids, proteins, cells, and tissues.
Can the animal body produce nutrients?
These nutrients are termed essential nutrients, meaning they must be eaten, and the body cannot produce them.
Can amino acids be synthesized?
Certain amino acids also must be procured from food and cannot be synthesized by the body. These amino acids are the “essential” amino acids. The human body can synthesize only 11 of the 20 required amino acids; the rest must be obtained from food. The essential amino acids are listed in Table 4. Table 1.
What is the body composed of?
Your body is composed of energy-producing particles, each of which is in constant motion. So, like everything and everyone else in the universe, you are vibrating and creating energy. , seeks to use the vibrational energy generated by and around your body to optimize your health. To many people, the concept of energy fields in ...
How does vibrational energy affect your mood?
help you achieve your goals and intentions. Vibrational energy experts claim that certain emotions and thought patterns, such as joy, peace, and acceptance, create high frequency vibrations, while other feelings and mindsets (such as anger, despair, and fear) vibrate at a lower rate.
Why does generosity raise vibrational energy?
Generosity is thought to raise your vibrational energy because it’s considered a pro-social behavior.
What is the best way to realign vibrational energy?
Proponents say rhythmic deep breathing is a good way to realign your vibrational energy.
How do thoughts affect your body?
For example, anxious thoughts trigger the release of stress hormones that stimulate your heart rate to speed up or slow down. The sound vibrations of music, likewise, affect thoughts, emotions, and body systems.
How does vibration affect your body?
Researchers have found that vibrations and the electromagnetic energy associated with them cause changes in your cells, which can then affect how your body functions. Different molecules vibrate at different rates — and those rates can speed up or slow down if conditions around the molecules change.
What is vibration in biology?
Vibrations are a kind of rhythm. Rhythms happen on a grand scale, like seasonal changes and tidal patterns. They also happen within your body.
