
What are the steps of DNA to RNA?
- From existing DNA to make new DNA ( DNA replication ?)
- From DNA to make new RNA ( transcription)
- From RNA to make new proteins ( translation ).
What are two ways RNA is different from DNA?
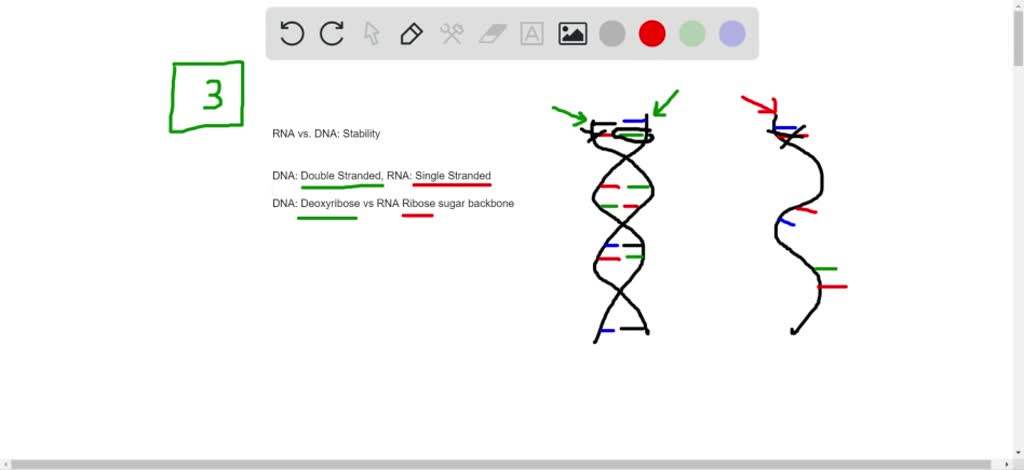
What is the main difference between DNA and RNA?
- like RNA SINGLE STRAND have many type (mRNA , tRNA ,rRNA ,prokaryotic RNA) in the prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell
- in prokaryotic cell RNA in the cell free without nucleus.and replicated with themselvies
- in eukaryotic all RNA INSIDE THE NUCLEUS.and replicated by templet strand of DNA
What is it called to go from DNA to RNA?
Transcription overview. Transcription is the first step of gene expression. During this process, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into RNA. Before transcription can take place, the DNA double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. The region of opened-up DNA is called a transcription bubble.
How and why does RNA copy the DNA?
RNA polymerase enzyme As the cell unzips DNA it makes a copy of one side of the chain DNA polymerase enzyme shuttles in nucleotides that match each unzipped part of the DNA. Replication When the strands have been completely unzipped and matching nucleotides are linked together, two copies have been created in a process
How is RNA made?
All of the RNA in a cell is made by DNA transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of DNA replication discussed in Chapter 5. Transcription begins with the opening and unwinding of a small portion of the DNA double helix to expose the bases on each DNA strand.
What is the RNA that is copied from genes?
Cells Produce Several Types of RNA. The majority of genes carried in a cell's DNA specify the amino acid sequence of proteins; the RNA molecules that are copied from these genes (which ultimately direct the synthesis of proteins) are called messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules.
How many subunits are in RNA polymerase?
Two depictions of the three-dimensional structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase, with the DNA and RNA modeled in. This RNA polymerase is formed from four different subunits, indicated by different colors (right). (more...)
What is the microscope used to see RNA polymerase?
Transcription of two genes as observed under the electron microscope . The micrograph shows many molecules of RNA polymerase simultaneously transcribing each of two adjacent genes. Molecules of RNA polymerase are visible as a series of dots along the DNA (more...)
Which intron sequences bind to a specific site on the RNA to initiate splicing?
The two known classes of self-splicing intron sequences. The group I intron sequences bind a free G nucleotide to a specific site on the RNA to initiate splicing, while the group II intron sequences use an especially reactive A nucleotide in the intron (more...)
Where does eucaryotic pre-mRNA take place?
Of the pre-mRNA that is synthesized, only a small fraction—the mature mRNA—is of further use to the cell. The rest—excised introns, broken RNAs, and aberrantly spliced pre-mRNAs—is not only useless but could be dangerous if it was not destroyed. How then does the cell distinguish between the relatively rare mature mRNA molecules it wishes to keep and the overwhelming amount of debris from RNA processing? The answer is that transport of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where it is translated into protein, is highly selective—being closely coupled to correct RNA processing. This coupling is achieved by the nuclear pore complex, which recognizes and transports only completed mRNAs.
Why is transcription important in bacteria?
The initiation of transcription is an especially important step in gene expression because it is the main point at which the cell regulates which proteins are to be produced and at what rate. Bacterial RNA polymerase is a multisubunit complex.
Which direction is RNA synthesized?
RNA is synthesized in the 5' -> 3' direction (as seen from the growing RNA transcript). There are some proofreading mechanisms for transcription, but not as many as for DNA replication. Sometimes coding errors occur.
What is the role of DNA in RNA synthesis?
One strand of DNA serves as the template for RNA synthesis, but multiple rounds of transcription may occur so that many copies of a gene can be produced.
What is the promoter of DNA?
The promoter is a DNA sequence that signals which DNA strand is transcribed and the direction transcription proceeds. Approximately 23 nucleotides must be synthesized before RNA polymerase loses its tendency to slip away and prematurely release the RNA transcript. 04. of 05.
What is the process of transcription in bacteria?
The initiation of transcription in bacteria begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter in DNA. Transcription initiation is more complex in eukaryotes, where a group of proteins called transcription factors mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
What are the steps of transcription?
Key Takeaways: Steps of Transcription 1 The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation. 2 Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. 3 The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What are the steps of gene expression?
The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation . Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
Why is RNA called messenger RNA?
The RNA is called messenger RNA because it carries the "message," or genetic information, from the DNA to the ribosomes, where the information is used to make proteins. RNA and DNA use complementary coding where base pairs match up, similar to how the strands of DNA bind to form a double helix. One difference between DNA and RNA is ...
How is RNA converted to cDNA?
The RNA can be converted to cDNA using the enzyme Reverse Transcriptase. This enzyme was first found in the host cell infected with a retrovirus. The retrovirus has the genes which encode for Reverse transcriptase. This enzyme uses the RNA as a template to synthesise DNA.
What enzyme is used to make RNA from DNA?
The process of transcription that is making RNA from DNA employs an enzyme called RNA polymerase. It would be better to address this RNA polymerase as DNA dependent RNA polymerase because this enzyme uses DNA as a template to form a RNA.
What is the name of the enzyme that produces DNA from RNA?
The DNA thus formed is called cDNA or copyDNA.
Why does DNA have introns?
Cause DNA has introns as well as exon. Introns are non transcribing parts in DNA. Whereas cDNA from RNA through reverse transcription process contain only transcribing parts i.e exons. The prokaryotic bacteria used to get protein expression did not have introns inside them. So for amplification of the desired cDNA we use PCR. And from those we get our desired protein expression in the bacteria. We can use RT PCR to study the transcriptional expression.REAL TIME PCR or q PCR to get expression of proteins at a particular developmental stage at a particular organism at a particular time in a particular cell or tissue as well.
What is the normal DNA of an eukaryotic cell?
This is where cDNA comes in. As part of a cell's DNA-->RNA-->Protein process, the normal DNA of a Eukaryotic cell is trans
Why is cDNA called cDNA?
The cDNA is so called because it is complementary to the RNA seq but has T instead of U.
What is the process of cDNA?
This is where cDNA comes in. As part of a cell's DNA-->RNA-->Protein process, the normal DNA of a Eukaryotic cell is transcribed into single-stranded mRNA, which now does not contain introns. This mRNA is then converted into cDNA, which is double-stranded, in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
What is the name of the molecule that transcribes RNA into cDNA?
The retrovirus (oncovirus) contains RNA. It also has a molecule called reverse transcriptase. This molecule transcribes RNA into cDNA. This cDNA is the DNA copy of viral RNA genome
Which part of the sugar is involved in base pairing?
They are very similar structures. The part that is involved in base pairing is actually the Nitrogen and the oxygen furthest from the sugar. See below:
Does RNA have uracil?
RNA has Uracil instead of thymine and DNA has thymine instead of uracil. So, how can RNA be converted into DNA?
Is thymine used in favor of RNA?
DNA is regularly and constantly transcribed to RNA, so Thymine is regularly used in favor of Uracil. There is a fantastic answer here on Biology.SE already dealing with why so I suggest reading that. The how is pretty straightforward, there are different molecules used! DNA polymerases incorporate Thymine whereas RNA polymerases incorporate Uracil. The reverse transcriptase that is encoded by the retrovirus does just this: it transcribes RNA to DNA, using Thymine instead of Uracil. Both Uracil and Thymine are present in the cell and are thus available for use.
