
What is a San in networking?
SAN is an acronym for storage area network. SANs consolidate storage in a single storage area separated from the local area network (LAN). Computers and devices connected to the SAN have access to storage devices like tape libraries and disk arrays available on the SAN servers as though it is local storage.
What is a SAN switch and how does it work?
At the heart of most storage area networks is the SAN switch. Its sole purpose is to move storage data traffic between servers and shared storage pools. A switch interconnects multiple host servers made up of storage servers and devices to create a SAN. Some switches can be used as a standalone device to build a simple SAN fabric.
What can you do with a San?
You can do many common tasks far easier and faster than with conventional file servers and direct attached storage (or hard disks). A SAN gives you “shared storage” on your network, which means that you can centrally manage all of your storage from one device as opposed to managing storage on each application server.
How do you connect to a San?
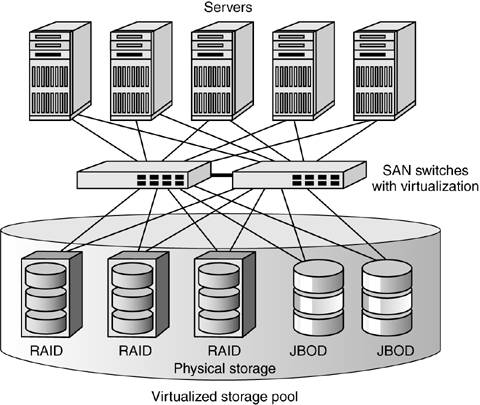
To access the SAN, so-called SAN servers are used, which in turn connect to SAN host adapters. Within the SAN, a range of data storage devices may be interconnected, such as SAN-capable disk arrays, JBODS and tape libraries. : 32, 35–36
Is SAN storage a server?
A SAN is built from a combination of servers and storage over a high speed, low latency interconnect that allows direct Fibre Channel connections from the client to the storage volume to provide the fastest possible performance.
What is SAN connectivity?
A storage area network ( SAN) organises a broad assortment of storage devices into a single storage resource that can then be provisioned, allocated and managed for the entire enterprise.
How do I access my SAN server?
If you are using a SAN server, select SAN Storage Server from the Storage Type drop-down list, and enter the host name, and login credentials. Click Next. Assign one or more Oracle VM Servers to perform any required administration on the server. Click Finish.
What protocol does SAN use?
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP)The most common SAN protocols are: Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP). The most widely used SAN or block protocol, deployed in 70% to 80% of the total SAN market. FCP uses Fibre Channel transport protocols with embedded SCSI commands.
How does a SAN work?
A SAN (storage area network) is a network of storage devices that can be accessed by multiple servers or computers, providing a shared pool of storage space. Each computer on the network can access storage on the SAN as though they were local disks connected directly to the computer.
How does a SAN appear to users on a network?
How does a SAN appear to users on a network? The storage device appears to be connected to a server like any other directly attached storage.
How do I connect SAN to Vcenter?
On the iSCSI Initiator properties window, go to the “Dynamic Discovery” tab. Click on Add. Default port to connect to SAN Storage is 3260. Click on Ok to connect to shared storage.
What is a cost effective way to connect a storage area network SAN?
ISCSI is one means of overcoming the cost of a SAN by using common Ethernet networking components rather than FC components. FCoE supports a converged SAN that can run FC communication directly over Ethernet network components -- converging both common IP and FC storage protocols onto a single low-cost network.
How do I connect to server storage?
There are two popular methods for connecting storage to servers.Direct attached storage (DAS) uses a direct connection between a server and its storage system. ... A storage area network (SAN) places a Fibre Channel (FC) storage switch between network servers and storage systems.
How is the data address in the SAN environment?
In switched SANs, the Fibre Channel switched fabric protocol FC-SW-6 is used under which every device in the SAN has a hardcoded World Wide Name (WWN) address in the host bus adapter (HBA). If a device is connected to the SAN its WWN is registered in the SAN switch name server.
How do I configure SAN storage?
Configuring SAN storageConfigure the SAN to create the LUNs to be used by queue managers, and allow access from the appliance host bus adapters. ... Define a volume for each LUN, using the LUID to identify it. ... Initialize the file system for the volume.More items...
Why is SAN faster than NAS?
SANs are the higher performers for environments that need high-speed traffic such as high transaction databases and ecommerce websites. NAS generally has lower throughput and higher latency because of its slower file system layer, but high-speed networks can make up for performance losses within NAS.
Where is SAN used?
SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
What are the advantages of SAN?
The advantages of a SANReduces LAN bandwidth problems. A key benefit of SANs is bandwidth improvement. ... Improved data security. Data security is paramount for every business. ... Responsive backup. ... Increased scalability. ... Reliable disaster recovery.
What are the two most popular SAN connection types?
There are two principal types of networking technologies and interfaces employed for SANs: Fibre Channel and iSCSI. Fibre Channel.
What are SAN switches?
A storage area network (SAN) switch is a device that connects servers and shared pools of storage devices and is dedicated to moving storage traffic. SAN switches make it possible to build vast high-speed storage networks that interconnect thousands of servers accessing petabyte-scale data.
What storage area networks are used for
Simply stated, a SAN is a network of disks that is accessed by a network of servers. There are several popular uses for SANs in enterprise computing. A SAN is typically employed to consolidate storage. For example, it's common for a computer system, such as a server, to include one or more local storage devices.
How a SAN works
A SAN is essentially a network that is intended to connect servers with storage. The goal of any SAN is to take storage out of individual servers and locate the storage collectively where storage resources can be centrally managed and protected.
Setting up the storage area network
To integrate all components of the SAN, an enterprise first must meet the vendor's hardware and software compatibility requirements:
SAN fabric architecture and operation
The core of a SAN is its fabric: the scalable, high-performance network that interconnects hosts -- servers -- and storage devices or subsystems. The design of the fabric is directly responsible for the SAN's reliability and complexity.
Understanding SAN switches
The SAN switch is the focal point of any SAN. As with most network switches, the SAN switch receives a data packet, determines the source and destination of the packet and then forwards that packet to the intended destination device.
Alternative SAN approaches
Although SAN technology has been available for decades, there are several enhancements and dedicated improvements reshaping SAN design and deployment. These alternatives include virtual SAN, unified SAN, converged SAN and hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI).
SAN benefits
Whether traditional or virtual, a SAN offers several compelling benefits that are vital for enterprise-class workloads.
How does SAN storage work?
The components of SAN include cabling, host bus adapters, and SAN switches attached to storage arrays and servers. SANs use block-based storage and high-speed architecture to connect servers to logical disk units (LUNs), a range of block storage from a pool of shared storage, and appear to the server as a logical disk.
What is a SAN host?
SAN hosts use host bus adapters (HBAs), separate network adapters dedicated to SAN access, to interface with a server’s operating system. This allows a workload to communicate storage commands and data to the SAN and its storage resources using the operating system.
What are the benefits of SAN storage?
SAN solutions offer several advantages for enterprise workloads, including:
How much does SAN storage cost?
The exact cost of SAN will depend on the workload and storage needs of your organization.
Why is it called SAN?
SAN is an acronym for storage area network. SANs consolidate storage in a single storage area separated from the local area network (LAN). Computers and devices connected to the SAN have access to storage devices like tape libraries and disk arrays available on the SAN servers as though it is local storage.
What is a storage area network?
A storage area network (SAN) is a dedicated network of storage devices used to provide a pool of shared storage that multiple computers and servers can access. Storing data in centralized shared storage architecture like SANs allows organizations to manage storage from a collective place and apply consistent policies for security, data protection, and disaster recovery.
How does a SAN work?
A SAN removes the storage responsibility from individual servers and collects it in a central place where it can be accessed, managed, and protected. Connecting storage to servers through a network separate from the traditional LAN optimizes storage traffic performance, as traffic doesn’t have to compete for LAN bandwidth with servers and workloads.
Is it the same as connecting a host to a SAN?
Connecting a host to your shiny new SAN is not the same as connecting a single disk, or even a direct-attached SCSI array. This article will explain the reasoning behind current best practices, and explain how to configure your storage for optimal reliability.
Do you save switch configurations?
Of course, don’t forget to save your switch and array configurations somewhere safe, and document your multipathing and file system decisions. The best part about multipathing is the testing stage. Go ahead, start copying a huge file and yank the fiber!
Does Veritas Volume Manager work with DMP?
Actually configuring multipathing, is less than trivial. If you want to make life easier, use Veritas Volume Manager with DMP (Dynamic MultiPathing). It runs on all operating systems, and it works the same in each. You’ll also get the added bonus of using operating system-neutral file systems, in case the need arises to move volumes between platforms.
Does Solaris support multipathing?
If not, then you get to try to use whatever native multipathing driver your OS includes. Solaris, for example, has excellent multipathing support. It works very well with storage that Sun has blessed, but may not work at all with some storage.
What is a SAN?
A storage area network ( SAN) organises a broad assortment of storage devices into a single storage resource that can then be provisioned, allocated and managed for the entire enterprise. Although issues like storage capacity, performance and management often receive the most attention, the connectivity between each SAN device plays a critical role in successful SAN deployment. Each switch and storage system on the SAN must be interconnected -- usually through optical fiber or copper cabling -- and the physical interconnections must support bandwidth levels that can adequately handle the peak data activities that occur. This overview details the role of Fibre Channel (FC), Ethernet and iSCSI connectivity on a SAN.
How does SCSI work?
In actual practice, a user or application will cause the operating system to generate corresponding SCSI storage commands. Those SCSI commands and data are then encapsulated and IP headers are added to make packets. The packets can then be sent over an ordinary Ethernet connection. The remote end of the iSCSI connection disassembles the encapsulated content and passes the SCSI commands to the SCSI controller and storage device. This also works in reverse, so any data or responses can be sent back to the user or application across the Ethernet connection.
What is the most common LAN cabling?
Traditional Ethernet LAN deployments used coaxial cables, but twisted-pair cabling (e.g., Category 5 or Category 6 Ethernet cables) is the most common LAN cabling. Ten GigE often relies on optical fiber with transmission distances up to 40 km, which makes the technology far more expensive and limits its use to network backbones. As copper cabling becomes available for 10 GigE, the technology should see far more use within data centers and SANs.
What is FC port?
FC is the quintessential SAN interconnect and virtually every storage switch and storage platform provides FC ports. Multiple FC ports support simultaneous data streams, but individual ports can often be aggregated into groups for even higher effective bandwidth. As an example, the All-In-One Buying Guide notes that the InServ E200 Storage Server from 3PAR Data Inc. supports up to 12 FC ports, while the TagmaStore AMS1000 from Hitachi Data Systems Inc. (HDS) provides up to eight FC ports. Servers and other devices can also be fitted with FC host channel adapters (HCAs) to enable an FC interface.
Is Ethernet used in a SAN?
While Ethernet connectivity is generally used on the greater local area network (LAN), its use in the SAN has been limited by its relatively slow bandwidth. Traditional Ethernet ports support 10/100 Mbps -- far slower than FC. This had limited Ethernet in the SAN to basic management tasks. For example, a storage device or switch might include a single Ethernet port that connects the device to the LAN where an administrator can manage the device across it. Ethernet typically uses two protocols; Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which handles the organisation of data into packets, and Internet Protocol (IP), which handles the way those data packets are addressed. In fact, the terms "Ethernet" and "TCP/IP" are often used interchangeably.
Is Ethernet bandwidth good for a LAN?
Ethernet bandwidth is increasing today, which boosts performance on the LAN and also makes Ethernet use more practical for carrying data on the SAN. One Gigabit Ethernet (GigE) is now common on many servers and switches, and the eventual emergence of 10 GigE promises to put Ethernet on par with 10 Gigabit (Gbit) Fibre Channel.
What is a SAN server?
SANs have their own networking devices, such as SAN switches. To access the SAN, so-called SAN servers are used, which in turn connect to SAN host adapters. Within the SAN, a range of data storage devices may be interconnected, such as SAN-capable disk arrays, JBODS and tape libraries.
What is a host SAN?
Servers that allow access to the SAN and its storage devices are said to form the host layer of the SAN. Such servers have host adapters, which are cards that attach to slots on the server motherboard (usually PCI slots) and run with a corresponding firmware and device driver. Through the host adapters the operating system of the server can communicate with the storage devices in the SAN.
How does QoS affect SAN?
QoS can be impacted in a SAN storage system by an unexpected increase in data traffic (usage spike) from one network user that can cause performance to decrease for other users on the same network. This can be known as the "noisy neighbor effect." When QoS services are enabled in a SAN storage system, the "noisy neighbor effect" can be prevented and network storage performance can be accurately predicted.
Why is a SAN serverless?
SANs in media and entertainment are often referred to as serverless due to the nature of the configuration which places the video workflow (ingest, editing, playout) desktop clients directly on the SAN rather than attaching to servers. Control of data flow is managed by a distributed file system such as StorNext by Quantum. Per-node bandwidth usage control, sometimes referred to as quality of service (QoS), is especially important in video editing as it ensures fair and prioritized bandwidth usage across the network.
What is a SAN?
A SAN is, at its simplest, a dedicated network for data storage. In addition to storing data, SANs allow for the automatic backup of data, and the monitoring of the storage as well as the backup process. A SAN is a combination of hardware and software.
What is a storage area network?
A storage area network ( SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage.
How many ports does a SAN switch have?
: 29 SAN switches are for redundancy purposes set up in a meshed topology. A single SAN switch can have as few as 8 ports and up to 32 ports with modular extensions. : 35 So-called director-class switches can have as many as 128 ports. : 36
How to set up a SAN?
Firstly, The storage devices separately connected each other showing a shared environment or seems like a Storage pool. Then insert a fiber switch between server and storage pool. Connect every device of the pool with the switch using a fiber cable. Connect every server with a fiber switch using fiber cable. Attach a Host Bus Adapter card (HBA) on each server and pool to communicate. This is the easy set up of SAN.
How is a SAN different from a LAN?
In LAN the storage drive is directly connected through the servers, While in SAN The storage devices are connected separately as a storage pool. All data stored in this pool and seems like a hard drive is attached to the server.
What is SAN?
A storage area network (SAN) is an at ease, high-pace information transfer network that provides access to the very last storage consolidation, information storage devices. Storage area Networks are generally made from hubs, switches, garage components, and storage gadgets which are interconnected with an expansion of technologies, topologies, and protocols
What are the disadvantages of a storage area network?
Disadvantages of storage area network: Expensive. SAN is expensive because fiber cables and fiber switches are used in this implementation. Data leakage. As client computers use the same set of shared data then it is the possibility of a loss of sensitive data. Not good work with fewer servers.
What is HBA in SAN?
HBA is deployed on all servers and storage devices to communicate in SAN implementation. All storage devices are connected to each other seems like a disk array.SAN implementation on disk array provides business continuity, good performance, and multiple host connections.
What is LAN in a server?
In a client-server architecture (LAN), in which storage device is legitimately associated with the server. If the storage device turns out to be full and we have to install another storage device to the server. This is the primary inadequacy in a client-server architecture. In this way, for this situation, we need to expel the past stockpiling storage and need to introduce another one. This is a time taking and expensive technique. Because the past stockpiling storage is squandered now.
What type of cable is used in SAN?
There are two types of cables used in SAN.ie Fiber cable, copper cable. Fiber cable: These cables are used for fast transmission. Fiber Cable is further classified into single-mode fiber and double-mode fiber. Copper cable: These cables are cheap compared to fiber. They have a low transfer rate as compared to fiber cables.
Fibre Channel vs. Ethernet
SAN switches fall into two main categories: Fibre Channel (FC) and Ethernet. Fibre Channel switches are the most common. They're compatible with FC technologies and are either modular or fixed. A modular switch is typically a director-class FC switch that's expandable and offers a high port count.
How a SAN switch works
Both Ethernet and FC switches manage traffic flow, but they can only support the specific technologies behind them. An Ethernet switch, for example, shares in the same benefits and limitations as Ethernet itself. The same goes for FC switches.
SAN switch vs. other network switches
Network switches are categorized and subcategorized differently from one source to another -- often, inconsistently or in ways that contradict each other -- making it difficult to understand their differences. Even so, most switches can be grouped into three broad categories:
What is a SAN on a network?
A SAN gives you “shared storage” on your network , which means that you can centrally manage all of your storage from one device as opposed to managing storage on each application server.
What is a SAN?
SAN is an acronym for storage area network – it is the shared storage box accessible to everything and everyone on your network. The term SAN is commonly used to refer to dedicated storage servers that use either the Fibre Channel (FC) or the iSCSI (Small Computer System Interface )command set, which works over your IP network protocol. By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. An iSCSI SAN works over your local area network (LAN) and simplifies the implementation and management of the SAN. Conversely, FC storage requires proprietary, expensive switches and host cards (HBAs), and by design forces you to put your SAN on a completely separate Fibre Channel network that doesn’t communicate with your existing Ethernet network.
What is the StarWind iSCSI initiator?
On Windows clients (your application servers), the free Microsoft iSCSI initiator or the free and more advanced StarPort Initiator is used to enable the client machine to connect to your new SAN. StarWind has also been validated with Linux and UNIX iSCSI initiators, iSCSI HBAs from Adaptec and QLogic, and hardware iSCSI accelerators from Alacritech.
How much RAM does Starwind need?
A server with 4GB of RAM and a 2GHz single core CPU should be fine for most applications.
What is iSCSI storage?
iSCSI storage is based on the iSCSI protocol, which means the disk drives in your storage appliance are presented over an IP network using the SCSI command set. Don’t confuse this with traditional SCSI disks; in fact, iSCSI storage is typically implemented with affordable Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) or Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) disks. iSCSI presents block based storage just as you get with your internal disk drives, whereas a NAS is a just a plain file server, which presents storage as file shares. A common scenario is to use a portion of your iSCSI SAN storage as back-end disks for file servers (NAS), consolidating both application data and file shares into one appliance.
How long does it take to build a SAN?
There you have it, building a SAN, even a highly available and fault-tolerant enterprise-class SAN, is a fairly straight-forward process that takes less than 30 minutes. While it does take a bit of pre-planning, the small amount of effort required to build your own storage server can result in a significant cost savings and is ideal for VMware, Hyper-V or any other server applications and server clustering. Using StarWind Software to build a SAN is easy and reduces complexity, saves time managing your storage and expands your storage capabilities affordably.
Can I use iSCSI on LAN?
With the iSCSI protocol, it is entirely possible to connect iSCSI storage directly into your existing corporate IP network, also known as your LAN. However, your LAN should not be designated for your SAN even though it is possible to use it for that purpose.
What is a SAN?
A SAN is block-based storage, leveraging a high-speed architecture that connects servers to their logical disk units ( LUNs). A LUN is a range of blocks provisioned from a pool of shared storage and presented to the server as a logical disk. The server partitions and formats those blocks—typically with a file system—so that it can store data on the LUN just as it would on local disk storage.
What is a storage area network?
Storage area networks (SANs) are the most common storage networking architecture used by enterprises for business-critical applications that need to deliver high throughput and low latency. A rapidly growing portion of SAN deployments leverages all-flash storage to gain its high performance, consistent low latency, and lower total cost when compared to spinning disk. By storing data in centralized shared storage, SANs enable organizations to apply consistent methodologies and tools for security, data protection, and disaster recovery.
What is FCP in SAN?
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP). The most widely used SAN or block protocol, deployed in 70% to 80% of the total SAN market. FCP uses Fibre Channel transport protocols with embedded SCSI commands.
What is NAS storage?
Both SAN and network-attached storage ( NAS) are methods of managing storage centrally and sharing that storage with multiple hosts (servers). However, NAS is Ethernet-based, while SAN can use Ethernet and Fibre Channel. In addition, while SAN focuses on high performance and low latency, NAS focuses on ease of use, manageability, scalability, ...
