What would drive a market toward the equilibrium?
What would drive a market toward the equilibrium? The behavior of sellers and buyers naturally drives markets toward their equilibrium. If the market price is above the equilibrium price, then there is an excess of the good that causes the market price to drop/fall.
What does it mean when a market is in equilibrium?
Market equilibrium, also known as the market clearing price, refers to a perfect balance in the market of supply and demand, i.e. when supply is equal to demand. When the market is at equilibrium, the price of a product or service will remain the same, unless some external factor changes the level of supply or demand.
What is true if equilibrium is present in a market?
The equilibrium price is the price of a good or service when the supply of it is equal to the demand for it in the market. If a market is at equilibrium, the price will not change unless an external factor changes the supply or demand, which results in a disruption of the equilibrium. Are you a student or a teacher?
Does a market ever reach equilibrium?
When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. This is a state of disequilibrium because there is either a shortage or surplus and firms have an incentive to change the price. Does the market ever reach equilibrium? The market never actually reach equilibrium, though it is constantly moving toward equilibrium.

What determines equilibrium in a market?
The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves.
What is market equilibrium and how price is determined in the market?
A market is in equilibrium if at the market price the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. The price at which the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied is called the equilibrium price or market clearing price and the corresponding quantity is the equilibrium quantity.
How is equilibrium price determined with diagram?
When we draw the demand and supply curves on a single diagram, the point of intersection of these two curves is the point of equilibrium. This is because at the point of intersection the demand and supply become equal to each other.
What are 4 factors that determine price in the market?
Four Major Market Factors That Affect PriceCosts and Expenses.Supply and Demand.Consumer Perceptions.Competition.
What is market equilibrium?
Market equilibrium. Definition of market equilibrium – A situation where for a particular good supply = demand. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. We say the market-clearing price has been achieved. A market occurs where buyers and sellers meet to exchange money for goods.
What would happen if there was an increase in income?
If there was an increase in income the demand curve would shift to the right (D1 to D2). Initially, there would be a shortage of the good. Therefore the price and quantity supplied will increase leading to a new equilibrium at Q2, P2.
Why is planned demand not equal to planned supply?
This is a state of disequilibrium because there is either a shortage or surplus and firms have an incentive to change the price.
What happens when there is a shortage?
If there is a shortage, firms will put up prices and supply more. As price rises, there will be a movement along the demand curve and less will be demanded.
What happens if the price is at P2?
If price was at P2, this is above the equilibrium of P1. At the price of P2, then supply (Q2) would be greater than demand (Q1) and therefore there is too much supply. There is a surplus. (Q2-Q1)
Why do demand and supply curves appear on the same graph?
Because the graphs for demand and supply curves both have price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis, the demand curve and supply curve for a particular good or service can appear on the same graph.
What is equilibrium price?
The equilibrium price is the only price where the plans of consumers and the plans of producers agree —that is, where the amount consumers want to buy of the product, quantity demanded, is equal to the amount producers want to sell, quantity supplied. This common quantity is called the equilibrium quantity.
Why do producers have to sell surplus?
This is because when there is a surplus, producers have to sell their excess supply (surplus) at a lower price in order for consumers to actually be willing and able to demand for it . In a shortage, there is a low quantity available so the price is bid up by consumers who have demand for the good or service.
Where do supply and demand curves intersect?
Supply and demand curves intersect at the equilibrium price. This is the price at which we would predict the market will operate.
What does it mean when a market is not at equilibrium?
However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity.
Where do the two curves intersect on the gasoline graph?
The graph shows the demand and supply for gasoline where the two curves intersect at the point of equilibrium.
Can a seller sell at a lower price than the equilibrium price?
The seller will not be able to sell at a price lower price than equilibrium price (since he/she) will make losses. Inquiring the price from many potential sellers helps you determine the lowest possible price a seller would be willing to sell at, which is more or less the equilibrium price.
What causes a new equilibrium point?
New Equilibrium point: Equilibrium price may change due to changes in either the supply or demand Variables. Demand and supply variables change due to external factors that include higher prices, availability of cheaper substitute goods, changes in income, changes in raw material prices and overhead costs, technology changes, government policies, seasonality of products, disruption in the economy, etc. Hence, the above factors might push the prices and reach a new equilibrium point.
How does an increase in earnings affect demand?
An increase in earnings will increase the disposable income in the hand of consumers and thereby increasing demand. In the below table (kindly compare it to the table above), we note that due to an increase in earnings, the demand has gone up by 10 units. In this case, demand and supply are equal to each other at the price of INR 7 compared to INR 6 in the above table. The increase in demand has raised the prices and reached a new equilibrium.
How do buyers and sellers react to price changes?
Buyers and sellers react to price changes. When prices are high, the buyer reduces consumption, and when prices are low, the seller reduces production. Theoretically, at a free market condition, the demand of a product equals the supply of a product, and the price remains constant. This state is market equilibrium.
What is market equilibrium?
The study of Market equilibrium focuses on analyzing the interrelationship or inter-dependence between prices of commodities or between prices of commodities and factors of production. Market equilibrium can be analyzed by partial equilibrium analysis and general equilibrium analysis.
What is the law of demand and supply?
Demand= 200-15P. Supply=5P Here 200 is the repository of all relevant non-specified factors that affect demand for the product. P is the price of the good. As per the law of demand, the coefficient is negative. The demand for the good would fall as the consumer’s income increased
When the prices are other than INR 6, the market is not at equilibrium?
When the prices are other than INR 6, the market is not at equilibrium; hence, the demand and supply forces will push the market towards equilibrium by adjusting the prices.
What is demand and supply equation?
The mathematical equation expresses the correlation between the number of goods demanded with the factors that impact the willingness and capability of a consumer to buy the products.
What happens when the price of a product is below equilibrium?
If the market price is below the equilibrium value, then there is excess in demand (supply shortage). In this case, buyers will bid up the price of the good or service in order to obtain the good or service in short supply. As the price goes up, some buyers will quit trying because they don't want to, or can't, pay the higher price. Additionally, sellers, more than happy to see the demand, will start to supply more of it. Eventually, the upward pressure on price and supply will stabilize at market equilibrium.
What is market equilibrium?
Definition of Market Equilibrium. Market equilibrium is a market state where the supply in the market is equal to the demand in the market. The equilibrium price is the price of a good or service when the supply of it is equal to the demand for it in the market. If a market is at equilibrium, the price will not change unless an external factor ...
Why does gas price increase in summer?
For some reason, oil refineries decide to shut down to do maintenance at the same time that there is an increase in demand for gas due to summer vacations. This usually results in a significant reduction in the supply of gas, which causes its price to increase.
What happens when the market price is above equilibrium?
If the market price is above the equilibrium value, there is an excess supply in the market (a surplus), which means there is more supply than demand. In this situation, sellers will tend to reduce the price of their good or service to clear their inventories.
What happens if the price of gasoline increases?
If the price increases too much, people will start driving less and will buy less fuel. As the demand for fuel goes down after the summer vacation period is over, and the supply increases as refineries gear up again, the supply of fuel will increase, which will push the price to equilibrium. Lesson Summary.
When does equilibrium occur?
Market equilibrium occurs when market supply equals market demand. The equilibrium price of a good or service, therefore, is its price when the supply of it equals the demand for it.
How many containers are in equilibrium at $300?
The equilibrium point is thus 1,200 containers at $300 each.
What is Market Equilibrium?
Market Equilibrium is a situation where the price at which quantities demanded and supplied are equal (Supply = Demand). When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change.
What is the initial equilibrium position of the supply curve?
In Figure 4, the initial equilibrium position, E1 is the point where demand curve D1D1 and supply curve S1S1 intersect. At this point, equilibrium price and quantity is P1 and OQ1 respectively. As the demand curve shifts from D1D1 to D2D2 and supply curve shifts from S1S1 to S3S3, there is a shift in equilibrium from E1 to E3.
What happens when the shift in supply curve is greater than the shift in demand?
If the shift in supply curve is greater than the demand curve, equilibrium price falls and output rises. Figure 4 shows the impact on equilibrium point when shift in supply curve is more than the shift in demand.
What is shift in supply and demand?
A shift in supply or demand curve also shifts the equilibrium point. Let us understand the mechanism of shift in market equilibrium in the case of shift of supply and demand curves respectively.
What is equilibrium point?
According to the economic theory, the price of a product in a market is determined at a point where the forces of supply and demand meet. The point where the forces of demand and supply meet is called equilibrium point. Conceptually, equilibrium means state of rest. It is a stage where the balance between two opposite functions, demand and supply, ...
What are the two forces that drive the market system?
Market system is driven by two forces, which are demand and supply. This is because these two forces play a crucial role in determining the price at which a product is sold in the market. Price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply in a market. According to the economic theory, the price of a product in a market is determined ...
Where is the initial equilibrium price in Figure 3?
In Figure 3, the initial equilibrium price is placed at PQ and quantity at OQ. As the supply curve shifts from SS to S1S1, the equilibrium point also shifts from PQ to MN. After the shift, the new equilibrium price is at MN and the quantity is at ON. However, demand remains the same in this case.
What happens when there is a surplus of goods and services?
When there’s a surplus of goods and services, there will be a decrease in demand, where supply will be greater than demand, price will fall where firms cut prices to sell surplus and there will be a contraction of supply and an extension of demand. When there’s a shortage of goods and services, consumers bid up prices competing for the available quantity supplied of goods and series, where there’s an extension of supply and a contraction of demand ad there will be a re-established equilibrium price at a higher rate.
What is equilibrium in the market?
Equilibrium refers to the idea that there is no tendency to change, and market equilibrium is a situation where the price and the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded of a particular good are equal. The interaction between demand and supply can change the price mechanism which determines the prices and quantity of the goods and services that will be bought and sold in the market.
How does an increase in supply affect the equilibrium price?
An increase in supply will shift supply to the right, it will lower the equilibrium price and raises the equilibrium quantity . There will be an extension in demand and a contraction in supply. A decrease in supply will shift supply to the right where there will be a raise in the equilibrium price and lowers the equilibrium quantity.
What happens when demand increases?
When there’s a decrease in demand, the demand will shift to the left where price will drop and there will be an extension in demand and a contraction in supply.
What does it mean when there is no tendency to change in price or quantity?
When there’s no tendency to change in price or quantity, it means that there’s no surplus or shortage of goods and services in the market (diagram 1). If there’s any mismatch in supply and demand, it will be balanced by changes in price and quantity demanded or supplied.
What is the principle of market equilibrium?
vn/Home/business/other/25850/ The Principle of Market Equilibrium The Principle of Market Equilibrium is the proposition that markets always move toward equilibrium, a situation in which no opportunities for individuals to better off themselves remains. Specifically, a properly competitive market reaches equilibrium when a good or service has an equilibrium price tag, at which level the quantity demanded and supplied are balanced (called equilibrium quantity). In an economic graph, Market Equilibrium is illustrated by the….
What does it mean when there is no tendency to change in price or quantity?
When there’s no tendency to change in price or quantity, it means that there’s no surplus or shortage of goods and services in the market (diagram 1). If there’s any mismatch in supply and demand, it will be balanced by changes in price and quantity demanded or supplied. When there’s a surplus of goods and services, there will be a decrease in demand, where supply will be greater than demand, price will fall where firms cut prices to sell surplus and there will be a contraction of supply and an extension of demand.
How does an increase in supply affect the equilibrium price?
An increase in supply will shift supply to the right, it will lower the equilibrium price and raises the equilibrium quantity . There will be an extension in demand and a contraction in supply. A decrease in supply will shift supply to the right where there will be a raise in the equilibrium price and lowers the equilibrium quantity. When the market prices for goods and services in the product markets is considered to be too high or too low, market failure may occur where the price mechanism may take account of private benefits and costs of production but doesn’t take into account social cost and benefits.
How does a shortage of goods and services affect the price of goods and series?
When there’s a shortage of goods and services, consumers bid up prices competing for the available quantity supplied of goods and series, where there’s an extension of supply and a contraction of demand ad there will be a re-established equilibrium price at a higher rate . Increase in demand will lead to a shift in the demand curve to the right where it will raise both equilibrium price and quantity. When there’s a decrease in demand, the demand will shift to the left where price will drop and there will be an extension in demand and a contraction in supply.
What is market equilibrium?
Equilibrium refers to the idea that there is no tendency to change, and market equilibrium is a situation where the price and the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded of a particular good are equal. The interaction between demand and supply can change the price mechanism which determines the prices and quantity of the goods and services that will be bought and sold in the market.
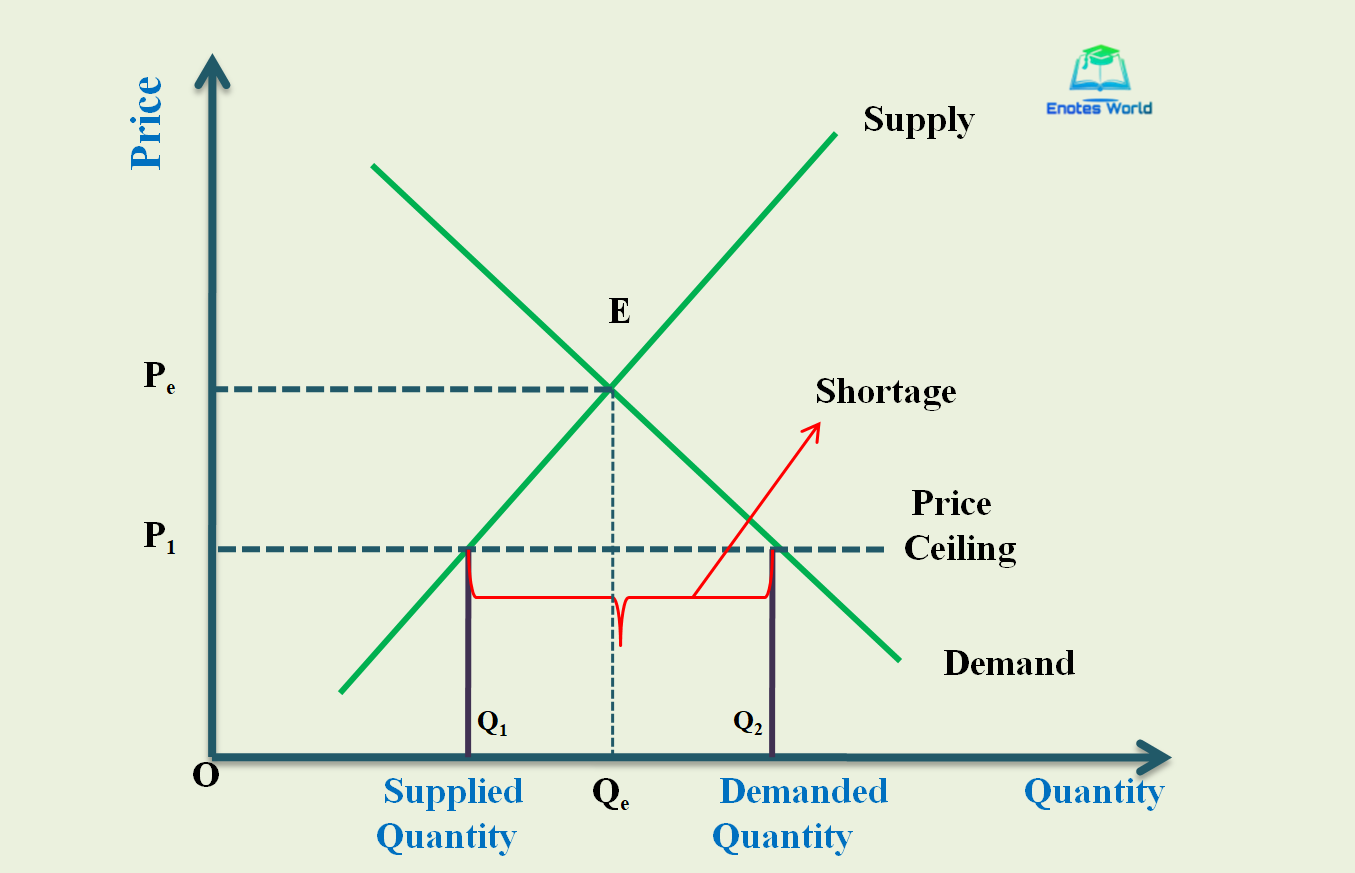
What is the price ceiling?
Governments impose price ceiling and floor prices in order to intervene the market prices. Price ceiling is the maximum price that can be charged for a good or service. For example, the petrol prices in the market maybe too high so the government would set a ceiling price that it can’t be higher than a particular amount.
What is floor price?
Floor price refers to the minimum price that can be charged for a particular good or services, it is established below market equilibrium. For example, the government may think that the market price for wheat is too low, so it may impose a floor price which will lead to an increase in the price of wheat and the market will be in disequilibrium. There are often failure of private sector to provide goods and services. The government may intervene in order to encourage the provision of merit goods like public education that have positive externalities, through subsidies to consumers to lower prices and increases consumption.