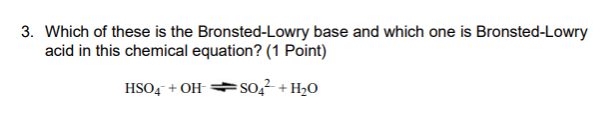
Is NaOH regarded as a Bronsted base?
Sodium hydroxide is a Bronsted-Lowry base because the hydroxide ions that are a part of sodium hydroxide accept protons. Click to see full answer. Consequently, is sodium hydroxide a Lewis base? NaOH is a base because when dissolved in water it dissociates into Na+ and OH- ions. In terms of Lewis theory a base is defined as a compound which ...
Why is NaOH considered a strong base?
What type of base is NaOH? Strong bases are characterized by the fact that they dissociate completely in aqueous solution. In this case, sodium hydroxide, NaOH , is classified as a strong base because it dissociates completely in aqueous solution to form sodium cations, Na+ , and hydroxide anions, OH− . Is KBr an acid or base?
Is LiOH a weaker base than NaOH?
No, LiOH is a strong base, like the other alkali bases. It is a bit weaker than bases like NaOH though, because it’s enthalpy of formation is different. Its conjugate acid, Li+, can act as a weak Lewis acid.
Is NaOH a strong or weak base?
NaOH is a strong base. It completely dissociates in an aqueous solution and releases a lot of OH--ions. No moles of it remain undissociated inside the solution. And the amount of OH--ions in an aqueous solution is very high and we know OH--ions have a tendency to accept the proton. So, more proton acceptors present in the solution ultimately make the NaOH a strong base.
How NaOH is a base according to Bronsted-Lowry?
Solution: The Brønsted-Lowry definition says that a base accepts protons (H+ ions). NaOH, Ca(OH)2, and KOH are all Arrhenius bases because they yield the hydroxide ion (OH-) when they ionize.
How do you identify a Bronsted-Lowry base?
4:099:39Identifying Bronsted Lowry Acids and Bases - Real Chemistry - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHere's the trick if you have a bronsted-lowry acid. After it donates a hydrogen it becomes aMoreHere's the trick if you have a bronsted-lowry acid. After it donates a hydrogen it becomes a conjugate base so that means fluorine is a conjugate base.
What makes a Bronsted-Lowry base?
A Brønsted-Lowry base is any species that can accept a proton from another molecule. In short, a Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor (PD), while a Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor (PA). Thus H+ is an acid by both definitions, and OH− is a base by both definitions.
Is hydroxide a Bronsted-Lowry base?
The ammonium ion is a Brønsted-Lowry acid, while the hydroxide ion is a Brønsted-Lowry base.
What is a Brønsted-Lowry base example?
Here, hydrochloric acid (HCl) "donates" a proton (H+) to ammonia (NH3) which "accepts" it , forming a positively charged ammonium ion (NH4+) and a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-). Therefore, HCl is a Brønsted-Lowry acid (donates a proton) while the ammonia is a Brønsted-Lowry base (accepts a proton).
What can act as a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
Water, by donating a proton to ammonia, acts as a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
Is NaOH an acid or base?
basesMetal hydroxides, such as LiOH, NaOH, KOH, and Ca(OH)2, are bases. Nonmetal hydroxides, such as hypochlorous acid (HOCl), are acids.
Which reactant is a Brønsted-Lowry base?
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor, and a Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor.
How do you classify Bronsted acids and bases?
Bronsted acids and bases are classified by their ability to donate or accept a proton. An acid is a proton donor, and a base is a proton acceptor .
Is NaOH a Lewis base?
NaOH is a Lewis base because the lone pairs on the hydroxide ion can be donated to other compounds.
Is hydroxide ion a Bronsted acid or base?
basesThe Bronsted-Lowry theory doesn't go against the Arrhenius theory in any way - it just adds to it. Hydroxide ions are still bases because they accept hydrogen ions from acids and form water.
How do you know if a base is Arrhenius or Brønsted-Lowry?
Take a look at the reaction below where the hydroxide ion attacks a proton on hydronium. Arrhenius Acid Definition: Hydronium breaks up to yield an H+ in solution. Arrhenius Base Definition: Hydroxide is an OH- dissolved in water. Bronsted-Lowry Base Definition: Hydroxide attacks and accepts the H+ from hydronium.
Which structure of ammonia has a lone pair of electrons?
Lewis structure of ammonia—a nitrogen with a lone pair of electrons that is also bound to 3 hydrogens—plus the Lewis structure of hydrochloric acid forms ammonium chloride.
What is an acid-base reaction?
Using the Brønsted-Lowry definition, an acid-base reaction is any reaction in which a proton is transferred from an acid to a base. We can use the Brønsted-Lowry definitions to discuss acid-base reactions in any solvent, as well as those that occur in the gas phase. For example, consider the reaction of ammonia gas, , with hydrogen chloride gas, , to form solid ammonium chloride, :
What is a strong acid?
A strong acid is a species that dissociates completely into its constituent ions in aqueous solution. Nitric acid is an example of a strong acid. It dissociates completely in water to form hydronium, , and nitrate, , ions. After the reaction occurs, there are no undissociated molecules in solution.
What is the relationship between acid and base?
The Brønsted-Lowry theory describes acid-base interactions in terms of proton transfer between chemical species. A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any species that can donate a proton, , and a base is any species that can accept a proton. In terms of chemical structure, this means that any Brønsted-Lowry acid must contain a hydrogen that can dissociate as . In order to accept a proton, a Brønsted-Lowry base must have at least one lone pair of electrons to form a new bond with a proton.
What is the reaction between nitric acid and water?
In the reaction between nitric acid and water, nitric acid, , donates a proton—shown in blue—to water, thereby acting as a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
What is a weak acid?
By contrast, a weak acid does not dissociate completely into its constituent ions. An example of a weak acid is acetic acid, , which is present in vinegar. Acetic acid dissociates partially in water to form hydronium and acetate ions, :
Is hydrofluoric acid a neutral molecule?
On right: zoomed-in representation of hydrofluoric acid solution showing most of the hydrofluoric acid is still in the neutral molecule form, HF, while a few are dissociated as protons and fluoride ions.
Why NaOH is base?
A base is defined as a proton acceptor or electron-pair donor. When NaOH dissolve in water, it split into two ions Na+ and OH–.
Why NaOH act as a Lewis base?
Lewis’s theory is a very important acid-base theory to check whether a compound (NaOH) acid or base?
What is the conjugate acid of NaOH?
In technical terms, Compounds differentiated from each other by a single proton (H+) are said to be Conjugate acid-base pairs.
Is NaOH alkali or not?
Alkali is a strong base that produces hydroxide ions when it is dissolved in water. All soluble hydroxides like lithium, cesium, sodium, potassium, etc. are alkali metals.
What is a strong base?
Strong base: A compound is a strong base when it completely dissociates in an aqueous solution and liberates a large number of hydroxide ions. All moles of the strong base dissociate into hydroxide anion and no part remains undissociated into the solution.
What is a weak base?
Weak base: A compound is a weak base when it partially or not completely dissociate in an aqueous solution. It means only some parts of the weak base dissociates in the solution to give OH- ion but some parts remain undissociated inside the solution.
How to know if a compound is acid or base?
Important note: To know whether a compound acid or base, simply count the number of hydrogen before and after in solution. When the number of hydrogen is decreased then the compound is base and when the number of hydrogen increased then the compound is acid. Take an example for knowing whether NaOH base or acid according to ...