
How long does it take to get soil test results back?
A: The analysis takes two to three working days from the time the lab receives the samples. In general, it takes 7 to 10 days from the time we receive the samples to the time you get your test reports back.
How long does soil analysis take?
You should receive test results in about two weeks. The lab analysis takes three to five working days from the time samples are received.
Is a soil test worth it?
Testing Garden Soil – Why Test Soil In A Garden. Getting a soil test is a great way to measure its health and fertility. These tests are generally inexpensive, though well worth any cost when it comes to growing and maintaining healthy plants in the garden.
How long does a geotechnical report take?
between two weeks and two monthsGeotechnical reports can take anywhere between two weeks and two months to produce (or longer!), and there are many factors that can affect that timeline. If you are looking to begin a project where Clearing and Grading Permit applications have been submitted, a geotechnical report will very likely be required.
How accurate is soil testing?
It will never be totally accurate. It will depend on where the soil cores are pulled from. Uneven manure or fertilizer application in the past can effect the sample. There are various other things that can distort a sample.
How deep do soil tests go?
The recommended sampling depth for gardens is 6 inches. This is the normal spading depth of most garden soils. Take soil samples to a depth of 4 inches. This is the actual soil depth and should not include roots or other accumulated organic material on the surface.
What happens if a soil test fails?
What happens if you fail a perc test? If your site fails a Soil & Site Evaluation with the Local Health Department, and your Improvement Permit application was denied, you can either appeal their decision or they will recommend you hire a Soil Scientist to evaluate the land for Alternative and Innovative system types.
What can I expect from a soil test?
Basic soil tests pinpoint the amount of organic matter, the pH and the level of macronutrients (nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P) and potassium (K)). These standard tests only provide information on soil characteristics. That means they do not test for pollutants, pesticides or other potentially toxic compounds.
Are store bought soil tests accurate?
Complete kits typically promise to test nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and pH, which are the most important basics. Though these test kits and meters may seem like the perfect alternative to lab testing, they typically aren't as accurate.
Is a geotechnical report the same as a soil test?
A geotechnical test and report will ascertain the characteristics of the soil to determine its capacity to support your building or structure. Proper soil testing enables you to evaluate the soils suitability for your project.
What does a Geotech report cost?
As a guide only, for a flat residential site, costs can range between $1000-$2000. For a steep residential site the costs can can start from $2000 upwards. We recommend getting a number of quotes to compare.
What happens during a geotechnical evaluation?
A geotechnical investigation will include surface exploration and subsurface exploration of a site. Sometimes, geophysical methods are used to obtain data about sites. Subsurface exploration usually involves soil sampling and laboratory tests of the soil samples retrieved.
What can I expect from a soil test?
Basic soil tests pinpoint the amount of organic matter, the pH and the level of macronutrients (nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P) and potassium (K)). These standard tests only provide information on soil characteristics. That means they do not test for pollutants, pesticides or other potentially toxic compounds.
What does a soil analysis tell you?
The soil test will tell you the percentage of organic matter you have in your soil and will “credit” you a certain amount of nitrogen for it. This will minimize the risk of applying excess nitrogen which might then wash out of your soil and into surrounding waterways.
How often should soil analysis be done?
every 3-5 yearMost will advise that you test your soils every 3-5 year for the chemical indices, however if a large correction in soil pH or fertility is called for by the initial soil test, it is a good idea to retest sooner rather than later to evaluate if the situation has been corrected.
What is the ideal time for soil sampling?
The right time to take soil samples is in rhythm with the crop rotation. Normally it's best to sample following back-to-back plantings of the same crop, which creates a consistent basis for comparing fields and picking out trends over time.
Why Soil Test?
All plants, including turfgrass and garden plants, need 16 essential nutrients to grow, most of them come from the soil. Plants also require favorable soil chemical conditions as indicated by the soil pH. For a lawn or garden to maintain quality or productivity, we may need to add fertilizer to supply extra nutrients or add lime to neutralize acidity and adjust the pH. A SOIL TEST identifies necessary fertilizer and lime requirements.
When is the best time to test soil for nutrients?
The best time to evaluate the nutrient status of the soil is during a time when plants aren’t growing, although any time of year is satisfactory. In any case, it’s more environmentally friendly to SOIL TEST than to guess about which fertilizers to use. For your soil test to be as accurate as possible, collect the soil sample before fertilizer is applied and use the proper sampling procedures.
How to collect soil samples?
Collecting a Good Soil Sample 1 Soil properties vary from place to place. The sample should be representative of the lawn or garden as a whole. 2 Do not sample unusual or non-representative areas. 3 Scrape plant debris from soil surface before sampling. 4 Sample lawns and gardens to a 6” depth. 5 Using a clean bucket and a soil probe or spade, combine cores or slices of soil from at least 15 locations scattered throughout the lawn or garden (see diagram). 6 Mix soil thoroughly and fill the sample bag with a pint of the mixture. 7 Submit samples to your county Extension office. They will send samples to the OSU Soil, Water and Forage Laboratory for testing.
What are the benefits of soil testing?
Benefits of Soil Testing. Take advantage of nutrients already in the soil. Identify nutrients that are lacking in the soil. Reduce fertilizer applications by applying only what is needed. Provide a proper balance of plant nutrients. Adjust soil pH to an optimum level.
How to combine cores of soil?
Using a clean bucket and a soil probe or spade, combine cores or slices of soil from at least 15 locations scattered throughout the lawn or garden (see diagram).
Why should soil, water and plant samples be submitted for testing?
Soil, water and plant samples should be submitted for testing to learn sampling techniques, understand test result interpretations and get recommendations.
Where to submit soil samples to OSU?
Contact your county Extension office for more information on soil testing. They will submit your samples to the OSU Soil Testing Laboratory and help you interpret the results.
How to get reliable soil test results?
Consistently reliable results can only be obtained by submitting samples to a soil-testing laboratory. The North Carolina Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services Agronomic Division will analyze your soil samples free of charge or for a small fee. Forms and boxes for samples are available from your local county Cooperative Extension center.
When to submit soil test report?
The soil-test report will make recommendations for the next growing season, so test soil several months before planting or fertilizing. For a cool season lawn, submit samples the previous summer; for a warm-season lawn, submit samples in the fall or winter. For a spring vegetable garden or flower bed, submit a sample in the fall or winter.
How does pH affect soil?
Also, as water from rainfall or irrigation passes through the soil, acids displace basic cations (positively charged ions) such as calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg), which are then leached from the soil. Acidity generally increases (pH decreases) with soil depth, so soils that are eroded are acidic unless properly limed. Heavy use of some nitrogen fertilizers also can increase soil acidity.
What happens when water passes through soil?
Also, as water from rainfall or irrigation passes through the soil, acids displace basic cations (positively charged ions) such as calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg), which are then leached from the soil . Acidity generally increases (pH decreases) with soil depth, so soils that are eroded are acidic unless properly limed.
What factors determine the amount of lime needed to raise the pH of soil?
Soil texture, organic matter content, crop to be grown, target pH, soil acidity level, cation exchange capacity (CEC), type and amount of clay, and current pH are factors to consider in determining the amount of lime needed to raise the soil pH.
Why do you need less lime in clayey soil?
Sometimes soils with an identical pH will have different lime recommendations. Soils low in organic matter or high in sand require less lime to change the pH than clayey soils or those with high organic matter. Clayey soils contain more potential acidity than sandy soils. As the pH falls below 5.5, aluminum becomes soluble at levels toxic to plants. In addition, soluble aluminum reacts with water to produce hydrogen ions, further reducing soil pH. The purpose of liming is to reduce exchangeable aluminum to levels that are not toxic to plants.
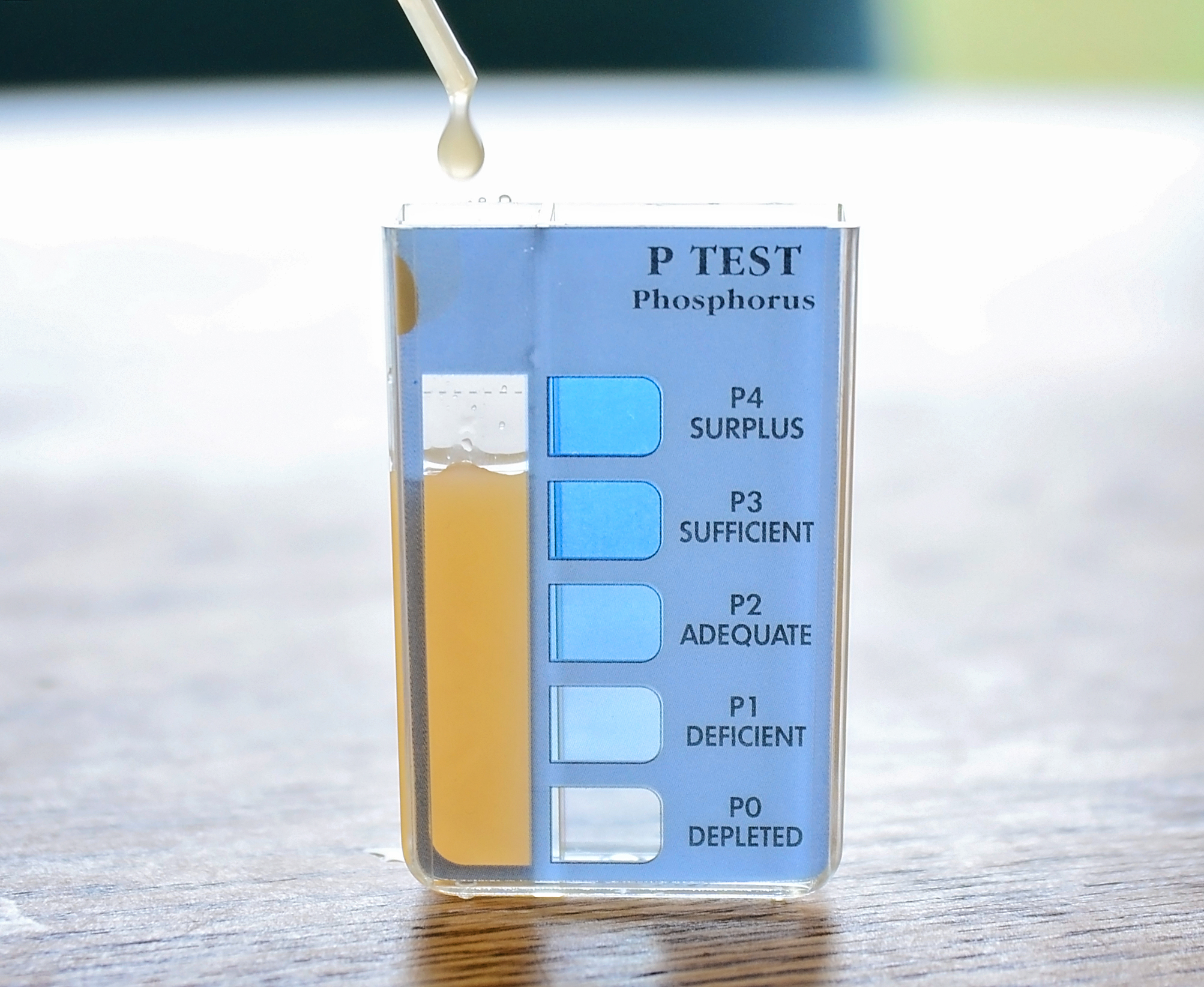
What is soil testing?
Soil testing is a quick and accurate method to determine the relative acidity of the soil (pH) and the level of several essential nutrients (phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, sulfur, manganese, copper, and zinc) needed. The test results will aid you in plant selection, soil preparation, and fertilization.
What is the analytical procedure used in soil testing?
Currently, most soil testing laboratories that operate in the North-Central states use the same analytical procedure when analyzing for a specific nutrient. These laboratories also participate in a quality control program that produces confidence in the analytical results coming from that laboratory.
What is the number associated with a nutrient on a soil test report?
The number associated with any nutrient on a soil test report is an index value associated with one of the five relative levels. It is not the amount of a nutrient that is available for crop use. It is not the total amount of a nutrient present in the soil. The number listed is an index value only and when combined with an expected yield can be used to develop a fertilizer guideline.
What are the reporting units for soil organic matter?
There are a variety of reporting units for soil organic matter content. Some laboratories report the organic matter in relative terms for low, medium, and high. Others report the measured percentage. The units chosen to report the analytical results do not have any effect on fertilizer guidelines.
Why do farmers take soil samples?
For many years, farmers have taken soil samples and sent them off for analysis to finetune their fertilizer management. The results of the laboratory analysis are often confusing. The units used to report the analytical results are not familiar. There are several numbers on the analysis sheet. There is a relationship between the analytical results and fertilizer and lime recommendations. Some explanation of the information which appears on the analytical report would probably be helpful.
What are the letters in soil test?
The numbers listed on most soil test reports are usually followed by one of the following letters: VL, L, M, H, or VH. These letters are abbreviations for very low, low, medium, high, and very high, respectively. These letters designate the relative level of the nutrient measured and provide a good indication of the probability of measuring an economic increase in yield if fertilizer supplying the nutrient in question is applied. For example, if the relative level is very low, there is a high probability that crop yields will increase if fertilizer supplying the nutrient in question is applied. By contrast, no increase in yield from the application of the nutrient would be expected if the relative level in the soil is in the very high range. Figure 1 illustrates the relative proportion of nutrient needed from either soil or fertilizer at the various soil test levels.
Can a soil testing laboratory use a range of values?
The range of values for each relative level shown in the above table is not used by all soil testing laboratories. A soil testing laboratory can use any range of values that it chooses. A difference in the range of values for each relative level is one source of confusion that adds to the difficulty of evaluating results from more than one soil testing laboratory. The ranges in the preceding table are the end result of a considerable amount of research conducted in the field.
What is soil testing?
Soil tests are tools that allow you to understand soil fertility in your fields. With the basic soil sampling tests and techniques, you can get an estimate of the average field fertility, but in order to get accurate and useful results, it's important to get a representative sample. Check out our soil sampling video to see how soil samples should ...
What is the first section of a soil sample?
The first section is composed of the information you filled out when you sent in the soil sample and forms -- name, contact, and field information.
What is section 3 of soil test report?
In section 3 of the soil test report, the recommendations are reported. The upper portion of section 3 is used for the recommendations of limestone and magnesium. Limestone is reported as pounds per acre required to get to a target pH of 6.5 and reducing soil acidity.
Where to find range table on soil test?
Although recommendations are not provided for trace minerals, a normal range table can be found on the back of your soil test result. Reading soil test results can be overwhelming and can be hard to digest all this information.
When to measure nitrogen?
If we measure nitrogen when you take soil tests, typically done in the fall through early spring , the value reported doesn't mean much.
What is the pH of soil?
A few keys to notice in section 4 are as follows: Acidity is not the same a soil pH, these are very different things. As we see in Image 2. The soil pH is 5.2 and the soil acidity is 8.7. If you have purchase additional test options, such as organic material, nitrate-N, or salts, results will be found in the sections. Also, trace mineral concentrations for zinc, copper, and sulfur are found in this section. Although recommendations are not provided for trace minerals, a normal range table can be found on the back of your soil test result.
What is soil test?
A soil test is used to determine the amount of these nutrients in the soil. The soil test results are subsequently used to make a soil test report. In addition to indicating the level of nutrients in your soil, the report will also tell you the pH value or how acidic or basic your soil is, and it will make a recommendation for ...
Why is soil testing important?
Testing the soil is very important because is some parts of the state the soil may already contains high levels of phosphorus or calcium, and may already be in the correct pH range (or higher).
How to get soil samples from Clemson University?
Bring a minimum of 2 cups of soil per composite sample in a clean jar or zip-lock bag to your county Extension office. Be sure to keep track of which part of your yard, landscape or garden the sample represents. At the Extension office they will ask you to fill out the information on a soil test bag, fill out a record sheet, and check the appropriate boxes for the analyses desired. There is a nominal fee for a standard soil test. Alternatively, a prepaid soil sample mailer kit can be ordered from Clemson University Agricultural Service Laboratory, or picked up at any county Extension office. This postage prepaid mailer kit can be mailed to the Agricultural Service Lab from home. Each soil test provides unbiased, scientific information on:
How deep should composite soil be?
The composite samples should include soil from the surface to a depth of 6 inches in all areas, except for lawns where core samples should be taken from a depth of only 2 to 4 inches. A simple garden trowel can be used to collect the core samples.
How long does it take for lime to dissolve?
Typically, lime is applied as pelletized dolomitic limestone, which takes several months to totally dissolve and change the soil pH. However, faster acting limestone is frequently available, but at a much higher price. A disadvantage to this faster acting limestone is that it does not last as long in the soil.
What is the pH of soil?
Soil pH: Soil pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline your soil is. Soil pH directly affects nutrient availability. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 as neutral. Numbers less than 7 indicate acidity, while numbers greater than 7 indicate an alkaline soil. Plants thrive best in different soil pH ranges.
What is the label on a soil bag?
Label the soil bag with name, address, county and the type of lawn, crop, or landscape plant.
How is the absorption rate of soil measured?
In many jurisdictions, the absorption rate of the soil is measured in the field with a perc test. Visual observations are used to identify the “limiting zone,” where the soil is unsuitable for treating sewage. This is determined by upper layer of the water table, or impermeable soil or rock.
What does it mean when soil is 2 in. long?
If you can form a ribbon of soil 2 in. or longer in the ribbon test, it indicates that the soil has high clay content and may fail a standard perc test.
How long does it take for a septic system to percolate?
The percolation rate is usually expressed in minutes per inch of drop. A rate of 60 minutes per inch (MPI), meaning the water dropped one inch in 60 minutes, is often the cutoff point for a standard gravity-flow septic system, although the maximum number varies from 30 to 120 MPI depending on local regulations. Some towns require additional “hydraulic” soil tests for sites that test above 30 minutes per inch.
How close to the ground is a leach field?
Typically, the water table or impermeable soil must be at least 3 feet below the bottom of the trenches in the leach field, but the exact distance varies with local regulations.
Why does a leach field fail?
Less commonly, a site can fail because the soil is too permeable, allowing the effluent to reach the groundwater before it is fully treated . Very steep slopes are also unsuitable for a conventional leach field.
What is the visual observation of sewage?
Visual observations are used to identify the “limiting zone,” where the soil is unsuitable for treating sewage. This is determined by upper layer of the water table, or impermeable soil or rock.
How to test for clay content?
To get a rough idea before investing time and money in testing, dig below the top few inches of topsoil (loam) to the lighter soil beneath and grab a handful. If the soil has a sticky, damp texture, and you can form a small lump of damp subsoil into a long, thin ribbon or worm shape that holds together, then the soil has significant clay content .
What Information Is on The Report form?
- The soil test results are sent to you by email or via the U.S. Postal Service on a computer-generated report form. Each report has a common format. • Lab ID: Each sample is given a unique number. Please refer to this number if you have any questions. • Sample Name: The name you gave to this soil sample. For example, Front Lawn. • Lab Run Date: The ...
Lead Screening
- All home grounds and gardens soil samples are screened for lead. At high levels, lead is toxic to humans, and young children are at the highest risk. Plants do not readily incorporate lead into their tissues, but high levels of lead may be found on leafy vegetables (e.g. lettuce) or root crops grown in contaminated soil. Depending on the results of the “Lead Screen”, a series of recomme…
Why Doesn’T The Lab Test Nitrogen?
- Nitrogen is a very unstable element. Its availability changes from week to week as a result of biological activity in the soil and weather conditions. To accurately measure nitrogen, samples must be frozen immediately and shipped quickly to the lab – a very expensive process. Therefore, nitrogen recommendations are based on crop need rather than on a soil nitrogen test.
Why Are There No Recommended Values Given For Minor elements?
- Soil fertilizer and lime recommendations are made based upon years of field research. Scientists have looked at the level of nutrients in the soil, analyzed crop growth, and determined how much of certain nutrients are needed each year for specific crops. Most of this research has concentrated on major plant nutrients – Mg, Ca, K and P – those needed by plants in the largest …
Glossary of Terms on The Report Form
- pH- Indicates whether the soil is acid or alkaline. 7.0 is a neutral level; less than 7.0 is acidic and greater than 7.0 is alkaline. Although NH soils are naturally very acidic (pH 4.5 – 5.5), most plants prefer a pH range of 6.0 – 6.5. Exceptions are acid loving plants such as blueberries, azaleas, rhododendrons, mountain laurel and holly, which prefer pH 4.5 – 5.5. Lime is most commonly us…