
The important agents of mechanical weathering are: The decrease in pressure that results from removal of overlying rock Freezing and thawing of water in cracks in the rock Formation of salt crystals within the rock Cracking from plant roots and exposure by burrowing animals
Full Answer
How is matter involved in weathering?
Weathering describes the breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on the surface of the Earth. Water, ice, acids, salts, plants, animals, and changes in temperature are all agents of weathering. Once a rock has been broken down, a process called erosion transports the bits of rock and mineral away.
What is the process of mechanical weathering?
Mechanical weathering is also known as physical weathering. In this type of weathering, a large rock is disintegrated into smaller pieces of rocks. When rocks disintegrate or break up without experiencing any change in their chemical composition, it is known as mechanical weathering.
What brings about mechanical weathering?
Ice wedging, pressure release, plant root growth, and abrasion can all cause mechanical weathering. in the cracks and pores of rocks, the force of its expansion is strong enough to split the rocks apart. This process, which is called ice wedging, can break up huge boulders.
What are 4 processes involved in mechanical weathering?
The physical breakdown of rock involves breaking rock down into smaller pieces through mechanical weathering processes. These processes include abrasion, frost wedging, pressure release (unloading), and organic activity.
Where does mechanical weathering happen?
Mechanical Weathering This process usually happens near the surface of the planet. Temperature also affects the land. The cool nights and hot days always cause things to expand and contract. That movement can cause rocks to crack and break apart.
What are the 5 processes of mechanical weathering?
There are five major types of mechanical weathering: thermal expansion, frost weathering, exfoliation, abrasion, and salt crystal growth.
What are the main agents of mechanical weathering?
Physical weathering is known as mechanical weathering, where rocks breakdown into smaller pieces by mechanical means. Agents of mechanical weathering include ice, wind, water, gravity, plants, and even, yes, animals [us]!
What is the most important mechanical weathering process?
The cycle of alternative freezing and thawing is one of the most important processes of mechanical weathering. Water expands 9% when it freezes, so when water seeps into cracks in rocks and then freezes, it acts as a pry bar and causes the rock to shatter.
What are 3 physical processes that cause mechanical weathering?
3 Mechanical Weathering Processes that Break Down RocksFrost wedging.Exfoliation.Biological activity.
What are the three major components to mechanical weathering?
The important agents of mechanical weathering are: The decrease in pressure that results from removal of overlying rock. Freezing and thawing of water in cracks in the rock. Formation of salt crystals within the rock.
What processes are involved in mechanical weathering quizlet?
MatchMechanical Weathering. Occurs when rock is physically crushed, split open, or ground into smaller pieces that eventually become soil.Thermal Expansion. Heating rock expands. ... Frost Wedging. ... Exfoliation. ... Salt Wedging. ... Root Pry. ... Animal Activity. ... Increasing Surface Area.More items...
What are the 3 processes of weathering?
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks at the Earth's surface, by the action of rainwater, extremes of temperature, and biological activity. It does not involve the removal of rock material. There are three types of weathering, physical, chemical and biological.
What are 3 physical processes that cause mechanical weathering?
3 Mechanical Weathering Processes that Break Down RocksFrost wedging.Exfoliation.Biological activity.
What is mechanical weathering and its example?
Mechanical weathering involves mechanical processes that break up a rock: for example, ice freezing and expanding in cracks in the rock; tree roots growing in similar cracks; expansion and contraction of rock in areas with high daytime and low nighttime temperatures; cracking of rocks in forest fires, and so forth.
What is the most important mechanical weathering process?
The cycle of alternative freezing and thawing is one of the most important processes of mechanical weathering. Water expands 9% when it freezes, so when water seeps into cracks in rocks and then freezes, it acts as a pry bar and causes the rock to shatter.
What are 5 types of mechanical weathering?
The 5 types of mechanical weathering include thermal expansion, frost weathering (or ice wedging), exfoliation, abrasion, and salt crystal growth.
What are 4 examples of mechanical weathering?
Some examples of mechanical weathering are exfoliation, water and salt crystal expansion, thermal expansion, abrasion by wind and water erosion, an...
What are the 5 causes of mechanical weathering?
The main causes of mechanical weathering are water, ice, salt/mineral crystals, the release of pressure, extreme temperatures, wind, and even the a...
What's the meaning of mechanical weathering?
Mechanical weathering refers to the process by which rock is mechanically or physically broken down into smaller and smaller pieces. It is not the...
How does frost shattering work?
We see that water acts in the same way. Frost shattering is a type of mechanical weathering where we see the breakdown of rock due to the expansion of ice. It may help you to recall this term if you remember that frost is the formation of tiny ice crystals. For example, if you look out your window on a cold, autumn morning, you might see the glistening of small ice crystals that formed on your lawn overnight.
Why is my road bumpy?
If water seeps into cracks within a road surface, which is basically rock, it can freeze and expand. This ice will force small cracks to widen, making for a bumpy road.
How do rocks weather?
The roots of plants and trees grow into cracks within rocks. As the roots grow in size, they widen the cracks. In the end, the roots often win the battle and push the rock, causing pieces of the rock to fall away.
Why are rocks smooth?
The stones are smooth due to the constant weathering force of water running over their surfaces. We also see the effects of abrasion in deserts where sand is picked up and carried by the wind. This flying sand acts like natural sandpaper, smoothing off the surface layer of rocks. Lesson Summary.
Why do rocks break down under pressure?
If that water contains salt, the salt crystals left behind in the cracks can expand when exposed to heat and cause additional weathering. Plant activity where the roots of plants and trees grow into cracks within rocks is another way rocks can break down under pressure.
What is GRUS in rock climbing?
Grus is an example of thermal expansion at work. Grus is the accumulation of coarse-grained and loose fragments left behind by weathering. So, we see that grus is the direct result of the physical breakdown and weakening of rock over time. Therefore, if you were a rock climber and you saw a pile of small rocks gathered at the base of a rocky structure, you would be smarter and safer to move to a different location for climbing.
How does temperature affect rock?
Rocks contain various minerals, and these minerals expand and contract at different rates when exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations such as day-night cycles. This causes stress and small cracks within the rocks and the gradual breakdown of the rock.
What is the process of ice breaking off pieces and slabs?
Frost wedging results when the formation of ice widens and deepens the cracks, breaking off pieces and slabs. Frost wedging is most effective in those climates that have many cycles of freezing and thawing. Frost heaving is the process by which rocks are lifted vertically from soil by the formation of ice.
What is the process by which rocks are lifted vertically from soil by the formation of ice?
Frost heaving is the process by which rocks are lifted vertically from soil by the formation of ice. Water freezes first under rock fragments and boulders in the soil; the repeated freezing and thawing of ice gradually pushes the rocks to the surface. Exfoliation.
How are rocks broken up?
Rocks are also broken up by friction and repeated impact with other rock fragments during transportation. For example, a rock fragment carried along in a river's current continuously bounces against other fragments and the river bottom and eventually is broken into smaller pieces.
Why do sheet joints form?
Because the outer layers expand the most, cracks, or sheet joints, develop that parallel the curved outer surface of the rock. Sheet joints become surfaces along which curved pieces of rock break loose, exposing a new surface.
What happens when temperature changes?
Daily temperature changes, especially in those regions where temperatures can vary by 30 degrees centigrade, result in the expansion and contraction of minerals, which weaken rocks. Extreme temperature changes, such as those produced by forest fires, can force rocks to shatter. Previous Geologic Structures.
What are the agents of mechanical weathering?
Less important agents of mechanical weathering include the burrowing of animals, plant roots that grow in surface cracks, and the digestion of certain minerals, such as metal sulfides, by bacteria.
What is Weathering?
Weathering is the disintegration of rocks due to exposure to the elements of nature. It doesn’t alter or transform the material, but only breaks it up into smaller and over time, fine-grained particles and sediments. It is the prelude to erosion. Weathering loosens and breaks up the exposed material, which is then transported from one place to another through various agents of erosion. A very important difference between weathering and erosion is that weathering occurs in one place, while erosion is the process of transporting the weathered particles to another location.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
A very important difference between weathering and erosion is that weathering occurs in one place, while erosion is the process of transporting the weathered particles to another location.
Why are riverbeds smooth?
This is due to constant abrasive friction with water and other rocks in the vicinity.
What is the best abrasive agent for weathering?
The soft desert sand is one of the best abrasive agents. Constant friction with sand eats away at the surfaces of the rock very effectively. The desert wind aids in quick erosion as well.
What happens when water freezes?
Due to the unusual mode in which water freezes, called anomalous expansion, a certain mass of ice has more volume than an equal mass of liquid water . Hence, the ice formed in the crevice forces the space a bit wider. In the morning, the frozen water thaws, leaving surplus space for more water, which then undergoes the same unusual expansion. Even though this isn’t necessarily a daily process, a continued cycle of freezing and thawing ultimately breaks the rocks along the crevice leading to fragmentation of the whole rock into many smaller particles.
How do rocks break?
This is a process wherein the rocks break in sheets along a number of joints parallel to the surface. It occurs when a protrusion from under the layer of surface rock is thrust upwards, due to either the erosion of the top layer or volcanic activities underneath it. Even as the new layer emerges on to the surface, it is still under pressure from the tectonic movements happening underneath it. This results in the formation of cracks or sheet joints. Due to the pressure, which is maximum at the outermost layer, the rock disintegrates along the crack to expose the underlying layer. This process is called exfoliation. One of the most famous rock formations formed by exfoliation is the Half Dome in Yosemite National Park.
How do rocks weather?
Apart from the processes listed above, rock surfaces can also be weathered by plants germinating within a rock or by the activities of burrowing animals. These are the major contributing factors towards mechanical weathering.
What is the physical breakdown of rock into smaller pieces called?
Mechanical weathering is the physical breakdown of rock into smaller pieces. Chemical weathering is the breakdown of rock by chemical processes.
Why does ice cause weathering?
Ice can cause mechanical weathering when glaciers cause rocks to scrape against each other. Ice can also cause mechanical weathering when water gets in cracks in rocks, and then freezes and expands. This widens the cracks, causing mechanical weathering.
How are rocks broken down?
Rocks are broken into smaller pieces by abrasion or pressure. Landforms are worn down by the agents of mechanical weathering. weathering. the breaking down of rock into smaller pieces by the action of wind, rain, and temperature change. mechanical weathering.
What happens when chemicals in the air and water interact with rocks and minerals to break them down?
occurs when chemicals in the air and water interact with rocks and minerals to break them down. erosion. the process in which wind, water, ice, or other things move pieces of rock and soil over Earth's surface (related word: erode) sediment.
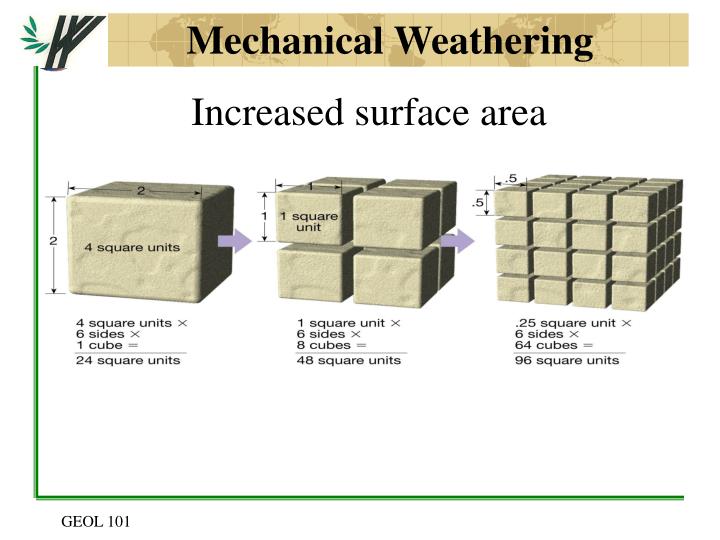
Process of Mechanical Weathering
- The main process in mechanical weathering is abrasion, a physical process by which rocks and clasts are reduced in size. Abrasion by ice, water, and wind processes loaded with sediments can have immense cutting power. The world’s greatest gorges, valleys, and ravines are largely a result of abrasion. In glacial regions, massive masses of moving ice...
Types of Mechanical Weathering
- There are five major types of mechanical weathering: thermal expansion, frost weathering, exfoliation, abrasion, and salt crystal growth. Shall we have a detailed look at them?
Examples of Mechanical Weathering
- Real world examples of mechanical weathering are easy to spot. They include the following: 1. The inclined Talus slope near Lost river in Virginia is a great example of Frost Weathering 2. Bornhardts are products of exfoliation. They are tall, domed, isolated rocks normally found in tropic areas. Sugarloaf Mountain in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, is perhaps the best example of a born…