Table 1
| Drug | Class | Use | Dose | Side effects, fetal |
| Flecainide | 1C | SVT AF VT | PO: 100–400 mg bid | negative inotrope, proarrhythmia |
| Amiodarone | III | SVT AF VT | IV: 5 mg/kg over 20 min; 500–1000 mg ove ... | proarrhythmic, hypothyroid |
| Sotalol | III | SVT AF VT | PO: 80–160 mg q 12h; increase to 160 mg ... | negative inotrope, proarrhythmia |
| Adenosine | IV | SVT | IV: 100–200 Ug/kg (into umbilical vein) | proarrhythmia |
How are fetal arrhythmias treated during pregnancy?
5 rows · Feb 25, 2019 · Fetal arrhythmias are usually detected during routine auscultation of the fetal heart or ...
What are the features of fetal arrhythmias?
Fetal arrhythmias are common, and they may resolve spontaneously in majority of the cases. Sustained fetal arrhythmias associated with major structural heart disorders, hydrops fetalis, and fetal heart failure warrant intrauterine pharmaceutical conversion of heart rhythm or early pacemaker implant in order to avoid fetal demise.
What is the prognosis of fetal arrhythmias?
Ultrasound is the primary modality for the diagnosis of fetal arrhythmias. The obstetrician observing an arrhythmia must first differentiate arrhythmia from fetal distress. Most confirmed arrhythmias are best evaluated and treated in utero, and unconfirmed rhythm disturbances vigilantly followed.
Can ultrasound characterize fetal heart rhythm?
Other manifest fetal arrhythmias such as premature beats, tachycardia, and bradycardia are commonly recognized. Methods: Heart rhythm diagnosis in obstetrical practice is usually made by M-mode and pulsed Doppler fetal echocardiography, but not all fetal cardiac time intervals are captured by echocardiographic methods.

How common is a fetal heart arrhythmia?
Detection of some dropped or extra beats (arrhythmia) is fairly common, occurring in 1 to 2 percent of pregnancies.Oct 30, 2018
What causes arrhythmia in a fetus?
The cause of most arrhythmias is unknown but some cases may result from an electrolyte imbalance, inflammation, medication or an inherited genetic condition. Severe cases of arrhythmia may be caused by a heart defect such as congenital heart block or by an inherited condition known as long QT syndrome.
How is fetal tachycardia diagnosed?
The diagnosis of fetal tachycardia is usually made during office auscultation or at the time of an ultrasound scan. A fetal heart rate of over 160-180 bpm requires a thorough maternal history and examination, screening for potential precipitating factors.
How arrhythmia is detected?
Tests to diagnose heart arrhythmias may include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). During an ECG , sensors (electrodes) that can detect the electrical activity of the heart are attached to the chest and sometimes to the arms or legs. An ECG measures the timing and duration of each electrical phase in the heartbeat.Oct 1, 2021
What is the most common fetal arrhythmia?
A premature atrial contraction, or PAC, is by far the most common arrhythmia we see. In PACs, extra heartbeats can come from the top of the heart, separate from the sinus node. These extra beats try to signal the AV node, which sometimes works (called “conducted”) and sometimes does not (called “nonconducted”).
Can you see heart defects on ultrasound?
Ultrasound technicians are diligent about getting clear pictures of the heart. “If the images are unclear or incomplete on the first attempt, we bring the patient back in a couple weeks to try again,” Dr. Chao says. “We are able to detect the majority of major heart defects with ultrasound.”Feb 14, 2019
What are fetal causes of fetal tachycardia?
The fetal tachycardia causes include maternal fever, dehydration or anxiety, maternal ketosis, medications like anticholinergic medications, sympathomimetic medications like terbutaline, fetal movement, preterm fetus, maternal thyrotoxicosis and maternal anaemia1.
How can you tell if fetus is in distress?
Fetal distress is diagnosed by reading the baby's heart rate. A slow heart rate, or unusual patterns in the heart rate, may signal fetal distress. Sometimes fetal distress is picked up when a doctor or midwife listens to the baby's heart during pregnancy.
What does fetal tachycardia indicate?
Fetal tachyarrhythmia is an abnormally fast fetal heart rate. In some cases the fast heartbeat may also have an irregular rhythm. Tachyarrhythmia is one of several types of fetal cardiac arrhythmias, congenital heart conditions involving an abnormal heartbeat. The condition is also sometimes referred to as tachycardia.
What are the 4 types of arrhythmias?
Different types of arrhythmias cause the heart to beat too fast, too slowly, or in an irregular pattern....Ventricular arrhythmiasVentricular fibrillation.Ventricular tachycardia.Premature ventricular beats (PVCs)Torsades de pointes.
Can arrhythmia be seen on ECG?
An ECG can show: An arrhythmia (both fast or slow ones) Damage to the heart from a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle (ischemia). This is also called a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
Is arrhythmia genetic?
Most arrhythmia syndromes are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, such that first-degree family members have a 50% chance of inheriting the disease. Identification of the mutation allows for predictive genetic testing in other living family members.Dec 1, 2016
Does caffeine cause fetal heart arrhythmia?
babies, however, the enzyme or enzymes necessary to metabolise caffeine are absent until several days after birth. Therefore, disturbances in the baby's heart rate caused by an excessive intake of caffeine by the mother should stop several days after birth. arrhythmia ofunknown origin occurs.
Is irregular fetal heartbeat normal?
Summary: Irregular fetal heartbeats are relatively common, but a Yale study, the largest of its kind to date, shows these arrhythmias are an indication of serious problems in only a fraction of affected fetuses.May 1, 2000
Can caffeine cause irregular fetal heartbeat?
It is possible that high levels of caffeine consumption may cause heartbeat irregularities, but currently, only case studies have been performed. It is suggested that pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to 200mL of caffeine a day–roughly the amount found in one cup of coffee.
Are you born with arrhythmia?
What causes an arrhythmia? Some people are born with arrhythmias, meaning the condition is congenital. Some medical conditions, including certain types of heart disease, high blood pressure, and hemochromatosis (iron build-up in the body), may be factors.
What are the different types of heartbeats?
Arrhythmias, abnormal or irregular heartbeats, can happen to babies still in the womb. Some types of irregular and abnormal heartbeats are relatively benign and will not affect the baby at all; others can be life-threatening. There are many types: 1 Tachycardia: The heartbeat is too fast. 2 Supraventricular Tachycardia: A rapid heart rhythm that begins in the upper chambers of the heart. 3 Bradycardia: The heartbeat is too slow. 4 Complete Heart Block: The heartbeat that starts in the atrium does not travel to the ventricle. A person with complete heart block may require a pacemaker. This may happen in fetuses whose mothers have lupus. 5 Premature Atrial Contractions: The heartbeat originates in a different part of the atrium than it normally would. These often occur in healthy people, have no symptoms, and typically do not cause problems. In rare cases they can cause supraventricular tachycardia.
Can fetal tachycardia cause heart failure?
Fetal tachycardia or bradycardia can cause heart failure either in the womb or at birth. Bradycardia related to complete heart block needs to be closely followed in-utero to watch for development of heart failure. Supraventricular tachycardia may require treatment before birth, because it can result in heart failure.
What causes fetal arrhythmia?
Fetal arrhythmia has been linked to a number of possible causes. In some cases, healthcare providers may not be able to pinpoint the source, especially if the abnormal rhythm is transient.#N#It is possible that high levels of caffeine consumption may cause heartbeat irregularities, but currently, only case studies have been performed.
Should I be concerned about arrhythmia?
The causes of arrhythmia are still relatively unknown.
Next Steps
Your health care provider’s first step will be to monitor the heart rate and well-being of your baby. However, there may be questions about the condition that warrants further investigation. In these rare cases, your healthcare provider may refer you to a fetal cardiologist for further evaluation.
How many pregnancies are fetal arrhythmias detected?
Introduction. Fetal arrhythmias are detected in 1–2% of pregnancies. Most fetal arrhythmias are benign and transient; however, in some cases, the irregularity of the fetal heart rhythm can indicate a serious condition—either of fetal or maternal origin. Persistent fetal arrhythmia can cause low cardiac output, heart failure, hydrops, ...
What causes fetal AV block?
Approximately half of fetal heart blocks are in cases with structural heart defects, and AV block in cases with structurally normal heart is often caused by maternal anti-Ro/SSA antibodies. The efficacy of prenatal treatment for fetal AV block is limited.
What is supraventricular tachyarrhythmia?
Supraventricular tachyarrhythmia(SVT) is defined by a non-sinus mechanism of the accelerated heart rate (fetal HR > 180 bpm); this large group of tachycardic disorders includes any non-sinus rapid rhythm that arises from structures above the bundle branches. Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias include atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation [3]. Based on the AV conduction type and time, SVTs are divided into two types: 1 Short ‘ventriculoatrial’ tachycardia; it usually involves re-entry mechanisms including atrioventricular re-entry (AVRT) using a bypass tract or atrioventricular nodal re-entry (AVNRT) [2]; 2 Long ‘ventriculoatrial’ tachycardia—atrial ectopic tachycardia or permanent junctional reciprocating tachycardia (PJRT) [3,12].
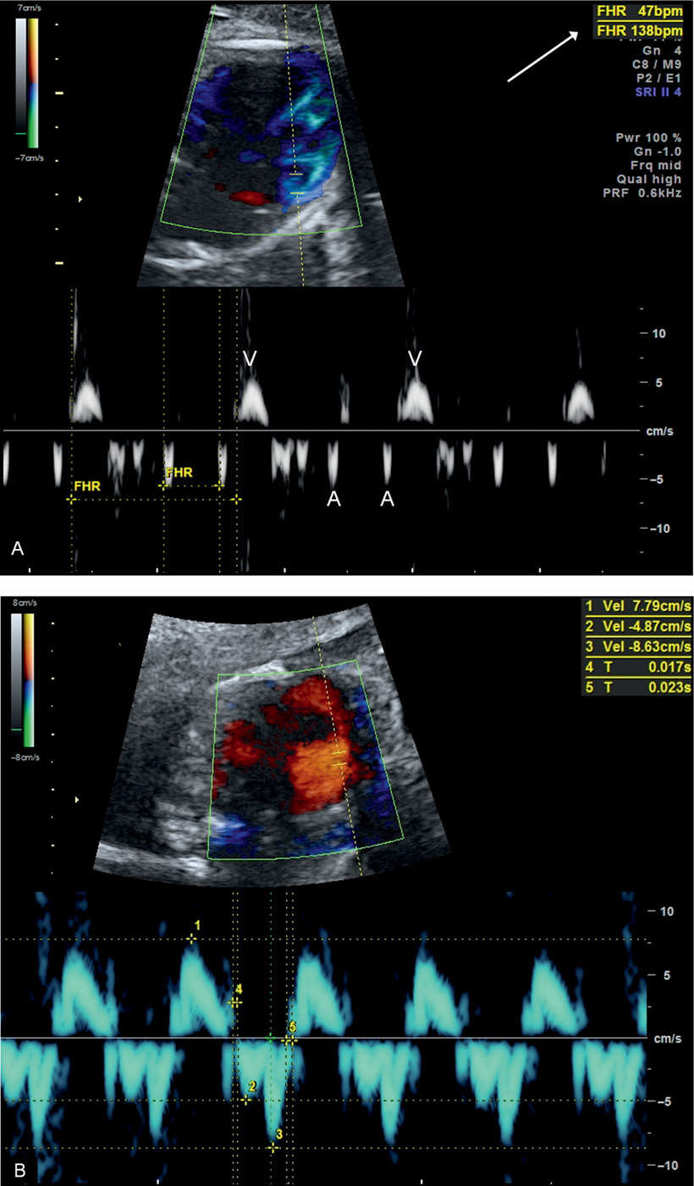
What is the E wave in cardiac cycle?
During a normal cardiac cycle, the filling of the ventricles during generalized diastole (E wave), the active filling of ventricles during atrial systole (A wave), and blood ejection into the aorta during ventricular systole will be recorded (Figure 2). The A wave corresponds to the P wave of the ECG.
Is ectopic beats benign?
Isolated ectopic beats are generally benign, regardless of the chamber of origin. Fetal ectopy is associated with congenital cardiac defects in only 1% of cases, and fetal echocardiography is not always recommended. In general, antiarrhythmic therapy is not needed for isolated PACs or PVCs.
Can fetal hydrops cause mirror syndrome?
Any type of fetal hydrops can cause the rare maternal mirror syndrome. Severe mirror syndrome or severe preeclampsia indicates delivery at any gestational age. Tachyarrhythmia is sometimes well tolerated, particularly the intermittent type which manifest near term with moderate ventricular rates (up to 220 bpm).
Is flecainide better than digoxin?
According to systematic data, both fleca inide and sotalol are more effective than digoxin in converting fetal SVT, and even more so in hydropic fetuses. A study from 2016 showed the superiority of flecainide over digoxin, especially in cases of long VA tachyarrhythmia [41].