Tissues are organized into four broad categories based on structural and functional similarities. These categories are epithelial
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
What is a tissue?
A tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion ...
What is the difference between tissue and organ?
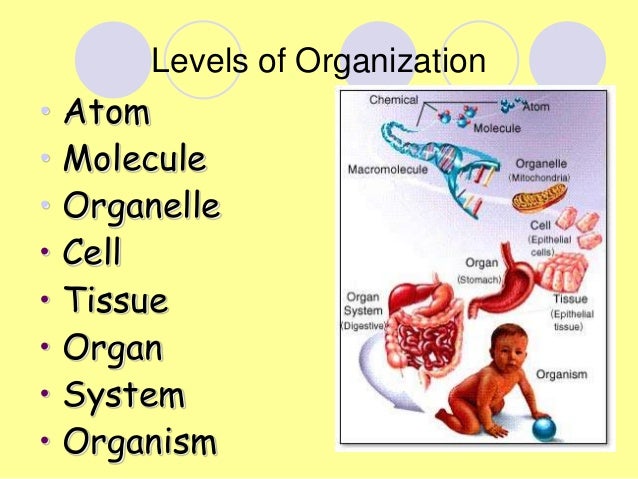
Group of cells positioned and designed to perform a particular function is called a tissue. An organ is a structure made up of a collection of tissues that carry out specialized functions for example in plants the root, stem and leaves are organs; wherein tissues of leaves include epidermis, palisade tissue, spongy tissue, xylem and phloem.
What are the 4 types of tissue in the body?
There are four main types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, connective and nervous. Each is made of specialized cells that are grouped together according to structure and function. Muscle is found throughout the body and even includes organs such as the heart. Our outer layer of skin is epithelial tissue.
What is the structure of connective tissue?
Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in the body. It consists of cells, that originate from mesenchyme, and an extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix is made up of a ground substance and protein fibers. There are several important cell types and three main fibers: collagen, reticular and elastic.

What is tissue study?
study of tissues formed by cells and cell products
What is a cell composed of?
individual cells or multicellular organs composed predominantly of epithelial tissue that secrete a substance for use elsewhere in the body or for elimination from the body
Where does origniate come from?
origniate from an invagination of epithelium that burrows into the depper connective tissues
Why does a cell look layered?
looks layered (stratified) because the cells' nuclei are distributed at different levels between the apical and basal surfaces
Which layer of epithelial tissue attaches to the basement membrane?
bottom fixed layer of epithelial tissue that attaches to the basement membrane
Which organ transports hormones?
hormonal secretions (that act as chemical messengers to influence cell activities elsewhere in the body) are transported by the blood or interstitial fluid (no ducts - ductless)
What is the term for the death of a cell?
pathologic death of cells or a protion of a tissue or organ
What are the four types of tissues?
The four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue, stratified squamous epithelial tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and connective tissue in small intestine.
Why is muscle tissue important?
Muscle tissue is essential for keeping the body upright, allowing it to move, and even pumping blood and pushing food through the digestive tract.
What are the functions of the digestive system?
For example, your digestive system is responsible for taking in and processing food, while your respiratory system—working with your circulatory system—is responsible for taking up oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide. The muscular and skeletal systems are crucial for movement; the reproductive system handles reproduction; and the excretory system gets rid of metabolic waste.
What are the organs of the human body made of?
From left to right: single muscle cell, multiple muscle cells together forming muscle tissue, organ made up of muscle tissue (bladder), and organ system made up of kidneys, ureter, bladder and urethra.
How is structure related to function?
At each level of organization—cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems—structure is closely related to function. For instance, the cells in the small intestine that absorb nutrients look very different from the muscle cells needed for body movement. The structure of the heart reflects its job of pumping blood throughout the body, while the structure of the lungs maximizes the efficiency with which they can take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
How do the respiratory system and circulatory system work together?
For example, the respiratory system and the circulatory system work closely together to deliver oxygen to cells and to get rid of the carbon dioxide the cells produce. The circulatory system picks up oxygen in the lungs and drops it off in the tissues, then performs the reverse service for carbon dioxide. The lungs expel the carbon dioxide and bring in new oxygen-containing air. Only when both systems are working together can oxygen and carbon dioxide be successfully exchanged between cells and environment.
Which muscle cells do not have striations?
From left to right. Smooth muscle cells, skeletal muscle cells, and cardiac muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells do not have striations, while skeletal muscle cells do. Cardiac muscle cells have striations, but, unlike the multinucleate skeletal cells, they have only one nucleus. Cardiac muscle tissue also has intercalated discs, specialized regions running along the plasma membrane that join adjacent cardiac muscle cells and assist in passing an electrical impulse from cell to cell.
What Is Body Tissue?
If you were to try to explain to someone what your body is made of, you might say two arms, two legs, feet and hands, a head and a torso. Or, you might go to the other extreme and say that you are made up of billions of cells. Both answers would be correct. However, there is a more specific way to describe what makes up a body. We are composed of several different types of tissue. But what exactly does that mean?
How are cells organized in the human body?
These groupings of cells form tissue structure, which then make up organs and various parts of the body.
What is epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is made up of epithelial cells, which are vastly different from the muscle cells we just talked about. These cells can be flat, cuboidal, or columnar. They are joined tightly together, making a single or stacked continuous sheet. Like a quilt that is tightly stitched, epithelium makes an excellent protective cover for the body, in the form of skin. Epithelial tissue can also be found lining some internal cavities and organs.
How many types of tissue are there in the human body?
We have determined that we are made up of four types of tissue. In addition to muscle tissue, we have connective, epithelial and nervous tissue in the body. So, what are these tissues made up of and how are they different from one another? Let's zoom in on each one to better understand.
What is the function of connective tissue?
As its name suggests, connective tissue makes up a connective web inside our body. Holding our body parts together and providing support are the main jobs of this tissue. We would certainly not be in good shape if all of our internal body parts were free-floating. Connective tissue fills in the spaces inside our body with a matrix made of fibers within a liquid, solid, or jelly-like substance. Think of a gelatin salad with fruit suspended inside, and you will have an idea of how certain types of connective tissue function.
What is human tissue made of?
As mentioned earlier, human tissue is made up of particular kinds of cells that work together. First let's look at muscle tissue. Muscle tissue is made up of excitable cells that are long and fibrous. These cells are ready for contraction, or the activation of tension in our muscles, making it possible for us to move our body parts. They are arranged in parallel lines and are bundled, making muscle tissue very strong. If you take a pile of rubber bands, line them up next to each other and attempt to stretch them, you may get the idea of the nature of the muscle tissue.
Which tissue is responsible for bringing the body parts together?
Connective tissue, which can be found filling the spaces in our body, holds our parts together and provides support. Nervous tissue transmits signals from nerves to the spinal cord and brain, allowing us to use our five senses. Keep reading to access the lesson transcript below. {"error":true,"iframe":true}.
