What is a normal INR level on warfarin?
Patients on blood thinners such as Warfarin are expected to have INR levels ranging from 2 to 3; however, some doctors prefer levels ranging from 2.5 to 3.5, INRTracker reports. INR levels at or above 5 often require a dose of vitamin K, the antidote for Warfarin, to bring the level down.
How to take warfarin safely?
Take warfarin safely
- Take your warfarin at the same time each day.
- If you miss a dose of warfarin, don't take an extra dose to make up for it. ...
- Wear medical alert jewelry that lets others know that you take warfarin. ...
- Don't take warfarin if you are pregnant or planning to get pregnant. ...
- Don't change your dose or stop taking warfarin unless your doctor tells you to.
How to adjust warfarin?
consider resumption of prior maintenance dose if factor causing decreased INR is transient [eg: missed warfarin dose (s)] if adosage adjustment is needed, increase maintenance dose by 10%–20% consider a booster dose of 1 ½ – 2 times daily maintenance dose
What is a typical recommended dose of warfarin?
Warfarin should usually be started at a dose of 5 mg per day.A 10-mg dose more frequently results in a supratherapeutic international normalized ratio (INR). Amiodarone, fluconazole, metronidazole, trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole, and many other drugs inhibit the metabolism of warfarin.
What should be monitored while taking warfarin?
The goal of warfarin therapy is to decrease the clotting tendency of blood, but not to prevent clotting completely. Therefore, the blood's ability to clot must be carefully monitored while a person takes warfarin.
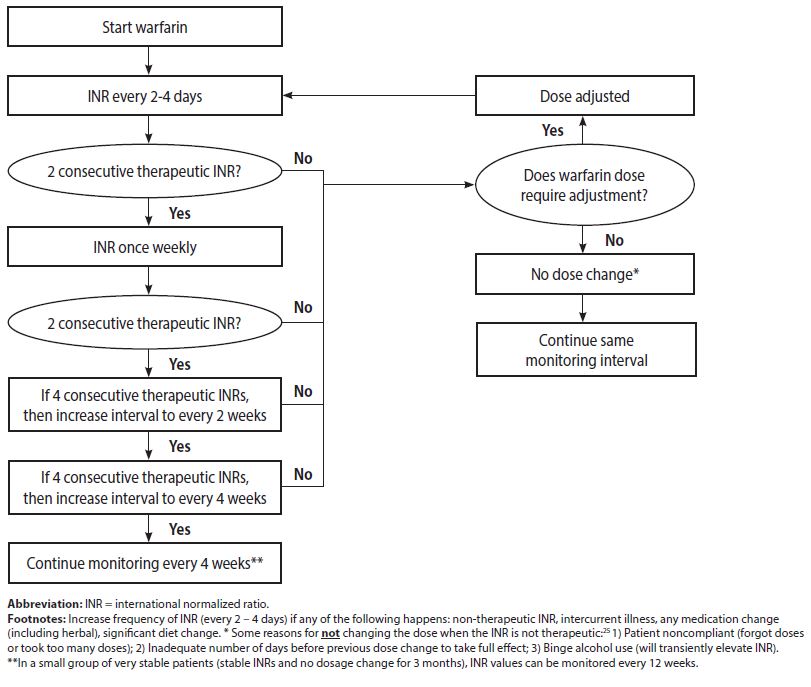
How often is warfarin monitored?
The safety and efficacy of warfarin therapy are dependent on maintaining the INR within the target range for the indication (Table 1). When a patient is started on an oral anticoagulant, INR monitoring should be performed daily until the INR is within the therapeutic range for at least 2 consecutive days.
Does warfarin require INR monitoring?
INR monitoring is essential for all patients treated with warfarin. International Normalised Ratio (INR) testing is well established as an integral part of warfarin treatment.
How often is INR checked for warfarin?
How often do I need an INR? When you first start warfarin, you may need to have blood tests every few days or weekly. When your INR and warfarin dose are stable, blood tests are often done every 2 to 4 weeks, sometimes longer.
Does warfarin require lab monitoring?
Patients prescribed warfarin must have their blood monitored frequently – at least once a month and sometimes as frequently as twice weekly – to confirm that the dose of warfarin prescribed is in a safe and effective range.
How often should INR be monitored?
Patients should take their warfarin once a day at the same time in the evening, with INR testing in the morning. The INR should be measured daily for the first five days.
What is normal INR range?
In healthy people an INR of 1.1 or below is considered normal. An INR range of 2.0 to 3.0 is generally an effective therapeutic range for people taking warfarin for disorders such as atrial fibrillation or a blood clot in the leg or lung.
What is a critical INR level?
INR levels above 4.9 are considered critical values and increase the risk of bleeding.
What is normal PT INR?
Normal Results Most of the time, results are given as what is called INR (international normalized ratio). If you are not taking blood thinning medicines, such as warfarin, the normal range for your PT results is: 11 to 13.5 seconds. INR of 0.8 to 1.1.
How do I monitor my INR with warfarin?
Monitoring Warfarin If the dose of warfarin is too high, the patient may be at risk of serious bleeding. It can be monitored by drawing blood from a vein and sending the blood to an accredited laboratory to test, or it can be monitored by testing blood from a fingerstick with an INR test meter outside of a laboratory.
When should INR be drawn?
The product labeling for warfarin recommends that the INR sample be drawn daily without regard to the timing of the warfarin dose, until the INR is in the therapeutic range. For atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism, the therapeutic range is 2.0 to 3.0.
What INR level is vitamin K?
A 1.0-mg vitamin K dose is likely most appropriate for patients with INR values between 4.5 and 10. The fear of over-correction of the INR has limited the widespread use of vitamin K; however, our review suggests that this occurs infrequently when small doses are administered orally.
When do you recheck INR?
Ideally, INR should be checked within 3-5 days of the first warfarin dose. Steady state is achieved in 10-14 days.
How often do you need blood work on Coumadin?
Blood tests are typically done from one or more times a week to once a month (if your results have been stable). Follow your provider's instructions for how often you need to get blood tests and when to adjust your daily warfarin dose.
Why do you have to take warfarin at 6pm?
Although some patients will take it in the morning, most commonly warfarin is taken at dinnertime (or later in the evening) so that the results from each INR test can be communicated to the patient in time for dose adjustments (if any) the same day.
How do you monitor anticoagulant therapy?
The level of anticoagulation may be monitored with the APTTActivated partial thromboplastin time and/or Anti factor Xa level, however monitoring(including the test and frequency) should be according to local guidelines. Prophylactic (low dose) heparin does not usually require monitoring.
Overview
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease or artificial heart valves. Less commonly it is used following ST-segment elevatio…
Medical uses
Warfarin is used to decrease the tendency for thrombosis, or as secondary prophylaxis (prevention of further episodes) in those individuals who have already formed a blood clot (thrombus). Warfarin treatment can help prevent formation of future blood clots and help reduce the risk of embolism (migration of a thrombus to a spot where it blocks blood supply to a vital organ).
Warfarin is best suited for anticoagulation (clot formation inhibition) in areas of slowly running b…
Contraindications
All anticoagulants are generally contraindicated in situations in which the reduction in clotting that they cause might lead to serious and potentially life-threatening bleeds. This includes people with active bleeding conditions (such as gastrointestinal ulcers), or disease states with increased risk of bleeding (e.g., low platelets, severe liver disease, uncontrolled hypertension). For patients undergoing surgery, treatment with anticoagulants is generally suspended. Similarly, spinal or lu…
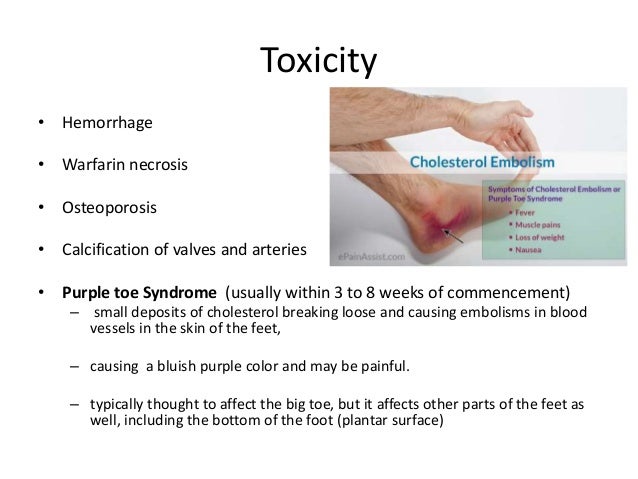
Adverse effects
The only common side effect of warfarin is bleeding. The risk of severe bleeding is small but definite (a typical yearly rate of 1–3% has been reported), and any benefit needs to outweigh this risk when warfarin is considered. All types of bleeding occur more commonly, but the most severe ones are those involving the brain (intracerebral hemorrhage/hemorrhagic stroke) and the spinal cord. Risk of bleeding is increased if the INR is out of range (due to accidental or deliberate over…
Overdose
The major side effect of warfarin use is bleeding. Risk of bleeding is increased if the INR is out of range (due to accidental or deliberate overdose or due to interactions). Many drug interactions can increase the effect of warfarin, also causing an overdose.
In patients with supratherapeutic INR but INRless than 10 and no bleeding, it is enough to lower the dose or omit a dose, monitor the INR and resume warfarin at an adjusted lower dose when t…
Interactions
Warfarin interacts with many commonly used drugs, and the metabolism of warfarin varies greatly between patients. Some foods have also been reported to interact with warfarin. Apart from the metabolic interactions, highly protein bound drugs can displace warfarin from serum albumin and cause an increase in the INR. This makes finding the correct dosage difficult, and accentuates the need of monitoring; when initiating a medication that is known to interact with warfarin (e.g., sim…
Chemistry
X-ray crystallographic studies of warfarin show that it exists in tautomeric form, as the cyclic hemiketal, which is formed from the 4-hydroxycoumarin and the ketone in the 3-position substituent. However, the existence of many 4-hydroxycoumadin anticoagulants (for example phenprocoumon) that possess no ketone group in the 3-substituent to form such a structure, suggests that th…
Pharmacology
Warfarin consists of a racemic mixture of two active enantiomers—R- and S- forms—each of which is cleared by different pathways. S-warfarin is 2–5 times more potent than the R-isomer in producing an anticoagulant response. Both the enantiomers of warfarin undergo CYP-mediated metabolism by many different CYPs to form 3',4',6,7,8 and 10-hydroxy warfarin metabolites, major being 7-O…