Why saponification value is determined?
The higher the saponification value, the lower the fatty acids average length, the lighter the mean molecular weight of triglycerides and vice versa. Practically, fats or oils with high saponification value (such as coconut and palm oil) are more suitable for soap making.
What is the saponification number and how is it determined?
Principle: Saponification value is defined as the number of milligrams of KOH required to completely hydrolyse (saponify) one gram of the oil/fat. In practice a known amount of the oil or fat is refluxed with excess amount of standard alcoholic potash solution and the unused alkali is titrated against a standard acid.
How do you calculate saponification number of fats?
0:113:03Estimation of Saponification Value of Oils & Fats - Amrita UniversityYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe saponification value represents. The number of milligrams of the base required to neutralize theMoreThe saponification value represents. The number of milligrams of the base required to neutralize the fatty acids resulting from the complete hydrolysis of one gram fat.
What is the saponification value of soap?
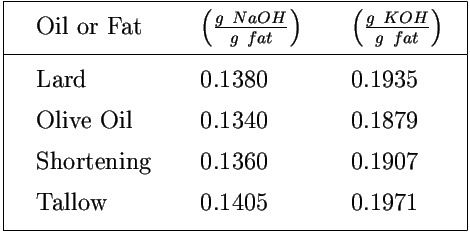
SAP values are the numeric values that allow you to calculate the precise amount of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH) required to fully saponify a given weight of oil/s.
What is saponification formula?
What is the saponification equation? General saponification equation is fat + chemical salt + water → glycerol + fatty acid salt (soap).
What is saponification method?
SaponificationSaponificationSaponification can be defined as a “hydration reaction where free hydroxide breaks the ester bonds between the fatty acids and glycerol of a triglyceride, resulting in free fatty acids and glycerol,” which are each soluble in aqueous solutions.https://www.sciencedirect.com › chemistry › saponificationSaponification - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics is the formation of a metallic salt of a fatty acid; such a salt is called a soap. The reaction involves treatment of free fatty acids and/or glycerides with a base and may be considered a special case of hydrolysis when a glyceride is reacted with a base.
How do you calculate saponification value of fats and oils?
SaponificationSaponificationSaponification is a process that involves the conversion of fat, oil, or lipid, into soap and alcohol by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, sodium hydroxide). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › SaponificationSaponification - Wikipedia value or number of fat = mg of KOH consumed by 1g of fat.
What is saponification number with example?
The saponification value of fatty acids with a long carbon chain is generally low. Fats with a short carbon chain will have a higher saponification value. For example, the saponification value of butter is 230–240, whereas that of human fat is 195–200.
What is the difference between acid value and saponification value?
The key difference between acid valueacid valueIn chemistry, acid value (AV, acid number, neutralization number or acidity) is a number used to quantify the acidity of a given chemical substance. It is the quantity of base (usually potassium hydroxide (KOH)), expressed as milligrams of KOH required to neutralize the acidic constituents in 1 gram of a sample.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Acid_valueAcid value - Wikipedia and saponificationsaponificationSaponification is a process that involves the conversion of fat, oil, or lipid, into soap and alcohol by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, sodium hydroxide). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › SaponificationSaponification - Wikipedia value is that acid value gives the mass of potassium hydroxide that is required to neutralize one gram of a chemical substance whereas saponification value gives the mass of potassium hydroxide required to saponify one gram of fat.
Why is NaOH used in saponification?
NaOH is widely used in the manufacture of solid soap because it is not soluble in water [22]. The use of the amount of NaOH that is lacking in the saponification reaction will cause the formation of residues / residual fatty acids (oil) after the reaction.
Why KOH is used in saponification?
Heating with alcoholic KOH saponifies the fats/oils. Fats are water insoluble and hence the rate of hydrolysis by aqueous KOH is slow so alcoholic KOH is used for the reaction. The amount of alkali consumed for saponificationsaponificationSaponification is a process that involves the conversion of fat, oil, or lipid, into soap and alcohol by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, sodium hydroxide). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › SaponificationSaponification - Wikipedia of fat is estimated by back titration with an acid.
How many soaps does 1kg of soap base make?
8-10 barsThis is for 1kg of soap base. Depending on the molds you use, you should be able to make 8-10 bars of soap.
What is saponification number with example?
The saponification value of fatty acids with a long carbon chain is generally low. Fats with a short carbon chain will have a higher saponification value. For example, the saponification value of butter is 230–240, whereas that of human fat is 195–200.
What is saponification number in Physical Pharmaceutics?
The saponification number is defined as the consumption of potassium hydroxide in milligrams by one gram of resin under standardized conditions.
How can you determine order of saponification reaction?
Reaction of ethyl acetate with sodium hydroxide (saponification) is a 2nd order reaction overall, and 1st order with respect to reactants. Moreover, reaction order drops and become sequential instead of been 2nd order when both reactants are used in the equimolecular concentrations.
What is saponification with an example?
Saponification is a process that involves the conversion of fat, oil, or lipid, into soap and alcohol by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, sodium hydroxide). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. A typical soap is sodium oleate.
What do you mean by Unsaponifiables?
Unsaponifiables are fatty substance components (oil, fat, wax) that do not produce soap when exposed to alkali and remain insoluble in water but so...
What is the saponification equation?
General saponification equation is fat + chemical salt + water → glycerol + fatty acid salt (soap). Fat and chemical salts are the reactants, while...
Why do we determine saponification value?
The saponification number is the amount of potassium hydroxide required to saponify one gram of fat. This data can be used to compute the number of...
What are the factors that affect saponification?
The effect of three parameters, such as ethanolic KOH content, reaction temperature, and reaction time, which were explored for the optimum saponif...
Does the saponification value of soap impact its quality?
The saponification value is sometimes used to check for adulteration. The higher the saponification number, the more capable the oil is in making s...
1. What is Saponification?
In saponification, the word ‘sapo' is a Latin word meaning soap. Saponification is the general term for the process of making soap. Soaps are fatty...
2. Explain Saponification reaction in detail?
The saponification reaction involves the reaction of sodium or potassium hydroxides with triglycerides (esters) to produce glycerol (alcohol) and p...
3. What is Saponification Value?
Saponification value or saponification number for a specific fat is the amount of base required to saponify 1 gramme of fat under specific conditio...
4. Give an example of Saponification Reaction?
Procedure for Saponification Experiment– Fill a beaker with 15ml of vegetable oil. Now, while stirring, add 10ml of ethanol and 20ml of 20% sodium...
5. What are general Saponification Reactions?
Saponification reaction can be written in words as – Ester + Water + Base Soap (Fatty Acid Sodium or Potassium Salts) + Alcohol or Saponification o...
What are the properties of microalgae oil?
Key aspects to evaluate the properties of microalgae oil are saponification value (SV), acid number (AN), iodine value (IN), specific gravity, density, kinematic viscosity, flash point, pour point, heating value, and cetane number. Table 1 illustrates the properties of algal fuel compared to conventional fuel. Saponification value (SV), iodine value (IV), acidity (AN), and peroxide value (PV) are the most commonly used parameters in characterizing the quality of oils and fats. These parameters are widely used to determine purity (SV), number of unsaturated compounds (IV) and free fatty-acid content (acidity). Physical properties of microalgae oil show its efficiency to use as biodiesel. Acid number (AN) indicates the corrosiveness of the oil; iodine values (IV) refer to the degree of unsaturation. AN and IV recorded within the limits indicate the less corrosiveness and higher saturation of the algae fuel. Similarly, the specific gravity and density enumerated its energy efficiency as fuel. Flash point expresses the lowest temperature at which the oil vaporizes to form an ignitable mixture. The temperature of the flash point recorded for microalgae oil determines the potential of the oil to form ignitable mixtures at relatively lower temperatures over conventional diesel fuel. Pour point is the lowest temperature at which the oil becomes semi-solid and loses its flow properties. It is also an important diesel quality parameter in tropical countries like India. The solidifying temperature of the microalgae oil shows its application as diesel. Similar to pour point, viscosity defines the fluids’ resistance to flow; heating value is the energy released as heat when a compound undergoes combustion. The less viscosity and higher energy values recorded for the algae oil denote its comparable features with standard norms and conventional fuel [154]. Cetane number refers to the ignition quality of the diesel engines where it can be operated efficiently. The relative cetane number of microalgae oil with standard fuel indicates ignition and operational quality of algae fuel.
How to determine saponification number?
The standard method for determination of saponification value of oil and biodiesel is ASTM D 1962 titration method, which was used to determine the saponification value of AMC oil and biodiesel. In this method, two beaker solutions are prepared as test and blank by dissolving 1 g sample of fat into 10 mL ethanol solvent into one beaker and taking only 10 mL ethanol solvent in another beaker. In the above mentioned two beakers 25 mL of 0.5 N ethanolic KOH is quantitatively added and named as test and blank. This test and blank beaker solutions are heated for 30 min at boiling temperature of water by taking care of evaporation of solution, using a reflux condenser. After that the samples are allowed to reach room temperature. Two to three drops of phenolphthalein indicator is added to both beaker solutions. Finally, test and blank solutions are titrated against burette solution 0.5N HCl. The saponification value was calculated using the following equation.
What is cetane number?
Cetane number refers to the ignition quality of the diesel engines where it can be operated efficiently. The relative cetane number of microalgae oil with standard fuel indicates ignition and operational quality of algae fuel. Table 1. Fuel properties for biodiesel standards.
What is the saponification value of potassium hydroxide?
The saponification value corresponds to the mass in mg of potassium hydroxide (KOH – commonly known as potash) needed to neutralize the free fatty acids and saponify the esters contained in a gram of material. Thus, it is a value that can be found experimentally.
What is the saponification value?
Saponification value is defined as the amount of potassium hydroxide (KOH) in milligrams required to saponify one gram of fat or oil under the conditions specified (AOCS Method Cd 3–25 and AOCS Method Cd 3c–91).
How to determine sv?
[ 17] or AOCS Official Methods Cd 3c-91 and Cd 3b-76. To determine SV, the sample is completely saponified with an excess of alkali, which excess is then determined by titration (in mg KOH/g) (see Table 6.3 ). The saponification number depends on the molecular weight and the percentage concentration of fatty acid components present in FAMEs of oil. The SV is effectively used to determine the average relative molecular mass of oils and fats. Lauric oils, with a higher percentage of ester bonds than longer chain oils, have a higher SV (240–250 mg KOH/g for CNO compared to 190–195 mg KOH/g for SBO). The distinction is quite relevant for biodiesel production in that oils with a high SV require more methanol, and produce more glycerol but less biodiesel than longer chain oils. Oils with high SN impart high foamability (e.g. palm kernel, coconut and babassu oils).
What is ISO standard 135?
ISO standard 135 specifies the amount of phthalate sample which is to be taken for analysis relative to its molecular weight. 50 ml of 1N alcoholic KOH and 5 ml of water are added to the sample which is then refluxed for 1 h. Phenolphthalein solution is then added and sample titrated with 1 N HCl.
What is the reaction of ester with water and base such as NaOH or KOH to give alcohol and sodium or?
In terms of chemistry saponification can be define as the reaction of ester with water and base such as NaOH or KOH to give alcohol and sodium or potassium salt of the acid. The oils which go through the saponification reaction are known as saponified oils. Saponified oils are mixed with sodium hydroxide and water.
How much sodium hydroxide to add to vegetable oil?
Take about 15ml of vegetable oil in a beaker. Now add 10ml of ethanol and 20ml of 20% sodium hydroxide to vegetable oil with stirring. Don’t touch solid NaOH directly by your hands and stir the solution carefully so that it should not spill out of the beaker.
What is the name of the reaction in which the ester group reacts with water and base?
In a saponification reaction, ester group reacts with water and base (mostly NaOH) and forms carboxylate ion and alcohol. Carboxylate ion changes into carboxylic acid. The saponification is named as saponification because soaps are made by hydrolysis of fats (esters) since olden times.
What is the reaction of sodium and potassium hydroxides?
Saponification Reaction (in detail) Saponification reaction involves reaction of sodium or potassium hydroxides with triglycerides (esters) to produce glycerol (alcohol) and fatty acid salts of potassium or sodium. The fatty acid salts of potassium or sodium are known as ‘soaps’. (Image to be added soon)
What is the significance of saponification?
It tells you about the length of carbon chain in fatty acid being used for saponification. 2. Saponification value of those fatty acids which have very long carbon chain is generally low. 3. Saponification value will be higher for fats containing short carbon chain.
What is the first step in the formation of an orthoester?
Step 1. Nucleophilic attack by hydroxide ion – Nucleophile hydroxide ion attacks on the ester group and forms orthoester. (Image to be added soon) Step 2. Removal of Leaving group i.e. alkoxide - Orthoester splits and form carboxylic acid (RCOOH) and alkoxide group (OR’). (Image to be added soon) Step 3.
What is saponification used for?
Uses of Saponification. 1. It is used in the fire extinguishers. Burning oils are converted into non-combustible salts which helps in extinguishing the fire. This reaction is endothermic, so it lowers the temperature of surroundings. 2. Oil paintings get damaged by saponification reaction. 3.
What is Saponification?
Saponification is simply the process of making soaps. Soaps are just potassium or sodium salts of long-chain fatty acids. During saponification, ester reacts with an inorganic base to produce alcohol and soap.
What happens in the second step of saponification?
In the second step, alkali neutralizes fatty acid to produce soap.
What is the reaction of sodium hydroxide and triglyceride?
In a saponification reaction, a base (for example sodium hydroxide) reacts with any fat to form glycerol and soap molecules. One of the saponification reaction taking triglyceride as an ester and sodium hydroxide as the base is as follows:
How to convert potassium to sodium?
In case sodium hydroxide is used for the saponification process, the saponification value must be converted from potassium to sodium by dividing the KOH values by the ratio of the molecular weights of KOH and NaOH (i.e. 1.403).
How many steps are needed to convert triglycerides to soap?
There can be either one-step saponification or two-step saponification process to convert triglycerides to soaps. The examples mentioned above are a one-step saponification process in which triglycerides, when treated with a strong base, splits from the ester bond to release glycerol and soaps (i.e. fatty acid salts).
What is the hydrolysis of an ester with NaOH or KOH to give alcohol and sodium or potassium salt of?
Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester with NaOH or KOH to give alcohol and sodium or potassium salt of the acid. Soap is now an essential everyday item and finds its importance in everyday life.
What soaps are used to clean paintings?
This way, the paintings get damaged gradually. Soaps formed are used in everyday life like sodium soaps are used for laundry, potassium soaps are used for cleaning and lithium soaps are used as lubricating greases. There are various other soaps which are used for different purposes.
