
What is the prognosis for Ards?
Outlook / Prognosis What is the outlook for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)? ARDS can be life-threatening and deadly. But improved care and ventilator treatments — including prone ventilation with patients lying face down to improve oxygen flow — are now helping more people survive and reduce risk of complications from ARDS.
How Ards should be treated?
People with ARDS usually are given medication to:
- Prevent and treat infections
- Relieve pain and discomfort
- Prevent blood clots in the legs and lungs
- Minimize gastric reflux
- Sedate
Is Ards curable?
There is no cure for ARDS. Treatment focuses on supporting you while your lung heals. The goal of this supportive care is to keep enough oxygen in the blood to prevent further damage to the body. It is also important to treat whatever caused ARDS in the first place. This treatment must be done safely, without leading to other problems.
How to diagnose Ards?
When symptoms of ARDS occur, a combinations of tests may be done:
- Chest X-ray to measure fluids in the lungs.
- A blood test to determine oxygen level in the blood to help determine the severity of ARDS.
- Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) to evaluate heart function.
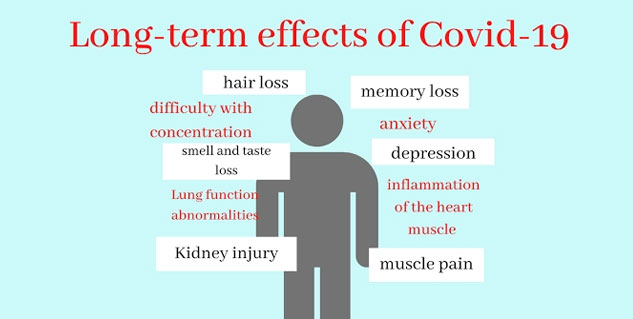
Can COVID-19 cause acute respiratory distress syndrome?
Lung damage in the course of this disease often leads to acute hypoxic respiratory failure and may eventually lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Respiratory failure as a result of COVID-19 can develop very quickly and a small percent of those infected will die because of it.
Can COVID-19 cause lung problems?
COVID-19 can cause lung complications such as pneumonia and, in the most severe cases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS.
Can asymptomatic COVID-19 patients experience lung damage?
Whilst asymptomatic individuals who test positive for COVID-19 may not overtly show any signs of lung damage, new evidence suggests that there may be some subtle changes that occur in such patients, potentially predisposing asymptomatic patients for future health issues and complications in later life.
How does COVID-19 affect the heart and lungs?
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, most commonly affects the lungs but It can also lead to serious heart problems. Lung damage caused by the virus prevents oxygen from reaching the heart muscle, which in turn damages the heart tissue and prevents it from getting oxygen to other tissues.
What are the most common organs affected by COVID-19?
Lungs are the main organs affected by COVID-19; however, the virus can also affect other organs, such as the kidneys, brain, and liver. Lungs are the main organs affected by COVID-19.
Do mild cases of COVID-19 cause scars on the lungs?
“The first is the severity of the coronavirus infection itself — whether the person has a mild case, or a severe one,” Galiatsatos says. Milder cases are less likely to cause lasting scars in the lung tissue.
What are the most common symptoms of the Omicron subvariant BA.5?
According to the University of California Davis Health, the reported symptoms of BA. 5 are similar to previous COVID variants: fever, runny nose, coughing, sore throat, headaches, muscle pain and fatigue.
How long can you be positive with COVID-19?
The CDC previously said people can possibly test positive for up to three months after contracting an infection.
How long do lingering symptoms last after COVID-19?
Symptoms. People with post-COVID conditions (or long COVID) may experience many symptoms. People with post-COVID conditions can have a wide range of symptoms that can last more than four weeks or even months after infection. Sometimes the symptoms can even go away or come back again.
Could mild cases of COVID-19 cause lasting scars in the lung tissue?
“The first is the severity of the coronavirus infection itself — whether the person has a mild case, or a severe one,” Galiatsatos says. Milder cases are less likely to cause lasting scars in the lung tissue.
What does COVID-19 pneumonia cause?
The pneumonia that COVID-19 causes tends to take hold in both lungs. Air sacs in the lungs fill with fluid, limiting their ability to take in oxygen and causing shortness of breath, cough and other symptoms.
What are some of the symptoms of the long haulers from COVID-19?
People with long COVID, or “long-haulers,” are COVID-19 survivors but they have persistent symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, headaches, palpitations, and impairments in mental health and cognition.
What is the treatment for ARDS?
Treatment for ARDS typically aims to increase blood oxygen levels, provide breathing support, and treat the underlying cause of the disease.
What are the symptoms of ARDS?
People typically experience extreme difficulty breathing and shortness of breath. This is often accompanied by rapid, shallow breathing. Low oxygen levels in the blood can also produce a range of other symptoms, including confusion, dizziness, excessive sweating, low blood pressure, and rapid heart rate. Some people may notice that their fingertips, lips, or skin take on a bluish hue, a sign of insufficient blood oxygen level.
What causes ARDS?
Doctors divide the causes of lung injury that lead to ARDS into two broad categories: direct lung injury and indirect lung injury. Direct lung injuries are those that occur in or directly affect the lungs. Indirect injuries are those that occur elsewhere in the body, yet ultimately end up harming the lungs.
How is ARDS diagnosed?
No single test can diagnose ARDS. Instead, doctors will try to assess possible underlying problems that may cause it. In general, a doctor will evaluate a patient’s medical history, perform a physical exam, and order diagnostic tests.
What is the outlook like for someone with ARDS?
ARDS is a serious condition. Even with treatment, about 25% to 40% of people with ARDS do not survive.
What makes Yale Medicine unique in its treatment of ARDS?
At Yale Medicine, the ICU team is very experienced in the use of evidence-based strategies to provide the highest-quality care to ARDS patients. These strategies include lung-protective ventilation, prone positioning, close attention to volume status, and other strategies to give the patient the best chance of recovery. The ICU at Yale also has an established mobility program, called the STEPS-ICU program, in which physical and occupational therapists work with ICU patients to help them start the recovery process as soon as they start to improve.
What is ARDS in medical terms?
Though it has become part of a vocabulary around COVID-19, the term Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome , or ARDS for short, refers to a type of lung damage that can result from a variety of causes, including illness, trauma, or even as a complication that occurs following certain medical procedures. ARDS is a dangerous, potentially fatal respiratory condition in which the lungs sustain a serious, widespread injury that diminishes their ability to provide the body’s organs with enough oxygen. The condition causes fluid to accumulate in the lungs, which in turn reduces blood oxygen to dangerously low levels. ARDS is a medical emergency.
What is ARDS in medical terms?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung condition in which sufficient oxygen does not enter blood. In a recent study it was shown that despite the fact that their lungs heal almost completely, survivors did not regain the physical or psychological health.
How long does lung inflammation last in the ICU?
This severe form of lung inflammation lead to average ICU stays of about four weeks and several months of inpatient treatment. The lungs healed well with time, but disabilities stayed. Disability from muscle and nerve damage, stiff joints, scarring from breathing tubes and post-traumatic stress disorder were part of the aftermath.
Is pulmonary function normal after 5 years?
Pulmonary function was found to be normal or nearly normal in all patients five years after their illness . However, many were reported to carry diagnoses of depression, anxiety or both. Transition to a normal life style appeared to be herculean.
What is ARDS?
ARDS or acute respiratory distress syndrome is a lung condition that causes fluid to build up in the tiny sacs (alveoli) of your lungs. These sacs help in transferring the inhaled oxygen into the blood. Fluid accumulation can reduce the concentration of oxygen in the blood.
What lifestyle changes to make after ARDS?
ARDS is a life-threatening condition. Recovering from ARDS can take a long time.
Schedule time for deep breaths
Shortness of breath and labored breathing are the first signs of ARDS. ARDS can affect your lung functions and reduce the capacity of your lung.
Stop smoking
Smoking introduces various toxic products such as nicotine, carbon monoxide, and tar in your lungs. These toxins irritate and inflame your lung tissues. In an attempt to cleanse your lungs of these toxins, there is an increase in mucus secretion. Gradually, airways get narrow, affecting your breathing.
What is the treatment?
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome is also known as shock lung or Adult Respiratory distress syndrome.
How is the treatment done?
ARDS is a serious lung condition. In this the fluid fills up the air sacs in your lung, due to which the amount of oxygen which is required for the body part to function does not reach to it and which results into organ failure.
Who is eligible for the treatment? (When is the treatment done?)
The treatment of ARDS revolves around providing oxygen to the patient so that he can breathe easily. When the patient is taken to the hospital in case of emergency or other then the doctor may suspect ARDS by couple of tests, or x-rays as he may think fit. After that if ARDS is found, the first step is to cure the breathing problem.
Who is not eligible for the treatment?
The long and complicated procedure to cure ARDS may lead to some side effects. These may be Fatigue, mental illness, bad life quality, memory problems, collapsed lungs, blood clots, infections or emotional problems.
Are there any side effects?
If the person has suffered ARDS or is Recovering, then it is necessary for him to quit smoking, and stop the consumption of alcohol so that no further complications may arise. Else that, he/she should get vaccinated as soon as they face any illness and should follow the doctors instructions well.
What are the post-treatment guidelines?
One cannot set the definite time period to recover from ARDS. The treatment of ARDS can go long for a period of 7 to 14 days or more. But for a young person it is easy to recover from ARDS within a few months, on the other side for an adult person it is difficult to survive or recover ARDS so soon.
How long does it take to recover?
Treatment costs are totally dependent on the place from where you are getting it. The costs associated with ARDS treatment are usually high and starts from the range of RS. 200000.
