Common tests & procedures
A hard bump on the front of your knee above your shin is a sign of Osgood-Schlatter disease. What are the treatments for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
What does Osgood-Schlatter disease look like?
Surgery is rarely used to treat Osgood-Schlatter disease. What is Osgood-Schlatter disease? Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that causes pain and swelling below the knee joint, where the patellar tendon attaches to the top of the shinbone (tibia), a spot called the tibial tuberosity.
How is Osgood-Schlatter disease treated?
To conclude, we should say that the diagnosis of Osgood Schlatter disease depends on certain factors and in most cases, doctors recommend physical examination followed by skeletal X-ray examination.
How is Osgood Schlatter disease (OSSL) diagnosed?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is very common. It is the most common cause of knee pain in children and teenagers. Who is affected by Osgood-Schlatter disease? Osgood-Schlatter disease happens in children and adolescents who are going through a growth spurt. This typically occurs around ages 11 to 14.
Who is most affected by Osgood-Schlatter disease?
See more

Does Osgood-Schlatter show up on xray?
The diagnosis of an Osgood-Schlatter disease is usually made on the basis of characteristic localized pain at the tibial tuberosity, and radiographs are not needed for diagnosis. However, radiographic results confirm the clinical suspicion of the disease and exclude other causes of knee pain.
Is Osgood-Schlatter a clinical diagnosis?
History. Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) is a clinical diagnosis. The individual's history and a physical examination are usually sufficient to make the diagnosis of OSD. Anterior knee pain usually is the presenting symptom.
What are Signs of Osgood-Schlatter?
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter Disease? OSD typically causes pain and swelling below the kneecap. The pain usually gets worse with running, jumping, going up stairs, and walking up hills. Severe pain may lead to limping.
How long does it take to heal Osgood-Schlatter?
How long does Osgood-Schlatter last? As mentioned, the pain typically only lasts a few weeks or months. However, it can sometimes last up to two years. The pain does not usually fully resolve until the end of your growth spurt.
What happens if Osgood goes untreated?
Left untreated, Osgood-Schlatter usually goes away as children grow and the tibial tubercle fuses into the shin bone. However, doctors can treat even the most severe cases. Treatment can consist of physical therapy, medication, ice and knee wraps. If necessary, children may have to take a break from sports activities.
Is Osgood-Schlatter genetic?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an osteochondrosis, which is a group of disorders of the growth plates that occur when the child is growing rapidly. Doctors are not sure what causes osteochondrosis, but the disorders do seem to run in families.
Does Osgood-Schlatter affect height?
The findings indicate a strong association between Osgood-Schlatter disease and patella alta. This increase in patellar height would require an increase in the force needed from the quadriceps to achieve full extension. This mechanism could be responsible for the apophyseal lesion.
Can you play sports with Osgood-Schlatter?
Can Teens With Osgood-Schlatter Disease Still Do Sports? Yes, teens with OSD can usually do their normal activities, including sports, as long as: The pain is not bad enough to interfere with the activity. The pain gets better within 1 day with rest.
How serious is Osgood-Schlatter?
Most adolescents with Osgood-Schlatter disease recover with no lasting health effects. Children grow out of the condition as their bodies grow. The bony growths can remain on the knees through adulthood. They usually aren't painful.
Does Osgood-Schlatter hurt Touch?
The main symptom of Osgood-Schlatter is pain at the bump below the knee with activity or after a fall. There may also be swelling around or enlargement of the bump. This bump is usually very tender to the touch. Forceful contraction of the thigh muscles can also cause pain.
Can Osgood-Schlatter cause permanent damage?
Osgood Schlatters will not cause permanent damage and will usually resolve when the child has reduced activity and stopped growing. It can, however, cause a bump to form on the shin bone underneath the tendon insertion.
What can Osgood-Schlatter lead to?
What You Need to Know. Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in young children and adolescents who are still growing. Most children will develop Osgood-Schlatter disease in one knee only, but some will develop it in both.
How do you get rid of Osgood Schlatters fast?
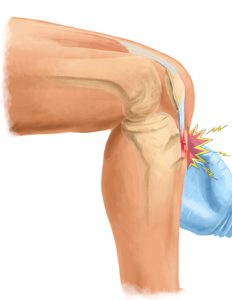
Osgood-Schlatter Disease TreatmentR.I.C.E. (rest, ice, compression, elevation).Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, to reduce pain and swelling.An elastic wrap or a neoprene sleeve around the knee to secure the joint.Stretching, flexibility, and physical therapy exercises for the thigh and leg muscles.
Should you ice Osgood Schlatters?
However, less active adolescents may also experience this problem. In most cases of Osgood-Schlatter disease, simple measures like rest, ice, over-the-counter medication, and stretching and strengthening exercises will relieve pain and allow a return to daily activities.
Do patella bands help Osgood Schlatters?
Patellar Straps (bands) This is thought to relieve some of the stress on the tendon and its attachment on the tibia and may relieve pain associated with patellar tendonitis and Osgood-Schlatter disease.
How do you treat tibial tuberosity pain?
Conservative treatment includes modifying physical activities, using ice packs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), braces, and pads. Symptoms usually resolve after the closure of the physis without any treatment, but symptoms may remain in some cases.
What is the cause of a bump on the upper part of the tibia?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is caused by inflammation in the area below the knee, where the tendon from the kneecap, called the patellar tendon, attaches to the shinbone, or tibia. This inflammation causes pain and swelling at the bump on the upper part of the tibia, called the tibial tubercle. The condition often develops in kids ...
What age does Osgood Schlatter disease occur?
Osgood-Schlatter disease typically occurs in boys 11 to 14 years old and in girls 9 to 12 years old. The condition tends to coincide with growth spurts, which are periods when a child’s bones, muscles, and tendons change rapidly but not always at the same rate. During growth spurts the growth plate is weaker and more likely to widen with the patellar tendon pulling in this area. Growth plates are bands of soft cartilage near the ends of bones where new bone forms as children and teens grow.
What doctor examines a child's knee?
An NYU Langone doctor asks about your child’s symptoms and health and thoroughly examines the knee to determine the cause of the pain. This includes applying pressure to the tibial tubercle, which is often tender or painful in children with Osgood-Schlatter disease.
What do doctors do when a child is in pain?
The doctor also assesses any swelling and asks about the type and severity of pain your child is experiencing. Your child may be asked to walk, run, jump, or kneel to determine if certain movements cause or worsen the pain.
What is the best way to see if a child has a knee problem?
Your child’s doctor may use X-rays to get a closer look at the knee. These can sometimes show changes at the tibial tubercle but mainly help in ruling out other conditions.
What are the symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease include pain, swelling, and tenderness at the tibial tubercle. A child may also walk with a limp due to pain in the affected knee.
How old is Osgood Schlatter?
However, children who are less active may also experience it. Osgood-Schlatter disease typically occurs in boys 11 to 14 years old and in girls 9 to 12 years old. The condition tends to coincide with growth spurts, which are periods when a child’s bones, muscles, and tendons change rapidly but not always at the same rate.
How to treat Osgood-Schlatter disease?
In most cases, Osgood-Schlatter disease can be treated successfully with simple measures, such as rest and over-the-counter medication.
When do you get Osgood Schlatter?
This is the main sign of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Osgood-Schlatter disease is typically diagnosed in adolescents during the beginning of their growth spurts. Growth spurts usually start between ages 8 and 13 for girls, and between ages 10 and 15 for boys. Teenage athletes who play sports that involve jumping and running are more likely ...
What to do if your child has a swollen knee?
A doctor will perform a physical exam and check your child’s knee for swelling, pain, and redness. This will usually provide the doctor with enough information to make an Osgood-Schlatter disease diagnosis. In some cases, the doctor may want to perform a bone X-ray to rule out other potential causes of knee pain.
Why does my growth plate hurt?
The growth plate is weaker and more prone to injury than other parts of the bone. As a result, it can become irritated during physical stress and overuse. The irritation can result in a painful lump below the kneecap. This is the main sign of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Osgood-Schlatter disease is typically diagnosed in adolescents during ...
What is the most common cause of Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease most commonly occurs in children who participate in sports that involve running, jumping, or twisting. These include: Osgood-Schlatter disease tends to affect boys more often than girls. The age at which the condition occurs can vary by sex, because girls experience puberty earlier than boys.
Does Osgood-Schlatter disease resolve on its own?
Osgood-Schlatter disease usually resolves on its own once a growth spurt ends. Until then, treatment is focused on relieving symptoms, such as knee pain and swelling. Treatment typically involves:
Is Osgood-Schlatter disease a minor condition?
Though Osgood-Schlatter disease is usually a minor condition, getting a proper diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications. If your child is experiencing symptoms of the condition, you should:
What is the condition where a tendon pulls against the top of the shinbone?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that happens when a tendon in the knee (the patellar tendon) pulls against the top of the shinbone. This causes pain in the knee and the upper shin. Tendons are bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones. The patellar tendon pulls on an area of the shinbone where new bone is forming, ...
How to relieve stress on patellar tendon?
Many children find relief by stretching their quadriceps (thigh muscles ) to release some of the tension on the patellar tendon. Some doctors also recommend using a brace called a patellar tendon strap. This thin strap fits around the knee under the kneecap. It can relieve some stress on the patellar tendon.
Why do kids get Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Children and adolescents get Osgood-Schlatter disease when they play sports that put repeated stress on the patellar tendon. There are certain activities –running and jumping—that cause your leg muscles to pull the patellar tendon, which pulls on the growth plate.
What is the condition where you have a bump on your knee?
If you are an adolescent and you have pain right below your kneecap, you may have Osgood-Schlatter disease. Your risk of developing the condition is higher if you play sports that involve jumping or bending your knees. A hard bump on the front of your knee above your shin is a sign of Osgood-Schlatter disease.
What causes pain in the upper shin and knee?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that causes pain in the knee and upper shin when tendons pull against the top of the shinbone. Sometimes called jumper’s knee, this condition usually happens to adolescents. It is treated at home with rest, ice and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs.
What is it called when a child's bones grow?
Sometimes called growing pains, Osgood-Schlatter disease often occurs when children are going through a growth spurt. During periods of rapid growth, the bones, muscles, and tendons shift and grow larger. These changes can put more stress on the patellar tendon and growth plate.
What does it mean when you have a bump on your knee?
A hard bump on the front of your knee above your shin is a sign of Osgood-Schlatter disease.
Why do we need medical imaging?
Medical imaging tests may be needed to accurately diagnose the condition and its staging (severity).
Is a lump in the knee indicative of Osgood Schlatters disease?
Clinical examination is usually all that is required as the enlarged lump and ‘Ouch’ reaction of the patient is pretty indicative of Osgood Schlatters Disease. Plus the age of the patient and history of the problem must match the classic group. However there are some more serious conditions such as infection or tumours that may need to be excluded if there is any uncertainty, and parents or carers of children with knee pain should always err on the side of caution and get a diagnosis from a qualified health practitioner such as a Medical Doctor or Physiotherapist/ Athletic Trainer.
Can ultrasound show tendon inflammation?
More recently ultra-sound scans can also show the level of tendon inflammation and as these are less dangerous for using around growth plates on children, they are often preferred to X-rays.
How To Diagnose Osgood Schlatter?
Doctors often recommend you for the diagnose of Osgood Schlatter disease according to underlying symptoms and other aspects, which include-
What is a bone x-ray?
Bone X-Ray Or Skeletal X-Ray Examination: Skeletal X-ray or bone X-ray checks the bones of your leg and knee to examine the affected area closely i.e. the area where your kneecap tendon attaches to your shinbone. Doctors mainly recommend such tests after an accident, fall or any physical trauma. Especially, this type of X-ray is recommendable if an affected person shows any sign or symptom related to swelling and pain, along with other related conditions. These are arthritis, cancer spreading to bones or bone cancer, infections, fractures, osteoporosis, and Osgood Schlatter. (4) (5)
How long does Osgood Schlatter pain last?
However, others experience consistent and debilitating pain, which makes doing any physical activity a challenging task. The discomfort may last from only a few weeks to about several years, while the symptoms often go away once the adolescent growth spurt completes. (1)
What causes a bump on the bottom of the knee?
Osgood Schlatter disease causes a painful and bony bump just below one’s knee or on one’s shinbone. The problem often takes place in adolescents and children, who often experience growth spurts at the time of entering puberty.
What is the best medicine for Osgood Schlatter?
These are as follows-. Tylenol and other similar types of acetaminophen medications.
What are the symptoms of Osgood Schlatter?
Advertisement. Leg or knee pain. Tenderness, swelling, and increase in warmth below your knees and on your shinbone. Worsening of the with running, exercise and other highly intensive activities. Limping after you perform any physical activity.
What are the two types of examinations for Osgood Schlatter?
These include the following-. Physical Examination: During the physical examination phase, doctors check the condition of an infected child’s knee to check any problem in it. These include pain, swelling, tenderness, and redness. ...
How long does it take for bone fragmentation to appear in the tibial tuberosity?
Bone fragmentation at the tibial tuberosity may be evident 3 to 4 weeks after the onset. It is important not to equate isolated 'fragmentation' of the apophysis with OSD, as there may well be secondary ossification centers.
What is an unresolved OSD?
Unresolved OSD is the term given to clinical and radiological findings of OSD that persist into adulthood.
What is the sonographic appearance of Osgood-Schlatter disease?
The sonographic appearances of Osgood-Schlatter disease include 3: swelling of the unossified cartilage and overlying soft tissues.
What is the ISBN for McGraw-Hill Medical?
5. Prentice WE, Voight ML. Techniques in musculoskeletal rehabilitation. McGraw-Hill Medical. (2001) IS BN:0071354980. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
What is the treatment for a hamstring insertion?
Treatment and prognosis. Treatment is usually conservative and involves rest, ice, activity modification (decreasing activities that stress the insertion, especially jumping and lunging sports), and quadriceps and hamstring strengthening exercises.
Can you excision a bone fragment?
In rare cases, surgical excision of the bone fragment (s) and/or free cartilaginous material may give good results in skeletally mature patients who remain symptomatic despite conservative measures.
Is apophysis fragmentation secondary to OSD?
It is important not to equate isolated 'fragmentation' of the apophysis with OSD, as there may well be secondary ossification centers.

Clinical significance
Symptoms
Treatment
Causes
Epidemiology
Diagnosis
Activities
- In most cases, Osgood-Schlatter disease can be treated successfully with simple measures, such as rest and over-the-counter medication. Osgood-Schlatter disease usually resolves on its own once a growth spurt ends. Until then, treatment is focused on relieving symptoms, such as knee pain and swelling. Treatment typically involves:
Prognosis
- Osgood-Schlatter disease most commonly occurs in children who participate in sports that involve running, jumping, or twisting. These include:
Prevention
- Osgood-Schlatter disease tends to affect boys more often than girls. The age at which the condition occurs can vary by sex, because girls experience puberty earlier than boys. It usually develops in girls between ages 11 and 12 and in boys between ages 13 and 14.