
What are the different causes of metabolic alkalosis?
The four types of alkalosis
- Respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there isn’t enough carbon dioxide in your bloodstream.
- Metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis develops when your body loses too much acid or gains too much base.
- Hypochloremic alkalosis. ...
- Hypokalemic alkalosis. ...
What are the possible complications of metabolic alkalosis?
What are the possible complications of metabolic alkalosis? Alkalosis may lead to tetany, The causes for this increase in base are as follows: Loss of acid (or loss of Hydrogen) which may happen via vomiting or through urination, dilute acid is given intravenously, Symptoms, Citrate …”>
How is metabloic acidosis diagnosed?
To diagnose metabolic acidosis the following tests can be done so that the exact treatment strategy can be figured out: Arterial Blood Gas (3). This is a test, which measures the pH scale of the blood along with the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide. If there is more acid in the blood, then the pH will be less than 7.0.
What is the difference is acidosis and alkalosis?
Acidosis vs Alkalosis. Summary: Difference Between Acidosis and Alkalosis is that Acidosis is the reduction in pH (increase in H+ concentration) below normal range. While Alkalosis is the increase in pH (decrease in H+ concentration) above the normal range. Acidosis. Acidosis is the reduction in pH (increase in H+ concentration) below normal range. . Acidosis is produc
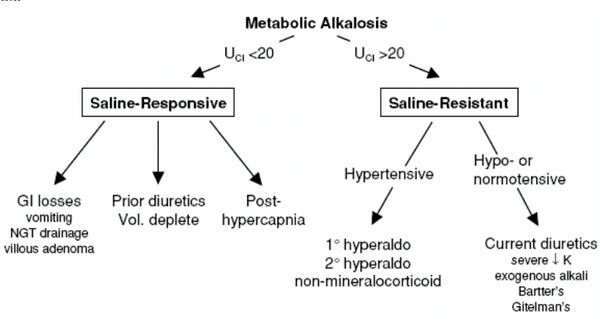
Which laboratory finding indicates metabolic alkalosis?
In any event, the only definitive way to diagnose metabolic alkalosis is with a simultaneous blood gases analysis that shows elevation of both pH and PaCO2 and increased calculated bicarbonate. Because pH and PaCO2 are directly measured, bicarbonate can be calculated.
What are three symptoms of metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis may not show any symptoms. People with this type of alkalosis more often complain of the underlying conditions that are causing it. These can include: vomiting....Severe cases of metabolic alkalosis can cause:agitation.disorientation.seizures.coma.
How do you diagnose metabolic acidosis?
The only definitive way to diagnose metabolic acidosis is by simultaneous measurement of serum electrolytes and arterial blood gases (ABGs) that shows pH and PaCO2 to be low; calculated HCO3- also is low. (For more information, see Metabolic Alkalosis.)
What are the characteristics of metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is primary increase in bicarbonate (HCO3−) with or without compensatory increase in carbon dioxide partial pressure (Pco2); pH may be high or nearly normal. Common causes include prolonged vomiting, hypovolemia, diuretic use, and hypokalemia.
What is the common cause of metabolic alkalosis?
The most common causes of metabolic alkalosis are the use of diuretics and the external loss of gastric secretions.
How do you fix metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is corrected with the aldosterone antagonist spironolactone or with other potassium-sparing diuretics (eg, amiloride, triamterene). If the cause of primary hyperaldosteronism is an adrenal adenoma or carcinoma, surgical removal of the tumor should correct the alkalosis.
How do you determine alkalosis and metabolic acidosis?
Step 1 — check the pH A pH of less than 7.35 indicates acidosis and a pH greater than 7.45 indicates alkalosis.
What blood tests show metabolic acidosis?
Tests may include:Arterial or venous blood gas.Basic metabolic panel, (a group of blood tests that measure your sodium and potassium levels, kidney function, and other chemicals and functions)Blood ketones.Lactic acid test.Urine ketones.Urine pH.
How is acidosis and alkalosis diagnosed?
Doctors can diagnose acidosis and alkalosis with a blood test. The blood test shows if your body's pH levels are out of balance. Your doctor will design a treatment for your acidosis or alkalosis based on what caused the condition.
What happens when you have metabolic alkalosis?
In metabolic alkalosis there is excess of bicarbonate in the body fluids. It can occur in a variety of conditions. It may be due to digestive issues, like repeated vomiting, that disrupt the blood's acid-base balance. It can also be due to complications of conditions affecting the heart, liver and kidneys.
What happens when the body is too alkaline?
Muscle spasms. Nausea. Vomiting. Numbness in your face, feet, or hands
Which values would be expected with metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body's pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process.
What happens when you have metabolic alkalosis?
In metabolic alkalosis there is excess of bicarbonate in the body fluids. It can occur in a variety of conditions. It may be due to digestive issues, like repeated vomiting, that disrupt the blood's acid-base balance. It can also be due to complications of conditions affecting the heart, liver and kidneys.
What are three causes of metabolic acidosis?
It can be caused by:Cancer.Carbon monoxide poisoning.Drinking too much alcohol.Exercising vigorously for a very long time.Liver failure.Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)Medicines, such as salicylates, metformin, anti-retrovirals.MELAS (a very rare genetic mitochondrial disorder that affects energy production)More items...
What happens when your body is too alkaline?
Muscle spasms. Nausea. Vomiting. Numbness in your face, feet, or hands
What are the signs of acidosis or alkalosis?
Some of the common symptoms of metabolic acidosis include the following:rapid and shallow breathing.confusion.fatigue.headache.sleepiness.lack of appetite.jaundice.increased heart rate.More items...
What tests are used to check for metabolic alkalosis?
Blood tests to measure blood gases, acid-base balance and electrolyte levels. Electrocardiogram (EKG) to check for an arrhythmia. Urinalysis that may help find the cause of the metabolic alkalosis.
What are the symptoms of metabolic alkalosis?
Many metabolic alkalosis symptoms are concerning and need prompt medical evaluation. If you are experiencing an arrhythmia, seizures or confusion, seek care right away.
What causes alkalosis in the body?
Other causes of metabolic alkalosis include medical conditions such as: Cystic fibrosis. Dehydration. Electrolyte imbalances, which affect levels of sodium, chloride, potassium and other electrolytes. High levels of the adrenal hormone aldosterone ( hyperaldosteronism ).
Why is metabolic alkalosis important?
Metabolic alkalosis is usually not life-threatening. It does not have lingering effects on your health once it is treated. But it’s important to seek medical care because it can lead to severe complications. Treatment with IV fluids helps many people make a full recovery. Addressing the cause can lower your risk of future episodes.
Why does alkalosis occur?
It can occur in a variety of conditions. It may be due to digestive issues, like repeated vomiting, that disrupt the blood ’s acid-base balance. It can also be due to complications of conditions affecting the heart, liver and kidneys.
What to do after alkalosis treatment?
You may wish to make small changes to lower your risk of future episodes. These changes may include: Decreasing the dose of or discontinuing steroids, laxatives, water pills or antacids.
What is the term for the body's acid-base balance?
What is alkalosis ? Alkalosis occurs when your blood and body fluids contain an excess of bases or alkali. Your blood’s acid-base (alkali) balance is critical to your well-being. When the balance is off, even by a small amount, it can make you sick.
What causes metabolic alkalosis?
Loss of acidic gastric contents will cause a metabolic alkalosis.
What is the most commonly used diuretic for metabolic alkalosis?
Acetazolamide: ( more )#N#Acetazolamide is the most commonly used diuretic for metabolic alkalosis and perhaps the most effective.#N#Make sure to monitor potassium levels carefully (acetazolamide may induce hypokalemia, which will aggravate treatment of the metabolic alkalosis).
Is hypoventilation a sign of metabolic alkalosis?
Hypoventilation (due to respiratory compensation for the metabolic alkalosis). Generally not a significant issue. For patients with a weak respiratory drive (e.g., obesity hypoventilation syndrome or COPD), severe metabolic alkalosis may promote hypoventilation.
Can metabolic alkalosis be treated with volume resuscitation?
Instead, resolving the underlying cause is generally sufficient. For example, a patient with hypovolemia may be treated with volume resuscitation.
Is metabolic alkalosis a treatment for renal failure?
This is a potential treatment of metabolic alkalosis among patients with renal failure.
Can alkalosis be reversed?
Alkalosis is moderate to severe (either causing symptoms). The process causing the alkalosis can't be easily reversed (e.g., patient develops contraction alkalosis from diuretics, but you need to continue diuretic therapy to achieve volume control).
Can hypomagnesemia cause alkalosis?
Hypomagnesemia may contribute to alkalosis and make it difficult to successfully treat the hypokalemia. Therefore, hypomagnesemia should also be corrected.
What is metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process. Before going into details about pathology and this disease process, some background information about the physiological pH buffering process is important. The primary pH buffer system in ...
What is chloride responsive metabolic alkalosis?
In chloride responsive metabolic alkalosis, this includes repletion of electrolytes, specifically chloride and potassium along with the replenishment of fluid. In scenarios, such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or edematous states, diuresis is essential using potassium-sparing diuretics.
What happens if the expected pCO2 does not match the measured value?
If the expected pCO2 does not match the measured value, an underlying metabolic alkalosis is a likely present.
What is the term for a disease where the body's pH is elevated to greater than 7.45?
A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase over this range is alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process.
Which two substances regulate cerebral blood flow in the setting of acute experimental metabolic alkalosis?
Arterial carbon dioxide and bicarbonate rather than pH regulate cerebral blood flow in the setting of acute experimental metabolic alkalosis.
What causes bicarbonate to increase in blood?
Several etiologies lead to increases in bicarbonate within the blood. The simplest of which is an overdose of exogenous sodium bicarbonate in a medical setting. Milk-alkali syndrome is a pathology where the patient consumes excessive quantities of oral calcium antacids, which leads to hypercalcemia and varying degrees of renal failure. Additionally, since antacids are neutralizing agents, they add alkaline substances to the body while reducing acid levels thus increasing pH. A pathology that is in line with normal physiology is the body’s natural compensation mechanism for hypercarbia. When a patient hypoventilates, CO2 retention occurs in the lungs and subsequently reduces pH. Over time, the renal system compensates by retaining bicarbonate to balance pH. This is a slower process. Once the hypoventilation is corrected, such as with a ventilator-assisted respiratory failure patient CO2 levels will quickly decrease, but bicarbonate levels will lag in reducing. This causes post-hypercapnia metabolic alkalosis, which is self-correcting. It is possible to calculate the expected pCO2 in the setting of metabolic alkalosis to determine if it is a compensatory increase in bicarbonate, or if there is an underlying pathology driving alkalosis using the following equation:
What tests are done to determine if you have metabolic alkalosis?
The doctor takes a medical history and does physical examination. If metabolic alkalosis is doubted, blood and urine test are conducted.
What is Metabolic Alkalosis?
A condition when the blood becomes completely alkaline is known as metabolic alkalosis . The normal pH of body is between 7.36-7.44. ( 1) The body is at the best working capacity when the acid-base balance is towards the alkaline side. Alkalosis occurs when either there are too many alkali-producing bicarbonate ions in the body or there are too few acid-producing hydrogen ions.
How Does The Body Deal With Metabolic Alkalosis?
When the food we eat is converted to energy in the cells, the body produces carbon-dioxide.
What is the term for the metabolic alkalosis in which hydrogen ions are retained in the body?
Chloride-Resistant Alkalosis: This type of metabolic alkalosis occurs when an excess of bicarbonate ions are retained in the body or hydrogen ions shift from blood to cells.
How does the kidney help with alkalosis?
By increasing the excretion of bicarbonate ions, the kidney plays its part to combat alkalosis. It is also an automatic process. Alkalosis can be treated by treating the underlying cause, but it’s important to see a doctor if any symptoms are noticed.
What is the normal pH level of blood?
The normal pH of blood is between 7.36 and 7.44. ( 1) If the pH rises above this level, metabolic alkalosis is diagnosed.
What causes blood to become more alkaline?
Potassium deficiency or hypokalemia leads to the shift of hydrogen ions around the cells to inside the cells. This causes the fluid and the blood to become more alkaline.
