Evidence for Evolution Molecular Biology Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of molecules such as DNA, RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known fo…
How does molecular biology support evolution?
- Darwin described evolution as natural variation and natural selection.
- We now know the natural variation is random mutation of the DNA. ...
- Natural selection is a self-evident truth, which is probably why the “creationists” are just too stupid to understand it.
What are the 5 pieces of evidence for evolution?
Five types of evidence for evolution are discussed in this section: ancient organism remains, fossil layers, similarities among organisms alive today, similarities in DNA, and similarities of embryos. Another important type of evidence that Darwin studied and that is still studied and used today is artificial selection, or breeding.
What is the best way to learn molecular biology?
Why I Majored in Molecular Biology
- Nicah Driza ’21. When I first moved to the U.S. ...
- Shaheed Muhammad ’21. Ever since I can remember, medicine and the human body have been sources of pure enchantment for me.
- Brenda Wong ’21. ...
- Chloe Boudreau ’23. ...
- Dolores Fritszche ’22. ...
- Sayde Perry ’22. ...
- Ysabella Alcaraz ’22. ...
- Fernando Bolio ’22. ...
- José Carranza ’22. ...
- Ciannah Correa ’22. ...
What does evidence support evolution?
The fossil record is the piece of classical evidence that is always given for evolution. Paleontologists digging at various sites across the world have always found the long preserved remains of exotic and mysterious creatures that clearly do not exist today.
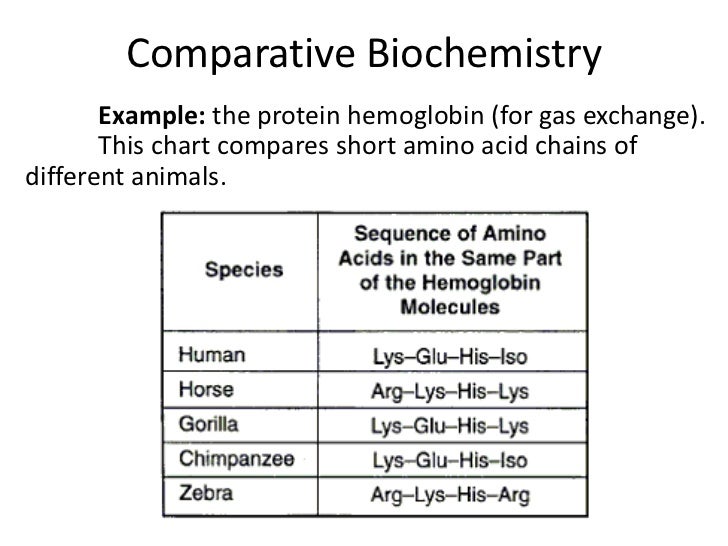
What is an example of molecular evidence of evolution?
For instance, analysis of the amino acid sequence for beta–globin, a subunit of the protein haemoglobin, shows a single difference between humans and gorillas, but over twenty amino acid differences between humans and horses. From this we can infer that humans are more closely related to gorillas than horses.
How does molecular biology provide evidence for evolution quizlet?
Molecular biology, the study of genes and DNA, can also be used to trace the process of evolution. We now know that homologous genes exist in similar organisms. These homologous DNA sequences provide evidence of a common ancestor.
What is an example of molecular biology to support evolution?
Examples of molecules that have been used to study evolution are cytochrome c, which is vital to the respiratory pathway, and ribosomal RNA, which performs protein synthesis. Once a good molecular clock is identified, using it to compare species is fairly simple.
How is molecular biology used in determining evolutionary relationships?
Using morphologic and molecular data, scientists work to identify homologous characteristics and genes. Similarities between organisms can stem either from shared evolutionary history (homologies) or from separate evolutionary paths (analogies).
What evidence supports the theory of evolution?
Fossil evidence supports evolution. The geographic information about many fossils provides evidence that two species with a common ancestor can develop differently in different locations. An is an early form of an organism from which later forms descend.
What are the 5 evidence of evolution?
Five types of evidence for evolution are discussed in this section: ancient organism remains, fossil layers, similarities among organisms alive today, similarities in DNA, and similarities of embryos.
What is molecular biology in evidence?
The field of molecular biology studies macromolecules and the macromolecular mechanisms found in living things, such as the molecular nature of the gene and its mechanisms of gene replication, mutation, and expression.
What is the molecular basis of evolution?
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes.
How does molecular biology relate to genetics?
Genetic is a science that explores genes and their inheritance, while molecular biology studies DNA and RNA at a molecular level, which includes processes of replication, transcription, translation. The connection between these sciences lies in the fact that genetic material is contained in DNA and RNA molecules.
How can molecular data inform evolutionary studies?
Today, almost all evolutionary relationships are inferred from molecular sequence data....This is because:DNA is the inherited material.We can now easily, quickly, inexpensively and reliably sequence genetic material.Sequences are highly specific and are often information rich.
Why is molecular biology important?
Molecular biology also plays a critical role in the understanding of structures, functions, and internal controls within individual cells, all of which can be used to efficiently target new drugs, diagnose disease, and better understand cell physiology.
Why is molecular evidence more accurate?
Abstract. Phylogenetic trees reconstructed from molecular sequences are often considered more reliable than those reconstructed from morphological characters, in part because convergent evolution, which confounds phylogenetic reconstruction, is believed to be rarer for molecular sequences than for morphologies.
What is molecular evolution?
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes.
How are fossils used as evidence for evolution?
Secondly, how are fossils used as evidence for evolution? The fossil record This supports Darwin's theory of evolution, which states that simple life forms gradually evolved into more complex ones. Evidence for early forms of life comes from fossils. By studying fossils, scientists can learn how much (or how little) organisms have changed as life developed on Earth.
What are homologous structures and analogous structures?
Homologous structures provide evidence for common ancestry, while analogous structures show that similar selective pressures can produce similar adaptations (beneficial features). Similarities and differences among biological molecules (e.g., in the DNA sequence of genes) can be used to determine species' relatedness.
Why are molecular clocks important?
While these molecules can evolve just as an entire organism can, some important molecules are highly conserved among species. The slight changes that occur over time in these conserved molecules, which are often called molecular clocks, can help shed light on past evolutionary events.
How to compare species using molecular clock?
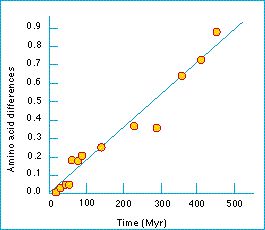
Once a good molecular clock is identified, using it to compare species is fairly simple. The most complicated step is the comparison of molecular sequences. The sequences of the molecule in the different species must be compared so that the number of amino acid or nucleic acid bases that differ can be counted. This number is then plotted against the rate at which the molecule is known to undergo neutral base pair substitutions to determine the point at which two species last shared a common ancestor. Depending on the rate of substitution, molecules may be used to determine ancient relationships or relatively recent ones. Ribosomal RNA has a very slow rate of substitution, so it is most commonly used in conjunction with fossil information to determine relationships between extremely ancient species.
What has Darwin made the most important advances in science?
One of the most useful advances has been the development of molecular biology. In this field, scientists look at the proteins and other molecules that control life processes.
What are the requirements for a molecular clock?
To serve as a molecular clock, a molecule must meet two requirements: 1) it must be present in all of the organisms being studied; 2) it must be under strong functional constraint so that the functional regions are highly conserved.
Does variability affect the functionality of a molecule?
This hypothesis states that most of the variability in molecular structure does not affect the molecule's functionality. This is because most of the variability occurs outside of the functional regions of the molecule.
What would happen if evolution operated on the premise that environmental pressure selects for mutations already present?
If evolution operated on the premise that environmental pressure selects for mutations already present, then the number of surviving colonies on each plate would vary drastically, meaning the variance was much greater than the mean.
Why is micro evolution a fact?
Micro-evolution is a fact, due to the innate ability of cells, through adaptation to change, especially a regards immunity. But to claim that apes became men and claim there are similarities in genetic codes is pure fantasy. Similarity in genetics of organisms or its molecular underpinnings is a fact.
What is the strand of evidence that cross confirms every other piece of data from the fossil record, geology,?
Molecular biology is one strand of evidence which cross confirms every other piece of data from the fossil record, geology, natural history, morphology and others. It is the record of random mutation and variation in the DNA which drives evolution.
How do bacteria evolve?
We see bacteria evolve into resistant strains by the survival to challenge of antibiotics. That is reflected in changes in their DNA. Humans are not all killed by plague because variation in genes, and therefore immunity, means that some of us are resistant. We can drive evolution artificially by breeding specific horse or dog characteristics specific to their function.
What is the force that creates new alleles and diversity?
to further elaborate, we see the force of “mutation” happening in DNA before it changes the phenotype, which in term of evolution is a force that create new alleles and diversity.
What is the cornerstone of evolution?
Molecular biology is the cornerstone of evolutionary biology but the really amazing thing is that it corroborates all the original observations of natural selection made by Darwin and others before molecular biology was even known about, and offers a explanation for it. Sponsored by Massive Bio, Inc.
Why are humans not killed by the plague?
Humans are not all killed by plague because variation in genes, and therefore immunity, means that some of us are resistant. We can drive evolution artificially by breeding specific horse or dog characteristics specific to their function. Oncology trials may be an option for myelofibrosis patients.
Evidence for Evolution Molecular Biology
The term evolution is used to describe heritable changes in one or more characteristics of a population of species from one generation to the other. The present state of mankind on earth is the outcome of three kinds of evolution chemical, organic and social or cultural evolution.
Paleontological Evidences
Paleontology is the study of prehistoric life through fossils. Fossils are described as the true witnesses of evolution or documents of various geological strata of evolution. Fossilization is the process by which plant and animal remains are preserved in sedimentary rocks. They fall under three main categories.
Comparative Anatomy
Similarities in structure between groups of organisms are accepted as indicators of relationship. For example, a comparative study of the forelimbs of different vertebrates exhibits a fundamental plan of similarity in structure.
Embryological Evidences
Embryology deals with the study of the development of individual from the egg to the adult stage. A detailed study of the embryonic development of different forms makes us to think that there is a close resemblance during development.
Evidence for Evolution Molecular Biology
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of molecules such as DNA, RNA and proteins across generations. It uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in the changes of molecules.
How does evolution intersect with geography?
The evolution of unique species on islands is another example of how evolution and geography intersect. For instance, most of the mammal species in Australia are marsupials (carry young in a pouch), while most mammal species elsewhere in the world are placental (nourish young through a placenta). Australia’s marsupial species are very diverse and fill a wide range of ecological roles. Because Australia was isolated by water for millions of years, these species were able to evolve without competition from (or exchange with) mammal species elsewhere in the world.
What is the best way to observe small scale evolution?
Direct observation. We can directly observe small-scale evolution in organisms with short lifecycles (e.g., pesticide-resistant insects).
Why do species share similar physical features?
Anatomy. Species may share similar physical features because the feature was present in a common ancestor ( homologous structures ).
What is evolution on a large scale?
Broadly speaking, evolution is a change in the genetic makeup (and often, the heritable features) of a population over time.
Why are physical similarities analogous?
This process is called convergent evolution. (To converge means to come together, like two lines meeting at a point.)
How are organisms distributed?
The geographic distribution of organisms on Earth follows patterns that are best explained by evolution, in combination with the movement of tectonic plates over geological time. For example, broad groupings of organisms that had already evolved before the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea (about million years ago) tend to be distributed worldwide. In contrast, broad groupings that evolved after the breakup tend to appear uniquely in smaller regions of Earth. For instance, there are unique groups of plants and animals on northern and southern continents that can be traced to the split of Pangaea into two supercontinents (Laurasia in the north, Gondwana in the south).
Why do whales have different forelimbs?
That's because they're adapted to function in different environments. However, if you look at the bone structure of the forelimbs, you'll find that the pattern of bones is very similar across species. It's unlikely that such similar structures would have evolved independently in each species, and more likely that the basic layout of bones was already present in a common ancestor of whales, humans, dogs, and birds.
Who first proposed the idea of biological evolution?
Contrary to popular opinion, neither the term nor the idea of biological evolution began with Charles Darwin and his foremost work, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859). Many scholars from the ancient Greek philosophers on had inferred that similar species were descended from a common ancestor. The word "evolution" first appeared in the English language in 1647 in a nonbiological connection, and it became widely used in English for all sorts of progressions from simpler beginnings. The term Darwin most often used to refer to biological evolution was "descent with modification," which remains a good brief definition of the process today.
Who discovered that organisms evolved over time?
Although it was Darwin, above all others, who first marshaled convincing evidence for biological evolution, earlier scholars had recognized that organisms on Earth had changed systematically over long periods of time. For example, in 1799 an engineer named William Smith reported that, in undisrupted layers of rock, fossils occurred in a definite sequential order, with more modern-appearing ones closer to the top. Because bottom layers of rock logically were laid down earlier and thus are older than top layers, the sequence of fossils also could be given a chronology from oldest to youngest. His findings were confirmed and extended in the 1830s by the paleontologist William Lonsdale, who recognized that fossil remains of organisms from lower strata were more primitive than the ones above. Today, many thousands of ancient rock deposits have been identified that show corresponding successions of fossil organisms.
Why do finches have different beaks?
The different species of finches on the Galápagos Islands, now known as Darwin's finches, have different-sized beaks that have evolved to take advantage of distinct food sources.
How did Darwin explain evolution?
Darwin proposed that evolution could be explained by the differential survival of organisms following their naturally occurring variation— a process he termed "natural selection." According to this view, the offspring of organisms differ from one another and from their parents in ways that are heritable—that is, they can pass on the differences genetically to their own offspring. Furthermore, organisms in nature typically produce more offspring than can survive and reproduce given the constraints of food, space, and other environmental resources. If a particular offspring has traits that give it an advantage in a particular environment, that organism will be more likely to survive and pass on those traits. As differences accumulate over generations, populations of organisms diverge from their ancestors.
What happens to an organism's offspring when it has traits that give it an advantage in a particular environment?
If a particular offspring has traits that give it an advantage in a particular environment, that organism will be more likely to survive and pass on those traits. As differences accumulate over generations, populations of organisms diverge from their ancestors. Figure.
What is a new species?
A new species is one in which the individuals cannot mate and produce viable descendants with individuals of a preexisting species. The split of one species into two often starts because a group of individuals becomes geographically separated from the rest.
How do genetic variations occur?
Genetic variations result from changes, or mutations, in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, the molecule that genes are made from. Such changes in DNA now can be detected and described with great precision. Genetic mutations arise by chance.
Where is evidence for evolution found?
The evidence for evolution is found at all levels of organization in living things and in the extinct species we know about through fossils . Fossils provide evidence for the evolutionary change through now extinct forms that led to modern species.
How do fossils show evolution?
Fossils provide solid evidence that organisms from the past are not the same as those found today; fossils show a progression of evolution. Scientists determine the age of fossils and categorize them all over the world to determine when the organisms lived relative to each other. The resulting fossil record tells the story of the past, and shows the evolution of form over millions of years ( [Figure 1] ). For example, highly detailed fossil records have been recovered for sequences of species in the evolution of whales and modern horses. The fossil record of horses in North America is especially rich and many contain transition fossils: those showing intermediate anatomy between earlier and later forms. The fossil record extends back to a dog-like ancestor some 55 million years ago that gave rise to the first horse-like species 55 to 42 million years ago in the genus Eohippus. The series of fossils tracks the change in anatomy resulting from a gradual drying trend that changed the landscape from a forested one to a prairie. Successive fossils show the evolution of teeth shapes and foot and leg anatomy to a grazing habit, with adaptations for escaping predators, for example in species of Mesohippus found from 40 to 30 million years ago. Later species showed gains in size, such as those of Hipparion, which existed from about 23 to 2 million years ago. The fossil record shows several adaptive radiations in the horse lineage, which is now much reduced to only one genus, Equus, with several species.
How are organisms distributed?
The geographic distribution of organisms on the planet follows patterns that are best explained by evolution in conjunction with the movement of tectonic plates over geological time . Broad groups that evolved before the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea (about 200 million years ago) are distributed worldwide. Groups that evolved since the breakup appear uniquely in regions of the planet, for example the unique flora and fauna of northern continents that formed from the supercontinent Laurasia and of the southern continents that formed from the supercontinent Gondwana. The presence of Proteaceae in Australia, southern Africa, and South America is best explained by the plant family’s presence there prior to the southern supercontinent Gondwana breaking up ( [Figure 4] ).
What are some examples of evolution?
For example, the bones in the appendages of a human, dog, bird, and whale all share the same overall construction ( [Figure 2] ). That similarity results from their origin in the appendages of a common ancestor. Over time, evolution led to changes in the shapes and sizes of these bones in different species, but they have maintained the same overall layout, evidence of descent from a common ancestor. Scientists call these synonymous parts homologous structures. Some structures exist in organisms that have no apparent function at all, and appear to be residual parts from a past ancestor. For example, some snakes have pelvic bones despite having no legs because they descended from reptiles that did have legs. These unused structures without function are called vestigial structures. Other examples of vestigial structures are wings on flightless birds (which may have other functions), leaves on some cacti, traces of pelvic bones in whales, and the sightless eyes of cave animals.
How does DNA evolve?
These duplications are a kind of mutation in which an entire gene is added as an extra copy (or many copies) in the genome. These duplications allow the free modification of one copy by mutation, selection, and drift, while the second copy continues to produce a functional protein. This allows the original function for the protein to be kept, while evolutionary forces tweak the copy until it functions in a new way.
What are the learning objectives of evolution?
Learning Objectives. The evidence for evolution is compelling and extensive. Looking at every level of organization in living systems, biologists see the signature of past and present evolution. Darwin dedicated a large portion of his book, On the Origin of Species, identifying patterns in nature that were consistent with evolution ...
What is the study of the development of an organism to its adult form?
Embryology, the study of the development of the anatomy of an organism to its adult form also provides evidence of relatedness between now widely divergent groups of organisms. Structures that are absent in some groups often appear in their embryonic forms and disappear by the time the adult or juvenile form is reached.
What evidence supports evolution?
Biogeography. Other evidence in support of evolution comes from biogeography, which is how species are distributed across Earth. This is what first suggested to Charles Darwin that species evolve from a common ancestor.
What is evolution in biology?
In biology, evolution refers to the process of organisms developing and changing over time. Explore the theory of evolution and review evidence that supports it found in paleontology, biogeography, embryology, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology. Updated: 09/28/2021
How does paleontology help us understand evolution?
Paleontology tells us how species change through time by studying the fossil record. Biogeography tells us how species are distributed geographically, which helps us understand why similar environments do not always support the same species. Comparative anatomy allows us to visually compare the homology of organisms so that we can see how different environmental demands may have led to similar structures with different functions. And when organisms are very distantly related, we can use molecular biology to understand evolutionary change and homology on the molecular level.
What is it called when organisms are related to each other?
It makes sense that organisms that are related to each other will have similar features. You may have your mother's hair or your father's eyes. But you also have two arms, two legs, a mouth, and a nose, just like other primates, such as monkeys and apes. This similarity in characteristics from a common ancestor is called homology.
Why do siblings have similar DNA?
Just like you and your siblings will have very similar DNA because you are related, so will organisms that inherited their DNA from a long-ago common ancestor. The degree of difference tells us how distant the ancestor is. For example, your DNA is very similar to that of your parents because you inherited it from them.
Why is paleontology important?
Paleontology. The field of paleontology is important to the support and understanding of evolution. This is the study of prehistoric life, including fossils, footprints, and past climatic events. As organisms die, they become part of the ground.
Why is evolution considered a scientific theory?
Evolution is a scientific theory because not only has it been studied and tested but we also have several different sources of evidence to support it.