
Is starch made from glucose?
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the glucose store of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. Secondly, how is starch made from glucose?
What is the process of making starch?
Starch is made by sedimentation process. Maize or Tapioca is ground and agitated in water. The supernatant cosisting of the cellulosic skin is drained out. The sediment is washed and rewashed with water to give a final mass which Is dried and pulverised.
What is the structure and function of starch?
Starch is a compound that belongs to plants in origin. It cannot be synthesized in animals. However, it makes a major source of diet for animals. Crops that are rich in starch are the major source of nutrition for humans and other animals. In this article, we will discuss the structure, properties, synthesis and metabolism of starch.
What is the source of starch in food?
Starch is a compound that belongs to plants in origin. It cannot be synthesized in animals. However, it makes a major source of diet for animals. Crops that are rich in starch are the major source of nutrition for humans and other animals.
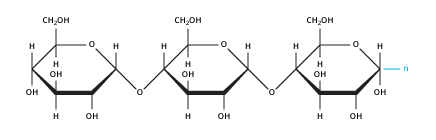
How do you get starch from glucose?
Starch is an example of a natural polymer. A polymer is a long and repeating chain of the same molecule stuck together. Starch is a long-chain polymer of glucose molecules joined together. As the plant adds one glucose molecule to the starch polymer, one molecule of water is released.
Why is glucose converted into starch?
Glucose is soluble , so it is converted to starch so that it can become insoluble and hence it cannot escape from cell , thus it can also be stored.
How is starch formed?
Starch is produced by dehydration synthesis. Plants store glucose that is not in use as starch. First, glucose is phosphorylated into glucose-1-phosphate. Starch granules are stored inside the amyloplasts located inside the cells of various plant organs.
How is starch produced?
Starch is manufactured in the green leaves of plants from excess glucose produced during photosynthesis and serves the plant as a reserve food supply.
How are starch and cellulose similar?
Starch and cellulose are two very similar polymers. In fact, they are both made from the same monomer, glucose, and have the same glucose-based repeat units. There is only one difference. In starch, all the glucose repeat units are oriented in the same direction. But in cellulose, each succesive glucose unit is rotated 180 degrees around the axis of the polymer backbone chain, relative to the last repeat unit. When bigshot scientists are talking bigshot scientist talk they say that the glucose units in starch are connected by alpha linkages, and that the glucose units in cellulose are connected by beta linkages. Does this make any difference? It makes a lot of difference! The most important difference in the way the two polymers behave is this: You can eat starch, but you can't digest cellulose. Your body contains enzymes that break starch down into glucose to fuel your body. But we humans don't have enzymes that can break down cellulose. Some animals do, like termites, who eat wood, or cattle, who eat grass, and break down cellulose in their four-chambered stomachs. So unless you're a termite or a cow, don't try to nourish yourself on woodchips. Cellulose is a lot stronger than starch. Starch is practically useless as a material, but celluose is strong enough to make fibers from, and hence rope, clothing, etc. Cellulose doesn't dissolve in water the way starch will, and doesn't break down as easily. Breaking down or dissolving in water just would be a little too inconvenient for something we use to make clothes. Not to mention, a good soaking rain would washaway all the wooden houses, park benches, and playground equipment ifcellulose were soluble in water. Continue reading >>
How is glucose used in photosynthesis?
The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be used in various ways by plants and algae. Storage Glucose is needed by cells for respiration. However, it is not produced at night when it is too dark for photosynthesis to happen. Plants and algae store glucose as insoluble products. These include: Use Some glucose is used for respiration to release energy. Some is used to produce: Plants also need nitrates to make proteins. These are absorbed from the soil as nitrate ions. Three factors can limit the speed of photosynthesis: light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature. Without enough light, a plant cannot photosynthesise very quickly, even if there is plenty of water and carbon dioxide. Increasing the light intensity will boost the speed of photosynthesis. Sometimes photosynthesis is limited by the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air. Even if there is plenty of light, a plant cannot photosynthesise if there is insufficient carbon dioxide. If it gets too cold, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease. Plants cannot photosynthesise if it gets too hot. If you plot the rate of photosynthesis against the levels of these three limiting factors, you get graphs like the ones above. In practice, any one of these factors could limit the rate of photosynthesis. Farmers can use their knowledge of factors limiting the rate of photosynthesis to increase crop yields. This is particularly true in greenhouses, where the conditions are more easily controlled than in the open air outside: The use of artificial light allows photosynthesis to continue beyond daylight hours. Bright lights also provide a higher-than-normal light intensity. The use of artificial heating allows photosynthesis to continue at an increased rate. The use of additional carbon dioxide released i Continue reading >>
What are the three elements that make up carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose) are relatively small molecules. They are often called sugars. Other carbohydrate molecules are very large (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose). Carbohydrates are: a source of energy for the body e.g. glucose and a store of energy, e.g. starch in plants building blocks for polysaccharides (giant carbohydrates), e.g. cellulose in plants and glycogen in the human body components of other molecules eg DNA, RNA, glycolipids, glycoproteins, ATP Monosaccharides Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are often called single sugars. They are the building blocks from which all bigger carbohydrates are made. Monosaccharides have the general molecular formula (CH2O)n, where n can be 3, 5 or 6. They can be classified according to the number of carbon atoms in a molecule: n = 3 trioses, e.g. glyceraldehyde n = 5 pentoses, e.g. ribose and deoxyribose ('pent' indicates 5) n = 6 hexoses, e.g. fructose, glucose and galactose ('hex' indicates 6) There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C5H10O5 and more than one with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers. Glyceraldehyde's molecular formula is C3H6O3. Its structural formula shows it contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) and two hydroxyl groups (-OH). The presence of an aldehyde group means that glyceraldehyde can also be classified as an aldose. It is a reducing sugar and gives a positive test with Benedict's reagent. CH2OHCH (OH)CHO is oxidised by Benedict's reagent to CH2OHCH (OH)COOH; the aldehyde group is oxidised to Continue reading >>
What is the name of the sugar that is absorbed through the intestine?
Glucose, a monosaccharide, is a form of sugar absorbed through the intestine into your bloodstream. Foods do not contain pure glucose, although diabetics sometimes carry pure glucose tablets or gels to raise their blood sugar quickly if they develop hypoglycemia, the medical term of low blood sugar.
What is the most common storage carbohydrate in plants?
Starch is the commonest storage carbohydrate in plants. It is used by the plants themselves, by microbes and by higher organisms so there is a great diversity of enzymes able to catalyse its hydrolysis. Starch from all plant sources occurs in the form of granules which differ markedly in size and physical characteristics from species to species. Chemical differences are less marked. The major difference is the ratio of amylose to amylopectin; e.g. corn starch from waxy maize contains only 2% amylose but that from amylomaize is about 80% amylose. Some starches, for instance from potato, contain covalently bound phosphate in small amounts (0.2% approximately), which has significant effects on the physical properties of the starch but does not interfere with its hydrolysis. Acid hydrolysis of starch has had widespread use in the past. It is now largely replaced by enzymic processes, as it required the use of corrosion resistant materials, gave rise to high colour and saltash content (after neutralisation), needed more energy for heating and was relatively difficult to control. Figure 4.2. The use of enzymes in processing starch.Typical conditions are given. Of the two components of starch, amylopectin presents thegreat challenge to hydrolytic enzyme systems. This is due to the residuesinvolved in a-1,6-glycosidic branch points which constitute about4 - 6% of theglucose present. Most hydrolytic enzymes are specific for a-1,4-glucosidic linksyet the a-1,6-glucosidic links must also be cleaved for complete hydrolysis ofamylopectin to glucose. Some of the most impressive recent exercises in thedevelopment of new enzymes have concerned debranching enzymes. It is necessary to hydrolyse starch in a wide variety ofprocesses which m be condensed into two basic classes: processes i Continue reading >>
What is the precursor of all the glucose subunits found in starch?
This ADP-glucose acts as a precursor of all the glucose subunits found in starch. The synthesis of ADP-glucose is linked to the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis. The glucose-6-phosphate generated in the Calvin-cycle is first converted to glucose-1-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase enzyme.
Where does starch biosynthesis occur?
The biosynthesis of starch occurs only in plant cells. Enzymes for starch synthesis are absent in animal cells. This process takes place in the chloroplast of plant cells. The first step in the biosynthesis of starch is the synthesis of ADP-glucose.
How much starch is in amylose?
Amylose makes around 20-30% of starch. It is an unbranched compound having linear chains of glucose molecules. these glucose molecules are linked via alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds. Amylose starch is a linear chain of alpha D-glucose subunits that usually contains around 300 to 3000 glucosyl residues or even more.
What are the properties of starch?
The properties of starch are the amalgam of the properties of these two components, amylose and amylopectin.
What is the branched polymer of amylopectin?
Amylopectin makes around 70-80% of starch. It is a branched polymer of alpha D-glucose subunits that are linked via the same 1-4 glycosidic bonds as in amylose. However, amylopectin also has alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds among the glucose molecules at the branch points.
Why do plants make starch?
Plants make starch during daytime when the glucose production is more than the glucose required by the cells. The extra glucose is stored in the form of starch. During the night, when the photosynthetic machinery of the plants is no more working, glucose production in plant cells is zero.
How big are starch granules?
For example, the starch granules in rice are around 2 micrometers while those present in potatoes are up to 100 micrometers.
What is starch made of?
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants as energy storage. [ …. ] In photosynthesis, plants use light energy to produce glucose from carbon dioxide.
What enzyme is used to synthesize starch?
The synthesis of starch in plant cells begins with the enzyme ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase), which catalyses the reaction of glucose-1-phosphate with ATP to form ADP-glucose (liberating pyrophosphate). The ADP-glucose is then used a substrate by starch synthase enzymes, which add glucose units to the end of a growing polymer chain ...
What happens to starch in leaves?
In leaves starch accumulates (in chloroplasts and amyloplasts) during daylight hours and is hydrolyzed back into water-soluble glucose at night, when the glucose is further metabolised into other sugars (mostly sucrose) and loaded into the phloem for export to other parts of the plant.
What enzymes use ADP-glucose as a substrate?
The ADP-glucose is then used a substrate by starch synthase enzymes, which add glucose units to the end of a growing polymer chain to build up a starch molecule (releasing the ADP in the process).
What is the energy used in photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, plants use light energy to produce glucose from carbon dioxide. The glucose is used to make cellulose fibers, the structural component of the plant, or is stored in the form of starch granules, in amyloplasts. ... Fruit, seeds, rhizomes, and tubers store starch to prepare for the next growing season.
How does glucose form in plants?
Plants will form glucose in the leaves from photosynthesis, providing a high concentration of glucose, forcing some down into the roots. When the plant is storing energy, it will convert glucose in the roots into starch, allowing for the glucose to continue flowing into the roots to be stored.
How to prove starch is prepared in leaves during photosynthesis?
To prove that starch is prepared in leaves during photosynthesis, iodine test is done. For this test, a plant leaf is plucked and washed then it is boiled in ethanol under water bath. Doing this the pigments are dissolved in ethanol.
Why do we digest starch?
Your body digests starch to make glucose, which is a vital energy source for every cell. Food companies use starch to thicken processed foods, and to make sweeteners. Scientists are investigating the effects of these sweeteners on health. A rotating model of a starch molecule.
What is starch in nutrition?
Nutrition, digestion and excretion. Add to My Bitesize. What is starch? Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Iodine solution is used to test for starch. The digestion of starch makes glucose. A case study video explaining how starch molecules react in cooking.
What is the name of the chain of molecules that are joined together by a plant?
A polymer is a long and repeating chain of the same molecule stuck together. Starch is a long-chain polymer of glucose molecules joined together. As the plant adds one glucose molecule to the starch polymer, one molecule of water is released. You can see this mechanism in the video opposite.
Is starch a carbohydrate?
Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules are made up of large numbers of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Starch is a white solid at room temperature, and does not dissolve in cold water. Most plants, including rice, potatoes and wheat, store their energy as starch. This explains why these foods – and anything made from wheat flour – are ...
