
What separates oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood?
Sol. According to the given diagram, the septum, (i.e. part B) a muscular wall found between the right and left chambers of the heart separates the oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood.
Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals?
- Q&A Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds? In birds and mammals have a double circulation system where both the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood maintains separate.
What is the direction of deoxygenated blood?
Deoxygenated Blood: The deoxygenated blood flows from the metabolizing tissues of the body through the right chambers of the heart to the lungs. Direction of the Blood Oxygenated Blood: Oxygenated blood flows away from the heart. Deoxygenated Blood: Deoxygenated blood flows towards the heart.
How does oxygenated blood flow through the body?
The oxygenated blood is rich in oxygen as well as other nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and vitamins. It flows from the heart to the metabolizing tissues throughout the body to supply oxygen and nutrients to the cells. Oxygenated blood flows through the systemic arteries in the body.
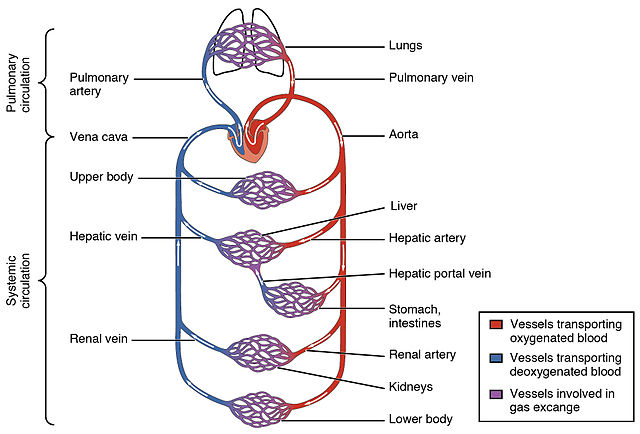
How is the separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood useful to human?
Double circulation prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood with each other. The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood allows a more efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells.
Why oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is separated in mammals?
As mammals and birds require to keep their body warm, they require a higher supply of oxygen. Thus, it is beneficial if the oxygenated blood remains separate as its mixing with deoxygenated blood can make the entire blood impure.
Does the heart separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
In the human heart, oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are separated. In the human heart, oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are separated.
How does deoxygenated and oxygenated blood not mix?
1 Answer. There is no mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated bloods in human heart due to the presence of inter-ventricular septum. This septa completely divides the ventricle into right and left to avoid mixing of blood.
What is the necessary to separate oxygenated?
They must separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood so that their circulatory system is more efficient and can maintain their constant body temperature. It is also better if the oxygenated blood stays separate, as its combination with deoxygenated blood will impure the entire blood.
Why is it necessary to separate the left side and right side of heart in mammals?
Solution : The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs (birds and mammals) which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
What is the color of deoxygenated blood?
dark redBlood is always red. Blood that has been oxygenated (mostly flowing through the arteries) is bright red and blood that has lost its oxygen (mostly flowing through the veins) is dark red. Anyone who has donated blood or had their blood drawn by a nurse can attest that deoxygenated blood is dark red and not blue.
What will happen if oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix in heart?
When abnormal passages exist in the heart, oxygenated and deoxygenated blood can mix in the heart. This depletes the oxygen in the blood and makes the heart work harder to deliver oxygen to the body.
What causes mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Another condition is patent ductus arteriosus, where a temporary channel that connects the pulmonary artery and the first segment of the descending thoracic aorta during fetal growth fails to close after birth, causing some mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Why is it necessary to prevent the mixing of oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood?
The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to the entire body. - The one-way valves which are present in the heart prevent the backflow of blood, so, Oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-rich blood cannot be mixed. Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood living organisms?
Separated oxygenated and deoxygenated blood makes a more efficient circulatory system. It easily transports oxygen to the cells which can absorb higher amounts of oxygen and hence produce more energy.
Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in animals and birds?
The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds is necessary to produce more energy in order to maintain their body temperature at different climatic Conditions.
What is the advantage of separate channels in mammals and birds?
Solution : It is necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds, because they need high energy and large amount of oxygen, The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood provides high oxygen supply to the organs.
What is double circulation in human beings why is it necessary?
There are two loops in which blood is circulated. One loop is oxygenated and the other is de-oxygenated. This double circulatory system is important because it ensures provision of oxygenated blood to the muscle and not a mixture of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood.
What is the color difference between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Answer: The oxygenated blood (mainly through the arteries) is... Read full
What is the benefit of retaining both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Answer: We must segregate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood f... Read full
What exactly is oxygenated blood?
Answer: Oxygenated blood is a blood cell that has a high prop... Read full
What similarities exist between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Answer: The two primary kinds of blood circulated all through... Read full
Why are oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separated in mammals?
Answer: Warm-blooded birds and mammals require equilibrium to live. A c... Read full
Main Difference – Oxygenated vs Deoxygenated Blood
Blood is the main circulatory fluid in animals with a closed circulation system. It circulates through the heart and blood vessels. The two main types of blood vessels are arteries and veins. The main function of blood in the body is to transport oxygen and nutrients to the metabolizing tissues of the body.
What is Oxygenated Blood
Oxygenated blood refers to the blood that has been exposed to oxygen in the lungs. It is also known as arterial blood. The blood flows to the lungs to take up atmospheric oxygen by hemoglobin in the red blood cells. It flows to the left chamber of the heart from the lungs through the pulmonary vein.
What is Deoxygenated Blood
Deoxygenated blood refers to the blood that has a low oxygen saturation when compared to the blood leaving the lungs. It is also known as venous blood. The tissues of the body take up oxygen from the oxygenated blood and return carbon dioxide as a metabolic waste.
Similarities Between Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Blood
Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are the two main types of blood circulated throughout the body.
Difference Between Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Blood
Oxygenated Blood: Oxygenated blood refers to the blood that has been exposed to oxygen in the lungs.
Why do animals need more oxygen?
Hence, these animals require more oxygen (O 2) for more cellular respiration to produce more energy to maintain their body temperature. ...
Is it better to have oxygenated blood or deoxygenated blood?
It is also better if the oxygenated blood stays separate, as its combination with deoxygenated blood will impure the entire blood.
How does blood flow through the body?
Your blood circulates throughout the body, pausing at different points along the way to drop off items needed to perform work and picking up the scraps that are no longer needed. It does this over about 60,000 miles of blood vessels. It’s also not just the heart where deoxygenated blood and oxygenated blood are separated but throughout the entire human body. For the most part, arteries carry the oxygenated blood thru a steadily narrowing system of pipes until it gets to the capillaries. Once at the capillaries oxygen and
Why do blue babies need operations?
They need operations to close the hole, for one to improve the efficiency of the pumping function of the heart, but also to optimise the function of the blood by separating oxygenated from deoxygenated blood.
What keeps the heart and the lungs separate?
Ordinarily, the walls (septum) of the heart keep them separate. However… there are congenital conditions (too many to go into here) in which they’re not separated and deoxygenated blood bypasses the lungs or deoxygenated and oxygenated blood inadvertently gets mixed and gets passed out to the rest of the body - also known as “blue baby syndrome” ...
What is the role of blood in the cycle of deoxygenation?
And continues the cycle of oxygenation and deoxygenation by supplying oxygen to cells and picking up the impurities. Then cleaned by nephrons in kidneys is given to lungs for oxygenation and thus continues the cycle.
How many miles of blood vessels does the heart have?
It does this over about 60,000 miles of blood vessels. It’s also not just the heart where deoxygenated blood and oxygenated blood are separated but throughout the entire human body. For the most part, arteries carry the oxygenated blood thru a steadily narrowing system of pipes until it gets to the capillaries.
Why does blood act as a transport medium?
In order to supply oxygen for cells and brain for the action of ATP molecules (keeping the cells alive and function) the blood acts as a transport medium. And continues the cycle of oxygenation and deoxygenation by supplying oxygen to cells and picking up the impurities.
What happens if the arterial blood has less oxygen?
The simple answer if that the arterial blood will have less oxygen and if there is a large amount of mixing the heart and lungs will have to work harder. There are some congenital conditions in which this can occur, most notably in ventricular septal defect (VSD) and in patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
