
Another way to test your sample for fecal coliforms is to use MacConkey Agar. MacConkey Agar is a selective medium that only allows Gram-negative bacteria to grow on it. When fecal coliform bacteria are grown on MacConkey Agar, the colonies will appear pink.
Why is McConkey agar differential and selective?
Why is MacConkey agar selective as well as differential? It’s selective to gram negative enteric bacteria because it contains bile salts, which inhibit most gram positive bacteria. It also contains lactose, which differentiates between gram negative lactose fermenter and gram negative non-fermenters.
How do you prepare MacConkey agar?
With prepared factory dehydrated MacConkey media:
- Hydrate it according to directions
- Mix well; cook (to boiling) continue to mix til totally dissolved. Cook to sterilize
- Cool til easily pourable
- Pour gently into pre-sterilized Petri dishes; leave cover slightly ajar til totally firm
- Turn over, stack and refrigerate
- QC it with appropriate bacteria
- Use it
What is Mac conkeys agar selective for?
MacConkey’s Agar is a selective medium. It prevents the growth of gram-positive bacteria because of the presence of bile salts and crystal violet. Only gram-negative bacteria has the ability to thrive on MacConkey agar.
What is the importance of lactose in MacConkey agar?
MacConkey Agar (MAC) is a selective and differential medium designed to isolate and differentiate enterics based on their ability to ferment lactose. Bile salts and crystal violet inhibit the growth of Gram positive organisms. Lactose provides a source of fermentable carbohydrate, allowing for differentiation.
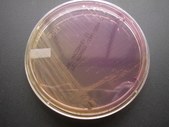
How the MacConkey agar helps in determining coliforms?
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture medium for bacteria. It is designed to selectively isolate Gram-negative and enteric (normally found in the intestinal tract) bacteria and differentiate them based on lactose fermentation.
Can coliform bacteria grow on MacConkey agar?
Testing for Coliform Bacteria Since all coliforms can ferment (eat) the sugar lastose, their presence is easy to test for in a microbiology lab, using a differential bacterial growth medium such as MacConkey's agar, on which coliforms will grow in pink bacterial colonies.
Why is E coli pink on MacConkey agar?
Streak plate of Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens on MacConkey agar. Both microorganisms grow on this selective media because they are gram-negative non-fastidious rods. Growth of E. coli, which ferments lactose, appears red/pink on the agar.
What type of bacteria grows on MacConkey agar?
Colony Morphology on MacConkey AgarOrganismTypeSalmonella sppNon-Lactose FermenterPseudomonas sppNon-Lactose FermenterYersinia sppNon-Lactose FermenterGram-positive bacteria8 more rows•Jun 29, 2022
For what purpose the MacConkey agar is used?
MacConkey agar is a selective and differentiating agar that only grows gram-negative bacterial species; it can further differentiate the gram-negative organisms based on their lactose metabolism.
Why do you use MacConkey agar?
MacConkey agar is used for the isolation of gram-negative enteric bacteria. It is used in the differentiation of lactose fermenting from lactose non-fermenting gram-negative bacteria. It is used for the isolation of coliforms and intestinal pathogens in water, dairy products and biological specimens.
What happens to E. coli on MacConkey agar?
◈ Differentiation : Gram-negative bacteria that grow on MacConkey plate are differentiated by their ability to ferment lactose. Colonies of Escherichia coli on MacConkey agar palte are pink to dark pink, dry and donut-shaped, surrounded by a dark pink area of precipitated bile salts.
Why MacConkey agar is selective and differential media?
MacConkey agar is an example of a medium that is both differential and selective. The presence of bile salts, as well as crystal violet, within the media prevent gram-positive organisms from growing.
What group of bacteria are inhibited on MacConkey agar?
MacConkey's is a selective medium that inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria due to the presence of crystal violet and bile salts. Gram-negative bacteria grow well on MAC.
Does Klebsiella grow on MacConkey agar?
Laboratory Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae colonies are pink (LF), mucoid (usually), and 3 to 4 mm in diameter. Colonies on Hektoen enteric agar and XLD are yellow. Large, mucoid, glistening pink colonies on a MacConkey agar plate, typical of the colonies produced by many Klebsiella and Enterobacter spp.
What group of bacteria are inhibited on MacConkey agar?
MacConkey's is a selective medium that inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria due to the presence of crystal violet and bile salts. Gram-negative bacteria grow well on MAC.
Does Bacillus subtilis grow on MacConkey agar?
MacConkey Agar Plate Record observations here on the growth and appearance of the three bacteria on MacConkey agar. Bacillus subtilis No or very little growth. Escherichia coli Heavy growth; pink to red. Pseudomonas fluorescens Heavy growth; not pink or red.
Does Staphylococcus grow on MacConkey agar?
MacConkey agar selects for organisms like Escherichia coli (Gram negative bacilli) while inhibiting the growth of organisms like Staphylococcus aureus (Gram positive cocci).
Can Klebsiella pneumoniae grow MacConkey agar?
⇒ Special requirements – Klebsiella pneumoniae has no complex nutritional requirements and readily grows in ordinary media like Nutrient Agar medium (NAM). Commonly the NAM & MacConkey Agar medium is used for the cultivation of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Laboratory.
What is MacConkey agar used for?
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture media commonly used for the isolation of enteric Gram-negative bacteria. It is selective as it allows the growth of gram-negative bacteria and differential as it differentiates the gram-negative bacteria based on their lactose metabolism. MacConkey agar is used for the selective isolation ...
What is the color of the indicator in MacConkey agar?
Lactose present in the medium is utilized by bacteria to form lactic acid that decreases the pH of the agar, and turns the indicator (neutral red) pink, thus differentiating lactose fermenters from non-lactose fermenters. Contents. 1 Composition of MacConkey Agar. 2 Principle of MacConkey agar. 3 Preparation of MacConkey Agar.
What causes a dry pink halo in MacConkey agar?
coli in MacConkey Agar. Strongly lactose fermenting bacteria produce sufficient acid which causes precipitation of the bile salts around the growth. It appears as a pink halo surrounding colonies or areas of confluent growth.
What are the ingredients in MacConkey agar?
MacConkey agar contains four key ingredients (lactose, bile salts, crystal violet, and neutral red) that make it a selective and differential media. Bile salts and crystal violet act as selective agents that inhibit the growth of Gram-positive organisms, and proliferate the selective growth of gram-negative bacteria.
How to tell if a Gram-negative bacteria is fermented?
If the lactose is fermented by the bacteria, the production of the acid drops the pH of the media. The drop in pH is indicated by the change of neutral red indicator to pink (neutral read appears pink at pH’s below 6.8).
What bacteria produce pink red colonies?
Lactose-fermenting bacteria produce pink-red colonies, after fermenting the lactose to acids and dropping the pH of the indicator ( neutral red) present in the medium. Since, non-fermenters can’t utilize lactose, colonies appear colorless or transparent.
How long to incubate Mac Conkey agar?
Sterility testing: Incubate uninoculated plates of Mac conkey agar for 48 hours at 35-37°C and observe for any growth. After 48 hours , the sterility test plate should remain clear. Discard the whole lot if any colonies are seen.
What is MacConkey agar used for?
Uses of MacConkey Agar 1 MacConkey agar is used for the isolation of gram-negative enteric bacteria. 2 It is used in the differentiation of lactose fermenting from lactose non-fermenting gram-negative bacteria. 3 It is used for the isolation of coliforms and intestinal pathogens in water, dairy products and biological specimens.
What is lactose fermenting used for?
It is used for the isolation of coliforms and intestinal pathogens in water, dairy products and biological specimens.
How to dissolve a medium?
Heat to boiling to dissolve the medium completely.
Can Proteus swarm on MacConkey?
Incubation of MacConkey Agar plates under increased CO2 has been reported to reduce growth and recovery of a number of strains of Gram-negative bacilli. Some strains of Proteus may swarm on this medium.
Is Shigella fermenting or non fermenting?
Lactose non-fermenting strains, such as Shigella and Salmonella are colourless and transparent and typically do not alter appearance of the medium. Yersinia enterocolitica may appear as small, non-lactose fermenting colonies after incubation at room temperature.
What is MacConkey agar?
MacConkey Agar Facts. MacConkey Agar is a modified neutral red bile salt agar by Alfred Theodore MacConkey. It is one of the earliest methods used to cultivate and identify enteric organisms. MacConkey Agar is useful in isolating pathogens present in foods and coliforms in water samples.
What is MacConkey agar Purpose ?
The purpose of MacConkey agar is to isolate Gram-negative enteric bacteria as well as to differentiate between lactose fermenting and non-fermenting lactose gram-negative bacteria.
What is the color of the colony on MacConkey agar?
Picture 2: Images show the growth of Enterobacteriaceae on a MacConkey Agar. It has the uninoculated plate. The colorless colony shows a lactose non-fermenting bacteria while the pink colonies show lactose-fermenting bacteria.
Why is lactose a differential medium?
Ironically, it is also a differential medium because it has the ability to differentiate different groups of bacteria based on the color change reaction. The pH indicator (neutral red) and the lactose produce acid in the medium which can significantly lower the pH level (below 6.8). It turns the color to red/pink.
How long to autoclave a medium?
Bring to boil to completely dissolve the medium. Autoclave 15 lbs pressure or at least 121 degrees Celsius for about 15 minutes. Let it cool.
What is the purpose of a bacterial growth media?
It uses a bacterial growth media, which is a combination of nutrients, moisture, and other chemicals necessary for the growth of bacteria.
Is MacConkey a selective medium?
The MacConkey medium is identified as a selective and a differential medium. It is a selective medium in the sense that it inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria primarily because of the presence of bile salts and crystal violet in the medium.
What is the selective and differentiating properties of MacConkey agar?
The selective and differentiating properties of MacConkey agar enables utilization for both research and clinical applications. The fermentation of lactose produces organic acids, particularly lactic acid, which decreases the pH of the agar. MAC contains a pH indicator that turns pink under acidic conditions.
What is Macconkey medium?
MacConkey Medium - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. MacConkey agar (MAC) is a bacterial culture medium named after bacteriologist Alfred T. MacConkey (1861-1931). MacConkey agar is a selective and differentiating agar that only grows gram-negative bacterial species; it can further differentiate the gram-negative organisms based on their lactose ...
What is the difference between lactose fermenters and non-lactose fermenters?
Therefore, lactose-fermenting-gram-negatives (lactose-fermenters) will form pink colonies, while non-lactose fermenters will form off-white opaque colonies.
What is a lactose positive species?
Example of Lac positive species: Escherichia coli, Enterobacteria, Klebsiella .
Why is MAC important?
A pure bacterial culture remains crucial to assess its virulence, its susceptibility to antibiotic therapy, and its genome sequence in order to facilitate the understanding and treatment of caused diseases . MAC's selective and differentiating properties as a culture medium allow isolating colonies of pure bacterial culture from a source sample. Typically in a clinical setting, the collected sample is placed on a panel of many growth media for identification and isolation of bacterial cultures.[3] MAC is one of the widely used growth media as it can work to selectively grow gram-negative bacteria and further differentiate them based on their fermentation profile. Many pathogenic gram-negatives can be differentiated by MAC, especially bacterial gastroenteritis causing species. The diagnostic potential is immense. MAC is essentially a versatile foundation, in which additional substrates, such as sorbitol, can be incorporated for further differentiation. Another example is the addition of antibiotics for testing drug resistance. In intensive care units, testing multi-drug resistance in gram-negative bacteria is an important surveillance measure.[4] Gram-negative enteric bacteria are a common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis, which is characterized by diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal cramping. Escherichia coliand Campylobacter jejuni are some of the common causes of bacterial gastroenteritis. When bacterial gastroenteritis is suspected, the patient's specimen can be sampled and cultured on a panel of bacterial cultures, which includes MacConkey medium. MAC contributes to the identification of the causal agent by providing lactose-fermentation profiles in gram-negative species. [5]
What is the Sorbitol MacConkey medium used for?
Sorbitol-MacConkey medium for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis.
Why is bacterial culture important?
A pure bacterial culture remains essential for the study of its virulence, its antibiotic susceptibility, and its genome sequence in order to facilitate the understanding and treatment of caused diseases. Bacterial cultures are still widely used laboratory techniques that many physicians rely on to make their final diagnoses. Many health care professionals are involved in this process, and proper communication and coordination will enhance patient-centered care, improve outcomes, patient safety, and enhance team performance. Bacterial culture from a patient's specimen is a commonly ordered test that many physicians use to aid their medical decision-making process. Nurses are frequently involved in obtaining and transporting samples from the patient to the laboratory. Clinical microbiologists must be trained with a thorough understanding of the principles to run the tests, interpret the results, and report the findings. Sterile sampling techniques and proper handling of the specimen during handling and transport of samples are required to avoid contamination. Any healthcare professionals handling these patient samples must be adequately trained in order to avoid contamination of the samples or accidental exposure and spread of potential pathogens. [6][7]
What is an agar strip?
Agar Strips C are ready-to-use culture media for assessment of airborne coliforms and E. coli with RCS® Air Samplers. Each individual agar strip is welded into a re-sealable sleeve and 100% visually controlled, ensuring maximum safety in critical environments. MacConkey agar is filled in a flexible backing film. MacConkey Agar is a weak selective medium for isolation of coliforms and E. coli. Bile salts and crystal violet largely inhibit the growth of the gram-positive microbial flora. Lactose and the pH indicator neutral red are used to detect lactose degradation.
What bacteria grow in pink to red?
Bacteria degrading lactose to acids grow in pink to red colored colonies. Additionally, Escherichia coli and other acid forming bacteria will show a zone of precipitated bile salt around the colonies. Bacteria not degrading Lactose will grow colorless.