To measure tunneling, use a cotton tip applicator under the wound edges. Remove it and place it next to a measuring strip to document the depth of the tunneling. Undermining is also measured using a cotton tip applicator where the area meets the wound edges.
How is tunneling measured in wound care?
To measure tunneling, a probe is gently inserted into the passageway until resistance is felt. The distance from the tip of the probe to the point at which the probe is level with the wound edge represents the depth of the tunnel. Clock terms are often used to describe the position of the tunnel within the wound bed.
What is the difference between undermining and tunneling wounds?
Tunneling can occur in any wound, but it occurs most commonly in surgical wounds and wounds occurring from a neuropathic cause. Undermining is caused by erosion under the wound edges, resulting in a large wound with a small opening. Much like an iceberg, what you see on the surface is not indicative of what lies below.
How do you measure tunneling depth?
To measure tunneling, a probe is gently inserted into the passageway until resistance is felt. The distance from the tip of the probe to the point at which the probe is level with the wound edge represents the depth of the tunnel.
What is the amount of undermining of a probe?
The amount of undermining is the distance from the probe tip to the point at which the probe is level with the wound edge. Clock terms are also used to identify the area of undermining.

How do you measure undermining?
Undermining is measured by inserting a probe under the wound edge directed almost parallel to the wound surface until resistance is felt. The amount of undermining is the distance from the probe tip to the point at which the probe is level with the wound edge.
How do you assess tunneling?
To measure tunneling, a probe is gently inserted into the passageway until resistance is felt. The distance from the tip of the probe to the point at which the probe is level with the wound edge represents the depth of the tunnel. Clock terms are often used to describe the position of the tunnel within the wound bed.
What is the difference between tunneling and undermining in a wound?
Tunneling wounds typically form unidirectional passageways between the skin surface and organ spaces whereas undermined wounds tend to present with more complex, less predictable spread. Subcutaneous tissue destruction in wound undermining is often extensive, involving fat, muscle, and connective tissue.
How do you measure wound depth?
Measuring the Wound's Dimensions The depth is usually measured by inserting a q–tip in the deepest part of the wound with the tip of finger. Therefore a 3 cm x 1 cm x 2 cm wound would indicate that the wound length is 3 cm, the width is 1 cm, and the depth is 2 cm.
What is undermining in a pressure ulcer?
Undermining is the region underneath the overlying loose skin around a pressure ulcer (see Figure 1). It is an important feature of a pressure ulcer because it reflects the real size of a pressure ulcer. For example, a pressure ulcer with a small surface area may have extensive undermining.
What does it mean when a wound is undermining?
The edges of the wound should pull together easily; if not, undermining needs to be done. Undermining means cutting the fibrous septae that connect the skin to the underlying fascia, and generally this is accomplished by using the scalpel to cut the septi just beneath the dermis as shown here.
Do you pack undermining wounds?
Undermining areas and sinuses should be packed with an appropriate dressing to facilitate healing.
What causes tunneling in a wound?
Tunneling is often the result of infection, previous abscess formation, sedentary lifestyle, previous surgery at the site, trauma to the wound or surrounding tissue, or the impact of pressure and shear forces upon many tissue layers causing a “sinkhole-like” defect on the skin.
What is most important when measuring wounds?
According to various studies, what is more important than the method used is the consistency of wound measurement (van Rijswijk, 2013). In other words, the method used is far less important than ensuring that wound measurement is performed on a regular basis (weekly is recommended).
How is a tunneled wound measured?
0:392:59Tunneling and Undermining - Wound Care Demonstration - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipUsing this particular manikin. I would like to just demonstrate what tunneling looks like soMoreUsing this particular manikin. I would like to just demonstrate what tunneling looks like so whenever you're assessing a wound you're going to be using a sterile q-tip typically. If I am going to be
What are 4 components of a wound assessment?
Tissue Loss. Clinical appearance of the wound bed and stage of healing. Measurement and dimensions. Wound edge.
What are the 5 principles of wound management?
The basic principles for the management of a wound or laceration are:Haemostasis.Cleaning the wound.Analgesia.Skin closure.Dressing and follow-up advice.
What is tunneling in excavation?
tunnels and underground excavations, horizontal underground passageway produced by excavation or occasionally by nature's action in dissolving a soluble rock, such as limestone. A vertical opening is usually called a shaft.
What are the tunneling methods in soil?
Needle beam method. Linear plate method. Forepoling method.
What is tunneling data?
Tunneling, also known as "port forwarding," is the transmission of data intended for use only within a private, usually corporate network through a public network in such a way that the routing nodes in the public network are unaware that the transmission is part of a private network.
What are the effects of tunneling on the ground?
But drilling tunnels or totally drilling has some adverse environmental effects such as air pollution, groundwater pollution, increasing noise, evacuation and accumulation of bran, traffic problems, earth summit possibility, earthquake, and land sliding possibility.
Do you pack undermining in wounds?
Yes, undermining wounds require wound packing in order to properly heal, as without packing the wound may collapse, which causes further damage. Th...
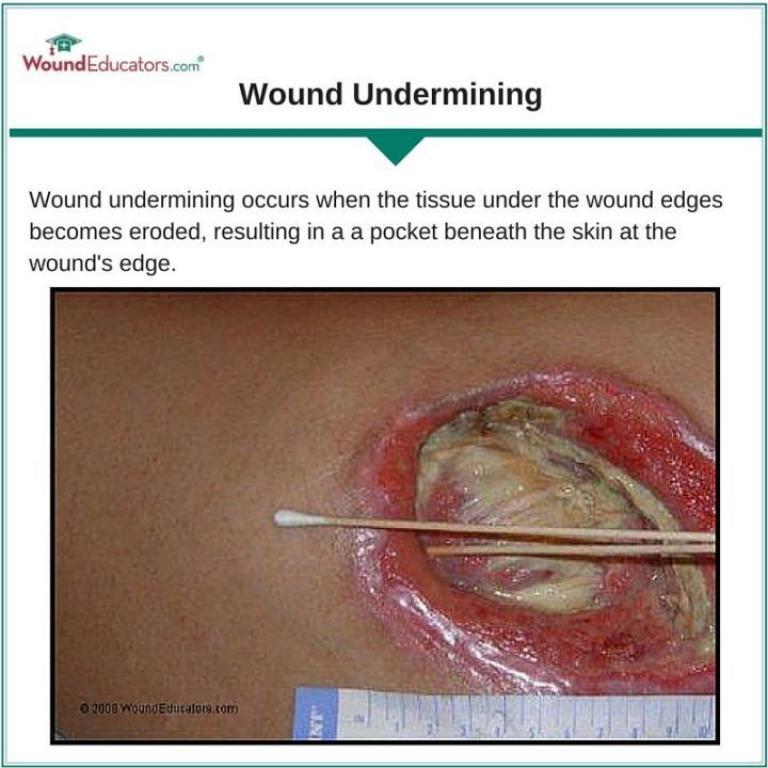
How is wound undermining measured?
A health practitioner will measure wound undermining with a sterile applicator using the clock method. The applicator will be inserted into the wou...
How do you know if a wound is tunneling?
The symptoms of a wound with tunneling are similar to the symptoms of if a wound is undermining. These symptoms are a fever due to wound infection,...
What does a tunneling wound look like?
A tunneling wound appears to be a tunnel or track that occurs from the wound edge to deep within the subcutaneous tissue. It will only occur in one...
What is tunneling and undermining?
Therefore, tunneling and undermining are two phenomena used in wound assessment. Tunneling penetrates more deeply into the tissue. It is a channel that goes in one direction from the wound base . Undermining results in a large wound that is less extensive. It may occur in one or more directions. Neither tunneling nor undermining is easily visualized. Both tunneling and undermining are serious conditions. They appear small when we observed from the skin’s surface. But these wounds are much bigger than we see from the outside.
What is the difference between tunneling and undermining?
Tunneling extends in one direction, while undermining may extend in one or more directions. So, this is the key difference between tunneling and undermining. Moreover, tunneling is a passageway or a channel, but undermining is a large wound with a small opening. Furthermore, tunneling penetrates more deeply into the tissue while undermining is less extensive. Besides, tunneling is caused by the destruction of subcutaneous tissue in a linear way, while undermining is caused by erosion of the tissue in wound edges.
What is Tunneling?
Tunneling is a channel or tunnel that extends from the wound base in a unidirectional manner. It produces a dead space. Sinus tract is a synonym for tunneling. It penetrates deeper into the tissue. Tunneling is caused due to the destruction of subcutaneous tissue in a linear fashion. Sometimes, tunnel may open at the end with another wound opening. Tunneling can be measured by a probe, and its location can be described using the clock method. There is a potential for abscess formation in tunneling. Tunneling is not easily visualized. It also takes a longer time to heal.
What is Undermining?
Undermining results in a large wound with a small opening. Therefore, it includes a wider area than tunneling. Generally, undermining occurs in more than one direction. Undermining is less extensive. It is caused by erosion under the wound edges. It can be measured by a probe holding parallel to the wound surface. There is less potential in abscess formation in undermining. Undermining is more commonly seen in patients with pressure wounds and neuropathic ulcers. Similar to tunneling, undermining is not easy to visualize. Moreover, undermining takes a longer time to heal.
Wound undermining is more commonly found in patients with pressure or neuropathic ulcers
Because tunneling and undermining are not readily visible, all wounds must he thoroughly probed to identify the full extent of tissue destruction. Wounds presenting with tunnels or undermining heal more slowly than wounds without these characteristics.
About the Author
Laurie Swezey, founder and president of WoundEducators.com, has been a Registered Nurse for more than a quarter century, with most of those years dedicated to wound treatment. Ms. Swezey is a Certified Wound Care Nurse and a Certified Wound Specialist.
