How is the mesoderm formed in the egg?
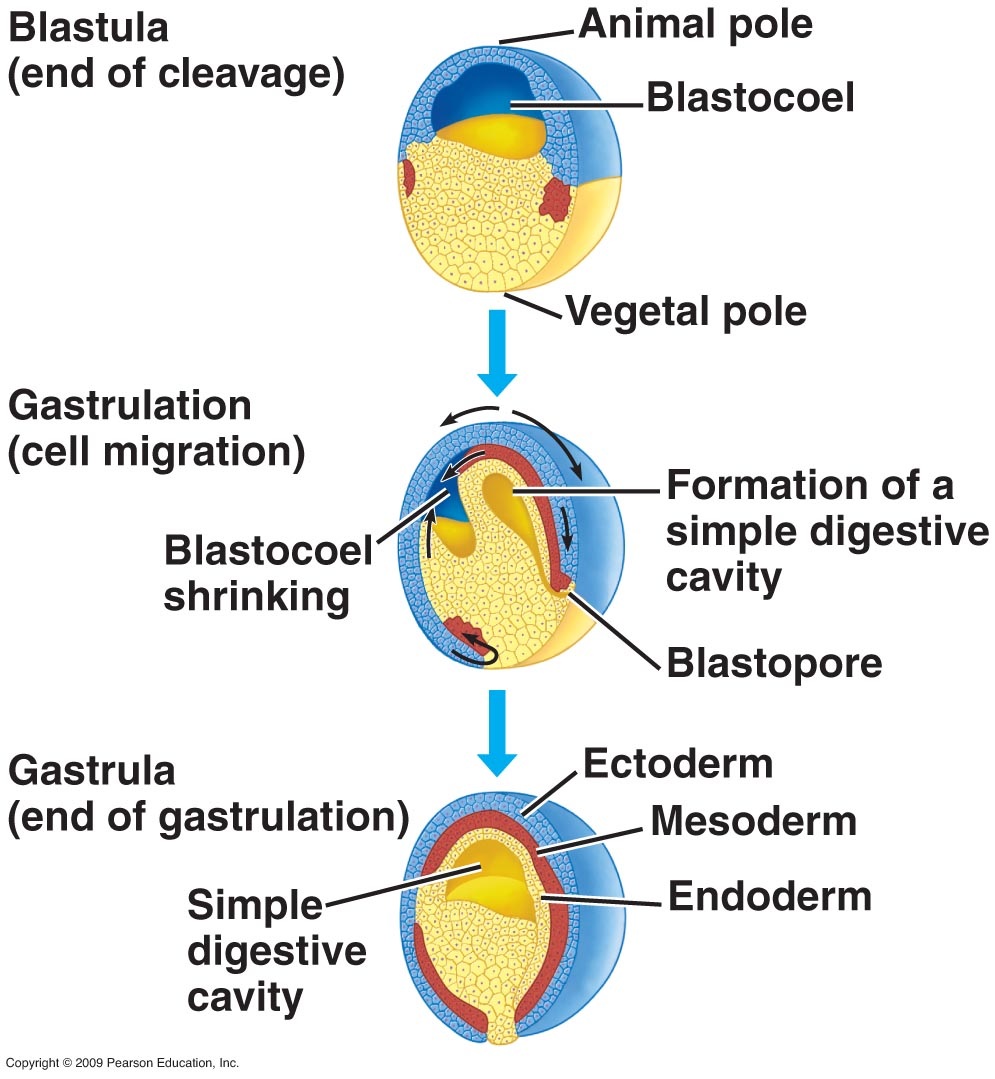
Mesoderm Formation The tissue layers, or germ layers, form during gastrulation. Early in development the egg consists of a darker animal region and a yolky vegetal region. Future mesoderm cells form from animal region cells at the boundary of these two regions as an equatorial band.
What does the mesoderm do?
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develop during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms.
How does the mesoderm differ from the endoderm?
The mesoderm differentiates to form most of the tissues, structures, and organs of the body. As the embryo lengthens, the mesoderm lying along the midline differentiates to form the notochord, a hollow cartilaginous nerve tube. In the adult the notochord… …the middle layer is the mesoderm, and the innermost layer is the endoderm (entoderm).
How are future mesoderm cells formed?
Future mesoderm cells form from animal region cells at the boundary of these two regions as an equatorial band. Unlike the other two germ layers whose fate is determined by maternal factors in the egg, future mesodermal cells form in response to signals from the future endoderm cells in the vegetal region.
Where does the mesoderm form?
The mesoderm is a germ layer that arises during gastrulation, and is present between the ectoderm, which will turn into skin and central nervous system cells, and the endoderm, which will produce the gut and the lungs (4).
What is mesoderm origin?
Cells of mesodermal origin are the most abundant in the human body, representing a great variety of cell types, including the musculoskeletal system (bone, cartilage and muscle), cardiovascular system (heart, blood and blood vessels), as well as the connective tissues found throughout our bodies.
What develops during mesoderm?
The mesoderm gives rise to the muscle cells and connective tissue in the body. The endoderm gives rise to the gut and many internal organs.
What is the mesoderm layer?
As we mentioned, the mesoderm is the layer of embryonic tissue directly between the ectoderm and the endoderm. The mesoderm is just as important as the ectoderm and endoderm in that it develops many of our muscle cells and organs, including our skeletal system, muscle system, and the main parts of our nervous system.
What is mesoderm in simple words?
ˈmē-, -sə- : the middle of the three primary germ layers of an embryo that is the source of many bodily tissues and structures (such as bone, muscle, connective tissue, and dermis) broadly : tissue derived from this germ layer.
Why is the mesoderm important?
The mesoderm is responsible for the formation of a number of critical structures and organs within the developing embryo including the skeletal system, the muscular system, the excretory system, the circulatory system, the lymphatic system, and the reproductive system.
Does the mesoderm form the brain?
In the human embryo, there are 3 layers of tissue from which body organs are derived: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Endodermal tissue forms the gut, lungs and liver; mesodermal tissue forms muscles, bones, and vasculature; and ectodermal tissue forms the nervous system and the epidermis.
How the three germ layers are formed?
The cells migrating inward along the primary axis of the embryo is the inner layer of the gastrula and develop into the endoderm. Some of the cells moving towards the primary axis but at a slower rate give rise to the mesoderm. Once the mesoderm is formed, the remaining epiblast cells form the ectodermal layer.
Which germ layer develops first?
endodermThe endoderm is one of the germ layers formed during animal embryogenesis. Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastrula, which develops into the endoderm. It is the first layer to be developed.
How is endoderm formed?
The endoderm originates from the yolky vegetal cells, ectoderm is from the animal region on top of the bastocoel cavity, and the presumptive mesoderm is induced in a ring of equatorial tissue by signals from the vegetal cells (Dale & Slack 1987, Moody 1987, Nieuwkoop 1969).
What is the difference between endoderm mesoderm and ectoderm?
The ectoderm gives rise to the skin and the nervous system. The mesoderm specifies the development of several cell types such as bone, muscle, and connective tissue. Cells in the endoderm layer become the linings of the digestive and respiratory system, and form organs such as the liver and pancreas.
How is the ectoderm formed?
The ectoderm originates in the epiblast, and is formed during gastrulation. Once the mesoderm forms, cells cease to ingress into the primitive streak; the remaining epiblast cells are hereafter called ectoderm. The ectoderm gives rise to two distinct lineages, namely, the surface ectoderm and the neural ectoderm.
Which organ is ectodermal in origin?
The ectoderm gives rise to the skin, the brain, the spinal cord, subcortex, cortex and peripheral nerves, pineal gland, pituitary gland, kidney marrow, hair, nails, sweat glands, cornea, teeth, the mucous membrane of the nose, and the lenses of the eye (see Fig. 5.3).
What is Endodermal origin?
Endoderm is one of the germ layers—aggregates of cells that organize early during embryonic life and from which all organs and tissues develop. All animals, with the exception of sponges, form either two or three germ layers through a process known as gastrulation.
What is mesoderm ectoderm and endoderm?
Ectoderm - It is the outermost layer that forms nails, hair, etc. Endoderm - It is the innermost layer that forms the stomach, colon, urinary bladder, etc. Mesoderm - It is the middle layer between ectoderm and endoderm which forms bones, cartilage, etc.
Is heart mesodermal in origin?
The heart derives from embryonic mesodermal germ-layer cells that differentiate after gastrulation into mesothelium, endothelium, and myocardium.
Where is mesoderm found?
Mesendoderm has been found in species from Echinoderms, such as sea urchins, to mice, Mus musculus. The process that gives rise to the mesoderm also creates a dorso-ventral pattern within the mesoderm.
What is the process of mesoderm and endoderm?
As organs form, a process called organogenesis, mesoderm interacts with endoderm and ectoderm to give rise to the digestive tract, the heart and skeletal muscles, red blood cells, and the tubules of the kidneys, as well as a type of connective tissue called mesenchyme. All animals that have only one plane of symmetry through the body, ...
What are the three germ layers of symmetry?
All animals that have only one plane of symmetry through the body, called bilateral symmetry, form three germ layers. Animals that have only two germ layers develop open digestive cavities. In contrast, the evolutionary development of the mesoderm allowed in animals the formation of internal organs such as stomachs and intestines (viscera). ...
What is the term for the three germ layers of cells that form organs and tissues?
Published: 2013-11-26. Keywords: embryos. Mesoderm. Mesoderm is one of the three germ layers, groups of cells that interact early during the embryonic life of animals and from which organs and tissues form. As organs form, a process called organogenesis, mesoderm interacts with endoderm and ectoderm to give rise to the digestive tract, ...
When was mesoderm discovered?
Mesoderm, along with the other two germ layers, was discovered in the early nineteenth century. In 1817 Christian Pander received an MD from the University of Würzburg, in Würzburg, Germany, after completing his dissertation. " Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte des Hühnchens im Eie " ( Contributions to the Developmental History ...
What is the first stage of embryonic development?
Gastrulation is an early stage of development during which an embryo, then a single-layered ball of cells called a blastula, reorganizes itself into a three-layered ball of cells, called a gastrula. During this process, the primary germ layers, endoderm and ectoderm, interact to form the third, called mesoderm.
Which process establishes polarity in the mesoderm?
Using those experiments, Nieuwkoop also demonstrated that the induction process establishes a polarity in the mesoderm, such that dorsal endoderm induces dorsal mesoderm, ...
What is the mesoderm?
Mesoderm Definition. The mesoderm is a germ layer present in animal embryos that will give rise to specialized tissue types. The mesoderm is one of three germ layers found in triploblastic organisms; it is found between the ectoderm and endoderm.
Which organs are formed from the mesoderm?
Many of the internal organs are formed from the mesoderm, most notably the heart and the kidney. The liver, pancreas, and gall bladder are all associated with the digestive system, and are all derived from the endoderm. 3.
What happens to the mesoderm during gastrulation?
During gastrulation the cells will rearrange until the mesoderm (and endoderm) are on the inside of the embryo, and the ectoderm is on the outside surface. This occurs by invagination of the mesoderm and endoderm cells; they migrate to the interior while the ectoderm spreads to cover the exterior.
What is the structure of the mesoderm called?
A is correct. The mesoderm forms a rod-like structure called the notochord. The notochord then signals the ectoderm to form the neural plate which folds in to form the neural tube.
What is the role of the notochord in vertebral formation?
The notochord acts as an anchor around which the vertebrae will form. The notochord itself is transient and will ultimately be incorporated as the inner portion of the vertebral disks. On either side of the notochord lie paired segments of mesoderm that are arranged successively.
Where do future mesoderm cells form?
Future mesoderm cells form from animal region cells at the boundary of these two regions as an equatorial band. Unlike the other two germ layers whose fate is determined by maternal factors in the egg, future mesodermal cells form in response to signals from the future endoderm cells in the vegetal region.
Which region of the mesoderm forms the heart and muscles?
The dorsal mesoderm will form the notochord, the central region will form the heart and muscles, and the most ventral region will form the blood and associated organs (e.g., the kidney ). Towards the end of gastrulation, the dorsal mesoderm forms a rod-like notochord that runs along the embryo from head to tail below where ...
Where do mesoderm cells migrate from?
These are mesoderm cells migrating from the primitive stria.
What is the cavity called when a plate mesoderm divides into 2 parts?
divides lateral plate mesoderm into 2 parts at about day 18-19. this cavity is called the Intraembryonic Coelom.
What are the 3 germ layers?
Having now reached week 3 in development we will now begin to look separately at the 3 transient germ layers ( ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) formed by the process of gastrulation. Beginning with the mesoderm layer, the middle embryonic connective tissue (mesenchyme) layer. Transient in terms of temporary structures that will become something else later in development.
What is the term for a cavity in the embryo?
Coelom is a general term for a "cavity" and can lie within the embryo (intraembryonic) and outside the embryo (extra embryonic). Later anatomical spaces within the embryo and fetus can also be described as coeloms.
Which muscle layer is the ventral hypomere?
hypaxial myotome (dorsolateral quarter) forms the ventral hypomere, 3 primary muscle layers which are different at neck, thorax and abdomen
Is mesoderm a layer?
Mesoderm initially forms a multilayered cellular layer separating ectoderm and endoderm, mesoderm also lies outside the embryo as extra-embryonic mesoderm (covered in placenta lecture). Embryonic mesoderm will form most of the adult connective tissues and muscle.
What is the process of mesoderm?
Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes ). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme .
What is the mesoderm?
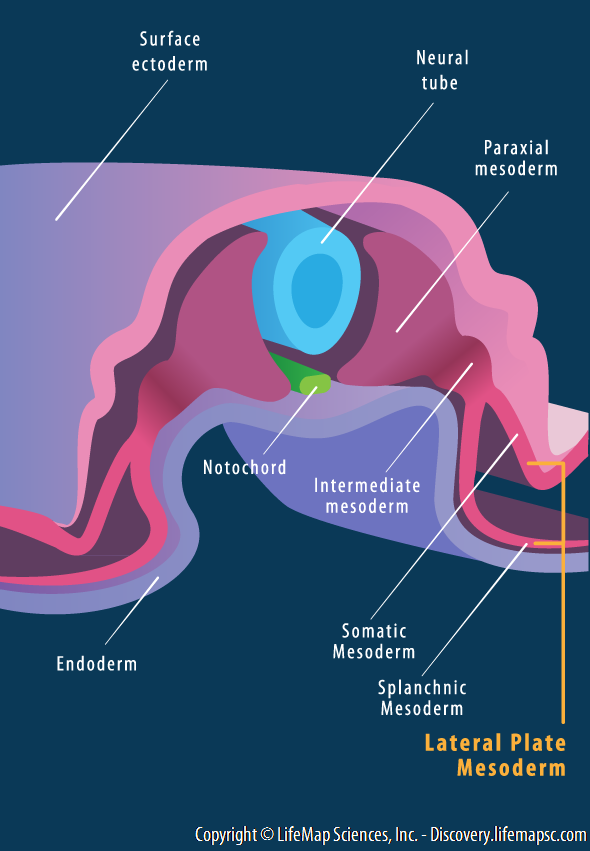
Definition. The mesoderm is one of the three germinal layers that appears in the third week of embryonic development. It is formed through a process called gastrulation. There are three important components, the paraxial mesoderm, the intermediate mesoderm and the lateral plate mesoderm.
What is the process of gastrulation?
During the third week a process called gastrulation creates a mesodermal layer between the endoderm and the ectoderm. This process begins with formation of a primitive streak on the surface of the epiblast. The cells of the layers move between the epiblast and hypoblast and begin to spread laterally and cranially. The cells of the epiblast move toward the primitive streak and slip beneath it in a process called invagination. Some of the migrating cells displace the hypoblast and create the endoderm, and others migrate between the endoderm and the epiblast to create the mesoderm. The remaining cells form the ectoderm. After that, the epiblast and the hypoblast establish contact with the extraembryonic mesoderm until they cover the yolk sac and amnion. They move onto either side of the prechordal plate. The prechordal cells migrate to the midline to form the notochordal plate. The chordamesoderm is the central region of trunk mesoderm. This forms the notochord which induces the formation of the neural tube and establishes the anterior-posterior body axis. The notochord extends beneath the neural tube from the head to the tail. The mesoderm moves to the midline until it covers the notochord, when the mesoderm cells proliferate they form the paraxial mesoderm. In each side, the mesoderm remains thin and is known as the lateral plate. The intermediate mesoderm lies between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate. Between days 13 and 15, the proliferation of extraembryonic mesoderm, primitive streak and embryonic mesoderm take place. The notochord process occurs between days 15 and 17. Eventually, the development of the notochord canal and the axial canal takes place between days 17 and 19 when the first three somites are formed.
What is the role of beta catenin in mesoderm differentiation?
Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of the transcription factor tcf-3 from repressing to activating, which initiates the synthesis of gene products critical for mesoderm differentiation and gastrulation .
What are mesoderm derivatives?
Some of the mesoderm derivatives include the muscle (smooth, cardiac and skeletal), the muscles of the tongue (occipital somites), the pharyngeal arches muscle (muscles of mastication, muscles of facial expressions), connective tissue, dermis and subcutaneous layer of the skin, bone and cartilage, dura mater, endothelium of blood vessels, red blood cells, white blood cells, and microglia, Dentine of teeth, the kidneys and the adrenal cortex.
How does the mesoderm differentiate from the rest of the embryo?
The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center . The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3.
What is the mesoderm in animals?
Tissues derived from mesoderm. In all bilaterian animals, the mesoderm is one of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and endoderm (inside layer), with the mesoderm as the middle layer between them.
Cell Lineages and Stem Cells in the Embryonic Kidney
Gregory R. Dressler, in Essentials of Stem Cell Biology (Second Edition), 2009
Embryonic
The intermediate mesoderm comes to lie in parallel ridges in the roof of the intraembryonic coelom on either side of the midline in the thoracic and abdominal regions. These ridges, known as the urogenital ridges, later form both the excretory and the reproductive organ systems. 17,18 The development of these two systems is closely interconnected.
Zebrafish Renal Development and Regeneration
Rachel C. Dodd, Alan J. Davidson, in Kidney Development, Disease, Repair and Regeneration, 2016
Early Specification and Patterning of the Intermediate Mesoderm
Egon Ranghini, Gregory R. Dressler, in Kidney Development, Disease, Repair and Regeneration, 2016
The reproductive system
Barry Mitchell BSc MSc PhD FIBMS FIBiol, Ram Sharma BSc MSc PhD, in Embryology (Second Edition), 2009
Ambiguous genitalia
Selma Feldman Witchel MD, Peter A. Lee MD, PhD, in Pediatric Endocrinology (Fourth Edition), 2014
Testicular Development and Descent
The urogenital ridge arises from the intermediate mesoderm as bilateral thickenings at the ventrolateral surface of the mesonephros. Many genes that are critical for formation of the bipotential gonad are also essential for formation of the urogenital ridge.

Mesoderm Definition
Mesoderm Formation
- The tissue layers, or germ layers, form during gastrulation. Early in development the egg consists of a darker animal region and a yolky vegetal region. Future mesoderm cells form from animal region cells at the boundary of these two regions as an equatorial band. Unlike the other two germ layers whose fate is determined by maternal factors in the ...
Mesoderm Function
- The mesoderm is responsible for the formation of a number of critical structures and organs within the developing embryo including the skeletal system, the muscular system, the excretory system, the circulatory system, the lymphatic system, and the reproductive system. It also gives rise to connective tissues, the dermis of the skin, the lining of the coelom, the adrenal cortex, an…
Quiz
- 1. What organisms do not have a mesoderm? A. insects B. fish C. corals D.amphibians 2. Which of the following organs is derived from mesoderm? A. pancreas B. kidney C. liver D.gall bladder 3. What structure is formed from the mesoderm? A. notochord B. neural crest C. neural tube D.neural plate