
During photosynthesis:
- light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll - a green substance found in chloroplasts in green plant cells and algae
- absorbed light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide (from the air) and water (from the soil) into a sugar called glucose
- oxygen is released as a by-product
What is the relationship between light and photosynthesis?
In photosynthesis, the sun’s energy is converted to chemical energy by photosynthetic organisms. However, the various wavelengths in sunlight are not all used equally in photosynthesis. Instead, photosynthetic organisms contain light-absorbing molecules called pigments that absorb only specific wavelengths of visible light, while reflecting others.
How does light play a role in photosynthesis?
How does light play a role in photosynthesis? The process of photosynthesis occurs when green plants use the energy of light to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into carbohydrates. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, a photosynthetic pigment of the plant, while air containing carbon dioxide and oxygen enters the plant through ...
What role does sunlight play in photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is when plants absorb water thru their roots system, CO2 thru stomata-pores in the leaves, and absorb sunlight via the chlorophyll in their leaves What performs photosynthesis? Most plants and algae perform photosynthesis, the organisms are called photoautotrophs. Nice work!
Why does blue light work best for photosynthesis?
More blue and red light might increase the rate of photosynthesis a bit but the plants aren’t able to increase their rate very much. This figure might help. The structure of the blue pigment molecules allows them to absorb photons of these wavelengths more efficiently.
How is light used in photosynthesis quizlet?
How is light used in photosynthesis? What are the products of light reactions and how are they used? The products are ATP and NADPH, and oxygen. ATP and NADPH supply energy for carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle .
How does light affect photosynthesis?
As you rise from low light intensity to higher light intensity, the rate of photosynthesis will increase because there is more light available to drive the reactions of photosynthesis.
Can photosynthesis happen without light?
During the day, photosynthesis is the dominant process in plants. This means that the plant produces more glucose than it uses during respiration. At night, or in the absence of light, photosynthesis in plants stops, and respiration is the dominant process.
How much light is used in photosynthesis?
The part of the solar spectrum used by plants has an estimated mean wavelength of 570 nm; therefore, the energy of light used during photosynthesis is approximately 28,600/570, or 50 kcal per einstein.
How does light intensity affect photosynthesis experiment?
As light intensity increases (distance between lamp and plant decreases) the volume of oxygen (or the rate of bubble production) increases. This indicates that the rate of photosynthesis increases with light intensity. However, at sufficiently high levels of light intensity, the rate oxygen evolution remains constant.
Why does more light increase the rate of photosynthesis?
Light intensity - Increasing light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis because more energy is provided. However, if the light intensity is increased above a certain threshold, the rate of photosynthesis will not increase because another factor (such as temperature) is limiting the rate of the reaction.
How does light intensity affect plants?
Light intensity influences the manufacture of plant food, stem length, leaf color and flowering. Generally speaking, plants grown in low light tend to be spindly with light green leaves. A similar plant grown in very bright light tends to be shorter, better branches, and have larger, dark green leaves.
What is the process of photosynthesis?
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis .The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O 2) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar).
What is the chemical used in photosynthesis?
ATP. Noun. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. C3 photosynthesis. Noun. Used by the majority of plants, it involves producing a three-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid during the Calvin Cycle, which goes on to become a sugar called glucose. C4 photosynthesis.
How does carbon dioxide change water into glucose?
Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. The plant then releases the oxygen back into the air, and stores energy within the glucose molecules.
What is the energy that plants use?
Inside the plant cell are small organelles called chloroplasts, which store the energy of sunlight. Within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast is a light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll, which is responsible for giving the plant its green color. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs energy from blue- and red-light waves, and reflects green-light waves, making the plant appear green.
Why are the leaves of plants green?
The plant leaves are green because that color is the part of sunlight reflected by a pigment in the leaves called chlorophyll. Photograph courtesy of Shutterstock. ATP.
What is the chemical element that forms the basis of all known life?
series of reactions that take place during photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide and water from the atmosphere are converted into sugar. carbon. Noun. chemical element with the symbol C, which forms the basis of all known life.
Where does the light dependent reaction take place?
The light-dependent reaction takes place within the thylakoid membrane and requires a steady stream of sunlight, hence the name light- dependent reaction. The chlorophyll absorbs energy from the light waves, which is converted into chemical energy in the form of the molecules ATP and NADPH.
What absorbs light in photosynthesis?
Pigments absorb light used in photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, the sun’s energy is converted to chemical energy by photosynthetic organisms. However, the various wavelengths in sunlight are not all used equally in photosynthesis.
How do plants absorb light energy?
This process begins with the absorption of light by specialized organic molecules, called pigments, that are found in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Here, we’ll consider light as a form of energy, and we'll also see how pigments – such as the chlorophylls that make plants green – absorb that energy.
What is light energy?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy that travels in waves. Other kinds of electromagnetic radiation that we encounter in our daily lives include radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays. Together, all the types of electromagnetic radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum.
What wavelengths do chlorophylls not absorb?
Chlorophylls do not absorb wavelengths of green and yellow, which is indicated by a very low degree of light absorption from about 500 to 600 nm. The absorption spectrum of β-carotene (a carotenoid pigment) includes violet and blue-green light, as is indicated by its peaks at around 450 and 475 nm. Optimal absorption of light occurs ...
What is the wavelength of a photosynthesis pigment?
Each photosynthetic pigment has a set of wavelength that it absorbs, called an absorption spectrum. Absorption spectra can be depicted by wavelength (nm) on the x-axis and the degree of light absorption on the y-axis. The absorption spectrum of chlorophylls includes wavelengths of blue and orange-red light, as is indicated by their peaks around 450-475 nm and around 650-675 nm. As a note, chlorophyll
What are the three pigments that are absorbed in photosynthesis?
In the diagram below, you can see the absorption spectra of three key pigments in photosynthesis: chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and β-carotene. The set of wavelengths that a pigment doesn't absorb are reflected, and the reflected light is what we see as color.
What molecules absorb light?
Instead, photosynthetic organisms contain light-absorbing molecules called pigments that absorb only specific wavelengths of visible light, while reflecting others. The set of wavelengths absorbed by a pigment is its absorption spectrum.
Where does light energy come from?
Light energy in the form of photons is transmitted to the external electrons of the molecule (s) of chlorophyll, which escape from it and produce a kind of electric current inside the chloroplast when it joins the transport chain of electrons (see the following illustration).
What happens in the light phase?
Light is absorbed by complexes made up of chlorophylls and proteins called photosystems, which are located in the chloroplasts. It’s called the light phase because it uses light energy, it can only occur in conditions of high light, whether this is natural or artificial. In dark conditions, this phase does not occur.
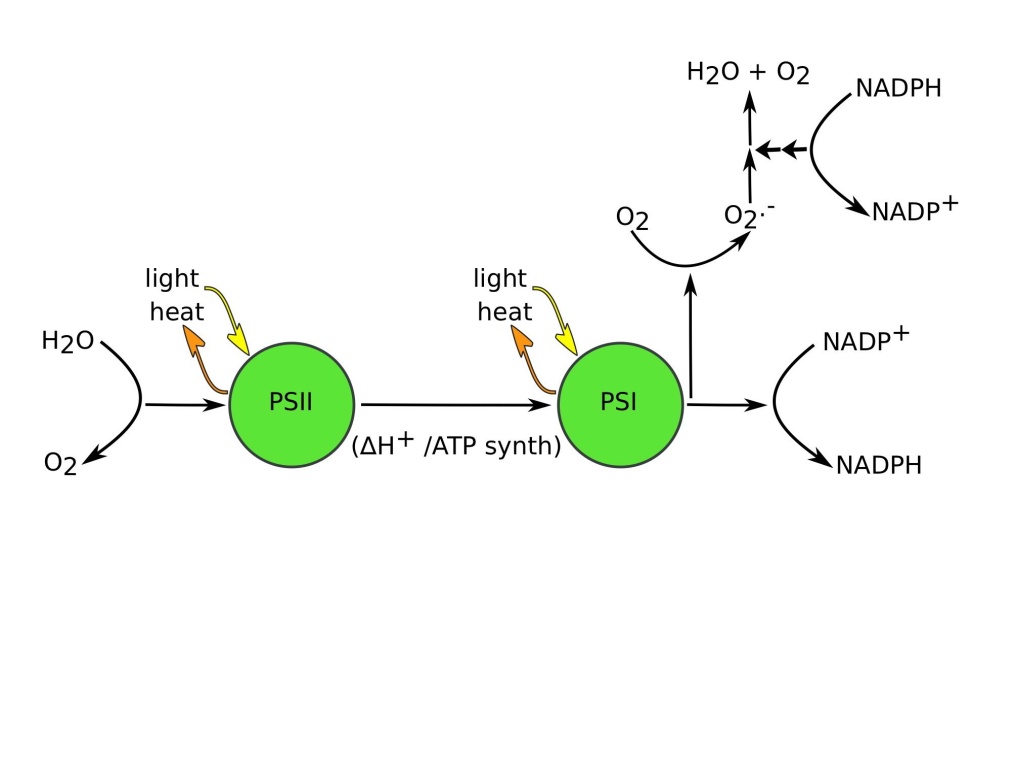
How does PSI capture light?
The PSI and PSII capture the light, increasing the energy of the electrons to levels higher than its original state. This energy is transported through different molecules of chlorophyll, until the water is separated in the centre of photosystem II into the following components: two protons (H + ), one atom of oxygen (O), and two electrons.
What is the function of photosystems I and II?
Photosystem I and photosystem II (PSI and PSII) are in charge of capturing light and using its energy to drive the transport of electrons through a chain of receptors. Or to put it another way, the electrons need to jump from the water molecules until they form ATP, passing through various intermediate chemical forms as in a transport chain.
How do photons influence the PSII?
The photons influence the PSII by exciting and releasing two electrons, which are transferred to the primary electron-acceptor, pheophytin. The electrons are replaced by the first electron donor in the Z scheme, with the electrons that come from the photolysis of water inside the thylakoid.
What is the first phase of photosynthesis?
The light phase is the first phase of photosynthesis, when light is absorbed by complexes made up of chlorophylls and proteins called photosystems (located in the chloroplast). During this phase, solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
What is the process of converting inorganic matter into organic matter?
Photosynthesis is the conversion of inorganic matter into organic matter with the help of the energy from sunlight (or from grow lamps in certain cases). In this process, light energy is transformed into stable chemical energy, with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) being the first molecule in which this chemical energy is stored.
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
An increase in light intensity may limit the availability of another vital factor for photosynthesis: In some cases, an increase in light intensity doesn’t automatically relate to more photosynthesis. Just as we have discussed earlier in this article, other reactants or factors come into play regarding the rate of photosynthesis.
Verdict
We hope this article has answered the question, “how does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis, and have provided you with enough clarity to satisfy/feed your curiosity.
