Some possible treatments include:
- Temporary hemodialysis to do the work that your kidneys should be doing, until they can recover
- Medicines to control the amounts of vitamins and minerals in your blood
- Treatments to keep the right amount of fluid in your blood
Is Prerenal failure reversible?
Prerenal failure is widely accepted as a reversible form of renal dysfunction, caused by factors that compromise renal perfusion. The term has been used as part of a dynamic process that begins with a reversible condition, prerenal state, and can progress to an established disease, acute tubular necrosis (ATN).
What is the best treatment for acute renal failure?
Treatment for acute kidney failure typically requires a hospital stay....Treatments that help prevent complications include:Treatments to balance the amount of fluids in your blood. ... Medications to control blood potassium. ... Medications to restore blood calcium levels. ... Dialysis to remove toxins from your blood.
What is the most common cause of Prerenal failure?
Intravascular volume depletion is the most common cause of pre-renal failure. Intravascular volume depletion can be the result of poor oral intake or excessive fluid loss.
What happens Prerenal failure?
Prerenal acute kidney injury (AKI) , (which used to be called acute renal failure), occurs when a sudden reduction in blood flow to the kidney (renal hypoperfusion) causes a loss of kidney function. In prerenal acute kidney injury, there is nothing wrong with the kidney itself.
Can kidneys recover from acute renal failure?
Acute kidney failure can be fatal and requires intensive treatment. However, acute kidney failure may be reversible. If you're otherwise in good health, you may recover normal or nearly normal kidney function.
What are the 2 ways to treat renal failure?
Treatment for end-stage kidney diseaseDialysis. Dialysis artificially removes waste products and extra fluid from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do this. ... Kidney transplant. A kidney transplant involves surgically placing a healthy kidney from a donor into your body.
How long can someone live with acute renal failure?
In acute failure, death may occur within a few days to a week without treatment. If the progress of CKD is rapid and the patient opts not to have treatment, life expectancy may be a few years at most.
What are the symptoms of Prerenal failure?
Prerenal AKI Symptoms Examples of this include: Severe dehydration symptoms may include sunken eyes, dry skin, decreased skin elasticity, dry mouth and eyes, rapid heart rate (tachycardia ), and dizziness or lightheadedness when standing or sitting up ( orthostatic hypotension ).
Can dehydration cause Prerenal failure?
Prerenal Failure The reduced flow can be the result of dehydration. This condition is reversible with the immediate administration of fluids and electrolytes, since no damage may have yet been done to the kidney organs. However, untreated prerenal failure develops into acute kidney failure.
Is Bun elevated in Prerenal failure?
In prerenal conditions, low urine flow rates favor BUN reabsorption out of proportion to decreases in GFR, resulting in a disproportionate rise of BUN relative to creatinine, creating a serum BUN-to-creatinine ratio of more than 20 in prerenal failure.
Can kidney function be improved?
Exercise may help kidney health Being active and having a healthy body weight is also important to kidney health. Some studies show kidney function improves with exercise. Talk with your healthcare professional or dietitian if you need to lose weight.
What happens if acute renal failure is left untreated?
As blood moves through the body, it picks up extra fluid, chemicals and waste. The kidneys separate this material from the blood. It's carried out of the body in urine. If the kidneys are unable to do this and the condition is untreated, serious health problems result, with eventual loss of life.
How long can you survive with acute renal failure?
If the progress of CKD is rapid and the patient opts not to have treatment, life expectancy may be a few years at most. However, even people who have complete renal failure may live for years with proper care and regular dialysis treatments. A kidney transplant may also result in a longer survival period.
Can you recover from acute kidney failure without dialysis?
People with kidney failure may survive days to weeks without dialysis, depending on the amount of kidney function they have, how severe their symptoms are, and their overall medical condition.
How long does it take for acute renal failure to resolve?
In some cases AKI may resolve in a couple of days with fluid and antibiotics. In other cases the illness affecting the kidneys and the rest of the body may be so severe that recovery takes two or three weeks or even longer.
What are the four major options of treatments for kidney failure?
Treatment Options for Kidney Failure include Kidney Transplant, Peritoneal Dialysis (Tummy Dialysis), Hemodialysis (Machine Dialysis), and Conservative Management.
How to treat kidney failure?
The treatment is focused at improving the kidney perfusion (blood circulation). The correct diagnosis or detection of the exact cause of kidney failure , helps determine the treatment. The effect of dehydration can be lowered by administering intravenous fluid. Other causes like infection, liver problem, and heart failure need to be treated according to the types and severity of symptoms. Since the output of urine increases significantly with the administration of intravenous fluids, patients diagnosed with prerenal failure are advised to be admitted in the hospital. The renal function improves fast with the increased output of urine.
Why can't the kidneys filter blood?
Following are the causes of this disorder: Atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries due to increased fatty deposits inside the arteries can significantly reduce the blood flow towards the kidneys.
What is the most common type of acute kidney failure?
Prerenal failure is the most common type of acute kidney failures. This article discusses the causes, symptoms, and treatment regarding the same. Prerenal failure is the most common type of acute kidney failures. This article discusses the causes, symptoms, and treatment regarding the same. Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is the sudden loss ...
Does renal function improve with increased urine output?
The renal function improves fast with the increased output of urine. Patients with severe symptoms are admitted in the intensive care units, as they have an increased risk of heart failure or liver failure. These patients may suffer from severe infections like viral hepatitis.
What causes prerenal ARF?
Ultimately, prerenal ARF is caused by sustained hypotension that reduces renal perfusion. However, many of the etiologies discussed below reduce renal perfusion over courses much longer than hours to days.
What is the definition of acute renal failure?
Recall that Acute Renal Failure is defined by a sudden (hours to days) reduction in the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR). Such reductions can occur when there is insufficient pressure perfusing the kidneys and thus the glomeruli. In such cases, there is simply not enough glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure to maintain sufficient levels of GFR (See: Glomerular Filtration Rate page)
Can GFR be maintained in the face of renal perfusion?
The answer is that neuroendocrine and autoregulatory mechanisms can usually maintain GFR in the face of falling renal perfusion over a wide range. However, at some point these mechanisms cannot sufficiently compensate and this precipitates a sudden drop in GFR, manifesting as ARF. True Hypovolemia.
Can hepatorenal syndrome cause prerenal ARF?
Finally hepatorenal syndrome can yield prerenal ARF although the pathogenesis can yield prerenal ARF through cryptic mechanisms. The symptomology of prerenal ARF is described in Acute Renal Failure. Note that in prerenal ARF there is no actual pathology of dysfunction in the kidney itself.
How to assess renal failure?
Once life-threatening conditions are addressed, the EMS provider should turn to gathering a complete patient history and performing a detailed examination. Use the SAMPLE (signs/symptoms, allergies, medications, past medical history, last oral intake and events preceding the call for help) mnemonic as a guide to asking basic questions. Question the patient about vomiting, diarrhea or inadequate fluid intake, and be alert for signs of dehydration. While patient questioning is occurring, ensure that other providers are assessing vital signs. Pulse oximetry, blood pressure, pulse, respirations and temperature should all be assessed and recorded.
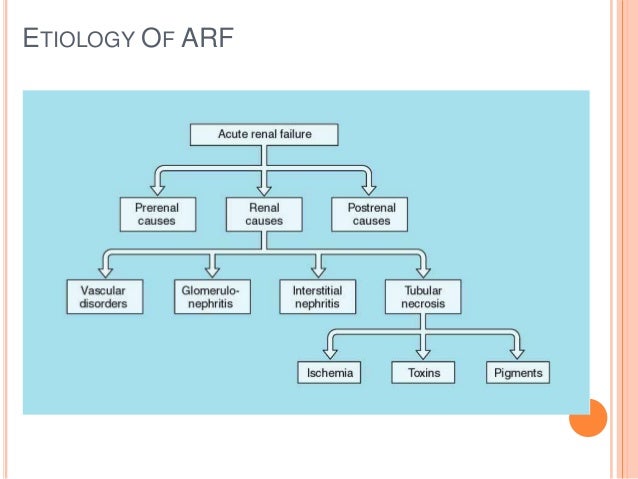
What are the causes of acute renal failure?
The causes of acute renal failure are commonly grouped into three major categories: pre-renal, intrarenal and post-renal failure. 3 Pre-renal is the most common for renal failure and arises from such conditions as rhabdomyolysis, hemorrhage, sepsis, burns, trauma and a host of other factors.
What is the role of a prehospital caregiver?
Prehospital caregivers play a vital role in ensuring that renal failure patients are quickly identified, properly treated and transported to an appropriate ED for continued care.
How long does it take for renal failure to occur?
Acute renal failure can occur over hours to days based on the underlying mechanism of injury and relative health of the individual. Complications that arise when acute renal failure is present include disturbances in fluid and electrolyte balances and accumulation of metabolic wastes in the blood.
Can kidney failure be treated with dialysis?
Depending on the level of severity, chronic renal failure may be treated with dialysis and possibly by kidney transplantation. Over time, chronic renal failure can lead to a permanent and irreversible loss of renal functioning, known as end stage renal disease (ESRD).
Can kidney failure be life threatening?
If the injury to the kidneys is significant and abrupt, the patient may experience acute renal failure, which can be life-threatening. In other cases, the kidneys are injured over time and shut down due to chronic renal failure.
What is the treatment for acute renal failure?
Treatment for acute renal failure (ARF) may involve vasopressor drugs to help raise the blood pressure, intravenous fluids to aid in rehydration, diuretics to increase urine output, and hemodialysis to help filter the blood while the kidneys are healing. Science Photo Library / Getty Images.
What is prerenal ARF?
Prerenal ARF, in which the blood flow to the kidneys is impeded.
What is the difference between CRS and kidney failure?
CRS is actually a two-way street in which the lack of blood flow from the heart can affect kidney function, while the failure of the kidneys can lead to the impairment of the heart. 2 . In the former state, diuretics are commonly used to increase the output of urine and aid in the excretion of toxins from the body.
How long can you live with end stage renal failure?
Without treatment, people with end-stage renal failure may survive for days or weeks. 7.
How to treat hyperkalemia?
The first course of action is to treat life-threatening symptoms like hypotension or shock with intravenous fluids and medications like epinephrine to raise the blood pressure. Insulin, inhaled albuterol, and diuretics can help treat hyperkalemia by clearing excess potassium from the body , reducing the risk of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. 6
Why is my kidney not functioning?
There are myriad reasons why a kidney may not function as normal, including trauma, infection, toxins, vascular diseases, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and even complications of surgery.
Can dehydration be treated with intravenous fluids?
Dehydration may be treated with intravenous fluids. 1 The infusion of fluids would be monitored with a central venous catheter (CVC) to ensure that you are neither overhydrated nor underhydrated. If your low blood pressure persists despite intravenous fluids, vasopressor drugs may be used to raise the blood pressure.
Overview of Kidney Anatomy and Function
We will begin with an overview of the kidneys. They are two bean-shaped organs, roughly the size of an adult fist, that lie in the retroperitoneal cavity. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left because of the liver placement. The adrenal glands sit right on top of each kidney.
Renal Failure Stages
Kidney health is determined by testing blood and urine. Blood tests measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the blood, and urine tests calculate the albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR) in the urine. The presence of protein in the urine could mean that the kidneys are not filtering well.
Acute vs. Chronic Renal Failure
Renal damage can be categorized as acute or chronic. In acute renal failure (ARF), damage to the kidneys happens suddenly, causing the kidneys to lose some or all function temporarily. Acute causes of renal failure include trauma, exposure to nephrotoxic substances, infection, and temporary interruption of blood flow to the kidneys.
Types of Dialysis
Dialysis is a form of renal replacement therapy. The two main types are hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Both modalities utilize a semi-permeable membrane to eliminate waste, toxins, and excess fluid from the body.
Treatment Goals
No matter which modality is chosen, all dialysis treatments have the same goals: to replace lost kidney function and return the body to homeostasis. Because fluid balance is a crucial goal of dialysis, accurate patient weights are extremely important. Each patient is prescribed an estimated dry weight (EDW) by a nephrologist.
Dialysis Settings
Both types of dialysis treatments can occur almost anywhere. Hemodialysis is generally performed in hospitals, outpatient clinics, or at a patient’s home. Electricity is required to operate the dialysis and RO machines and there needs to be a water source to make the RO water.
Transplant
13.5% of dialysis patients in the U.S. (about 100,000 people) are currently listed as actively awaiting a kidney transplant (1). A kidney transplant is a surgical procedure in which the ESRD patient, with Renal Failure Stage 5, receives a kidney from either a living or deceased donor.
What is prerenal state?
A prerenal state is a condition in which kidney dysfunction has occurred because of inadequate blood flow to the kidney tissue.
Why is it important to maintain your kidneys?
It is imperative to modify your lifestyle habits to preserve your kidney’s health, and thus your overall well-being . This is more so important with advancing age as the risks of kidney stones and damage increase in old age.
What is the filter of the kidney?
The filters of the kidney ( glomeruli) The blood vessels within the kidney ( vasculature) The small tubes that connect the glomeruli to the area within the kidney that collects newly made urine ( tubules) The space adjacent to the glomeruli, vasculature, and tubules within the kidney ( interstitial space)
Can kidney failure cause discomfort?
While there are exceptions, most situations in which the kidneys fail to function properly are not accompanied by a perceivable discomfort. So, in scenarios in which kidney dysfunction or damage is suspected, one must look for changes in certain laboratory tests.
Does salt help with kidney problems?
Instead, in most cases, a combination of water and salt is much more effective. An example of this occurs in cases of intravenous fluid administration.
