How long does it take for uranium to decay?
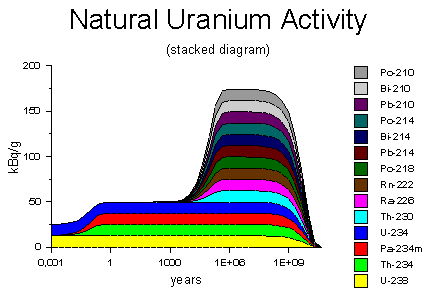
4.5 billion years Uranium undergoes radioactive decay very slowly. The half-life for U238 is 4.5 billion years. After one half-life, a container that originally held 10,000 kg of pure U238 would be reduced to 5,000 kg of U238, along with approximately 5,000 kg of associated daughter products.
What is the half life of uranium 238?
The half-life of uranium-238 is 4.5 billion years (opens in new tab). It decays into radium-226, which in turn decays into radon-222. Radon-222 becomes polonium-210, which finally decays into a stable nuclide, lead.Mar 9, 2022 Does uranium decay into thorium?
How long does it take to make lead from uranium?
It starts with Uranium 238 which goes through (including but not limited to) Uranium 234, Thorium-230, Radium-226, Radon-222 and eventually ends up as Lead-206. The entire process takes about 4.6 billion years.
What is the end product of radioactive decay of uranium?
Three stable lead nuclides are the end products of radioactive decay in the three natural decay series: uranium (decays to lead-206), thorium (decays to lead-208), and actinium (decays to lead-207). More than 30 radioactive isotopes have been reported. What is the final daughter of uranium?
Why is the conversion rate of uranium not going to be converted?
What is the process of radioactive decay?
What is the uranium that is converted to plutonium?
How long does U-238 last?
What happens after half life?
How many half lives are left after a sample is analyzed?
Is uranium soluble in water?
See 2 more
About this website
Why is the conversion rate of uranium not going to be converted?
The overall conversion rate depends highly on the design of the reactor. Even then, you aren't going to convert most of it because other things will happen to the uranium, notably fission.
What is the process of radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity or nuclear radiation) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy (in terms of mass in its rest frame) by emitting radiation , such as an alpha particle, beta particle with neutrino or only a neutrino in the case of electron capture, or a gamma ray or electron in the case of internal conversion . A material containing such unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Certain highly excited short-lived nuclear states can decay through neutron emission, or more rarely, proton emission. Radioactive decay is a stochastic
What is the uranium that is converted to plutonium?
Of the two isotopes of uranium naturally found, only U-238 (99.3%) will convert to plutonium. It absorbs a neutron, normally in a nuclear reactor, and becomes U-239, which goes through two beta decays to become Pu-239. This decay takes about two and a half days.
How long does U-238 last?
A bit longer actually, as its half-life is 4.5 billion years, but its mean lifetime is the half-life/ln (2), or about 6.5 billion years. Nothing, nothing at all short of being bombarded by neutrons, will change that average time to decay. There is no other decay as far as its nucleus is concerned.
What happens after half life?
After one half life, 50% of the sample will have decayed. After two half lives, 75% will have decayed. After two half lives, 87.5% so on and so on.
How many half lives are left after a sample is analyzed?
After 10 half-lives, only about 1/1000 of the original sample will be left; and after 20 half-lives, only about one millionth of the original sample will be left.
Is uranium soluble in water?
Uranium oxide is slightly soluble in water. So rain falls on the ground, dissolves a minute amount of uranium, runs down rivers carrying the uranium into the sea. There, the sun evaporates water concentrating the uranium. This process has been running for 4 billion years and will continue as long as the sun shines, perhaps another 4 billion years. The concentration of uranium in seawater is currently 3.3 parts per billion. If you multiply by 1.4e12 tonne of seawater you get 4.6e9 tonne Uranium. That’s a lot.
How long does a radionuclide decay?
Every radionuclide has a specific decay rate, which is measured in terms of ". half-life. half-life The time required for half of the radioactive atoms present to decay or transform. Some radionuclides have half-lives of mere seconds, but others have half-lives of hundreds or millions of years. .".
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the emission of energy in the form of ionizing radiation ionizing radiation Radiation with so much energy it can knock electrons out of atoms. Ionizing radiation can affect the atoms in living things, so it poses a health risk by damaging tissue and DNA in genes.. The ionizing radiation that is emitted can include alpha particles alpha particle A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of two neutrons and two protons. Alpha particles pose no direct or external radiation threat; however, they can pose a serious health threat if ingested or inhaled., beta particles beta particle A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of small, fast-moving particles. Some beta particles are capable of penetrating the skin and causing damage such as skin burns. Beta-emitters are most hazardous when they are inhaled or swallowed. and/or gamma rays gamma rays A form of ionizing radiation that is made up of weightless packets of energy called photons. Gamma rays can pass completely through the human body; as they pass through, they can cause damage to tissue and DNA.. Radioactive decay occurs in unbalanced atoms called radionuclides.
What is gamma radiation?
gamma rays A form of ionizing radiation that is made up of weightless packets of energy called photons. Gamma rays can pass completely through the human body; as they pass through, they can cause damage to tissue and DNA. . Radioactive decay occurs in unbalanced atoms called radionuclides.
What is the term for the element that emits ionizing radiation?
Elements that emit ionizing radiation are called radionuclides. When it decays, a radionuclide transforms into a different atom - a decay product. The atoms keep transforming to new decay products until they reach a stable state and are no longer radioactive.
Is each series of radionuclides radioactive?
Each series has its own unique decay chain. The decay products within the chain are always radioactive. Only the final, stable atom in the chain is not radioactive. Some decay products are a different chemical element. Every radionuclide has a specific decay rate, which is measured in terms of ".
Is an element stable or unstable?
Some of these forms are stable; other forms are unstable. Typically, the most stable form of an element is the most common in nature. However, all elements have an unstable form. Unstable forms emit ionizing radiation and are radioactive.
Why is the conversion rate of uranium not going to be converted?
The overall conversion rate depends highly on the design of the reactor. Even then, you aren't going to convert most of it because other things will happen to the uranium, notably fission.
What is the process of radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity or nuclear radiation) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy (in terms of mass in its rest frame) by emitting radiation , such as an alpha particle, beta particle with neutrino or only a neutrino in the case of electron capture, or a gamma ray or electron in the case of internal conversion . A material containing such unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Certain highly excited short-lived nuclear states can decay through neutron emission, or more rarely, proton emission. Radioactive decay is a stochastic
What is the uranium that is converted to plutonium?
Of the two isotopes of uranium naturally found, only U-238 (99.3%) will convert to plutonium. It absorbs a neutron, normally in a nuclear reactor, and becomes U-239, which goes through two beta decays to become Pu-239. This decay takes about two and a half days.
How long does U-238 last?
A bit longer actually, as its half-life is 4.5 billion years, but its mean lifetime is the half-life/ln (2), or about 6.5 billion years. Nothing, nothing at all short of being bombarded by neutrons, will change that average time to decay. There is no other decay as far as its nucleus is concerned.
What happens after half life?
After one half life, 50% of the sample will have decayed. After two half lives, 75% will have decayed. After two half lives, 87.5% so on and so on.
How many half lives are left after a sample is analyzed?
After 10 half-lives, only about 1/1000 of the original sample will be left; and after 20 half-lives, only about one millionth of the original sample will be left.
Is uranium soluble in water?
Uranium oxide is slightly soluble in water. So rain falls on the ground, dissolves a minute amount of uranium, runs down rivers carrying the uranium into the sea. There, the sun evaporates water concentrating the uranium. This process has been running for 4 billion years and will continue as long as the sun shines, perhaps another 4 billion years. The concentration of uranium in seawater is currently 3.3 parts per billion. If you multiply by 1.4e12 tonne of seawater you get 4.6e9 tonne Uranium. That’s a lot.

Overview
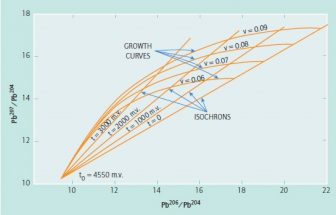
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range.
The method is usually applied to zircon. This mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead when forming. As a result, newly-formed zircon dep…
Decay routes
Uranium decays to lead via a series of alpha and beta decays, in which U and its daughter nuclides undergo a total of eight alpha and six beta decays, whereas U and its daughters only experience seven alpha and four beta decays.
The existence of two 'parallel' uranium–lead decay routes ( U to Pb and U to Pb) leads to multiple feasible dating techniques within the overall U–Pb system. The term U–Pb dating normally impli…
Mineralogy
Although zircon (ZrSiO4) is most commonly used, other minerals such as monazite (see: monazite geochronology), titanite, and baddeleyite can also be used.
Where crystals such as zircon with uranium and thorium inclusions cannot be obtained, uranium–lead dating techniques have also been applied to other minerals such as calcite / aragonite and other carbonate minerals. These types of minerals often produce lower-precision …
Mechanism
During the alpha decay steps, the zircon crystal experiences radiation damage, associated with each alpha decay. This damage is most concentrated around the parent isotope (U and Th), expelling the daughter isotope (Pb) from its original position in the zircon lattice.
In areas with a high concentration of the parent isotope, damage to the crystal lattice is quite extensive, and will often interconnect to form a network of radiation damaged areas. Fission trac…
Computation
Under conditions where no lead loss or gain from the outside environment has occurred, the age of the zircon can be calculated by assuming exponential decay of uranium. That is
where
• is the number of uranium atoms measured now.
See also
• Lead–lead dating (Pb–Pb dating)