How long does a popliteal nerve block take to work?
Popliteal nerve block performed with a short-acting local anesthetic can last between 30 minutes to one hour. When performed with long-acting local anesthetics, the nerve block can provide between 12 to 36 hours of pain relief after foot surgery. What are the risks and complications of a popliteal nerve block?
How long does popliteal fossa block last?
Popliteal fossa block performed with long-acting local anesthetics such as ropivacaine can provide 12–24 hours of analgesia after foot surgery. When used as a sole technique popliteal fossa block provides excellent anesthesia and postoperative analgesia, allows use of a calf tourniquet, and avoids the disadvantages of neuraxial blockade.
How long does a nerve blocker last?
Yet, how long it lasts, depends on various factors. The neural blockade is a method of introducing anesthesia into the whole body or the necessary parts, and when the anesthesia is introduced, it will numb the whole body or apart, which will help in pain control. The method of nerve blocks can be both non-surgical and surgical.
What is popliteal nerve block surgery?
Popliteal nerve block is a type of anesthetic procedure that blocks the sciatic nerve and blocks pain in the lower leg, including foot. The sciatic nerve starts in the lower back (lumbar spine) and travels down the leg, deep inside the thigh.

Broken Bones: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
Broken bones are a common type of injury. Bones are some of the hardest tissues in the body, but they can break when they are...
Picture of Hip Fracture
Hip fractures typically occur as a result of a fall. See a picture of Hip Fracture and learn more about the health topic.
Picture of Fractured Spine
Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe "band-like" pain that radiates around from the back to the side of the body....
Picture of Stress Fracture
A fracture that occurs during the course of normal activity is called a minimal trauma fracture or stress fracture. See a picture...
INTRODUCTION
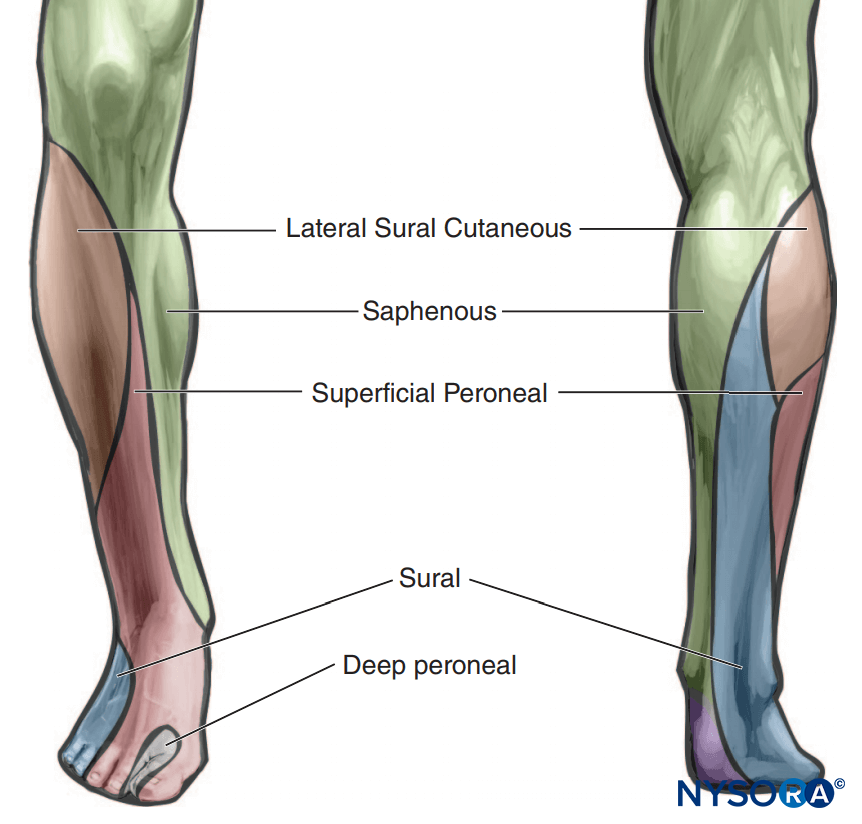
Distal sciatic nerve block (popliteal fossa block) is a very clinically valuable technique that results in anesthesia of the calf, tibia, fibula, ankle, and foot. This section describes the landmarks and nerve stimulator techniques to perform a popliteal sciatic nerve block.
TECHNIQUES
The patient is in the prone position. The foot on the side to be blocked should be positioned so that even the slightest movement of the foot or toes can be easily observed. This is best achieved by allowing the foot to protrude off the edge of the bed.
COMPLICATIONS AND HOW TO AVOID THEM
A retrospective review of 400 continuous popliteal catheters revealed one case of infection (abscess formation requiring surgical drainage) and two cases of nerve injury resulting in paresthesias. Table 4 provides specific instructions on possible complications and how to avoid them.
SUMMARY
Popliteal sciatic block is useful technique to accomplish anesthesia and analgesia for ankle and foot surgery. Posterior and lateral approaches are both highly effective and applicable in numerous clinical scenarios.
How long does it take for a nerve block to wear off?
Usually, it takes about 1 to 4 days for the nerve block to wear off completely if it was done in the nonsurgical method, and if it was done surgically, the nerves must be repaired before they become useless, unless they were destroyed before. The healing time can take different times. Yet, most of the time, surgical nerve blocks are permanent. Sometimes the numbness can even last for 2 weeks.
Why Does A Nerve Block Last That Long?
Once the nerve bundles are injected, the medication starts working, and the impulses will not reach the CNS, which will cut off the sensation of pain. Sometimes one might feel entirely numb, while some might feel the sensation described as “pins and needles”. Yet in the surgical method, certain nerves are cut off or destroyed completely, so that they don’t send out the signals impulses to the central nervous system. Sometimes, the nerve block is the only remedy for the pain, and sometimes the medication injected as a nerve block may be combined with some other anesthetic.
What is neural blockade?
The neural blockade is a method of introducing anesthesia into the whole body or the necessary parts , and when the anesthesia is introduced, it will numb the whole body or apart, which will help in pain control. The method of nerve blocks can be both non-surgical and surgical. Surgical nerve blocks can be messy, but non-surgical methods are much simpler. In the non-surgical method, the specific single nerve or a bundle of nerves are injected with the medication.
How long does a nerve block last?
A nerve block can last anywhere from 12 to 36 hours depending on the type used. Surgical nerve blocks may be permanent. A nerve block may be used as the sole form of pain relief or combined with another type ...
How long does it take to recover from a nerve block?
The entire procedure will likely take less than 30 minutes.
What is the name of the type of nerve block that is injected outside the spinal cord to numb the abdomen?
Nonsurgical nerve blocks. Epidural: Medication is injected outside the spinal cord to numb the abdomen and lower extremities. An epidural is probably the most commonly recognized type of nerve block and is often used during childbirth.
What is a nerve block?
A nerve block, or neural blockade, is a method of producing anesthesia — a loss of feeling used to prevent or control pain. Nerve blocks can be surgical or nonsurgical. Nonsurgical nerve blocks involve injection of a medication around a specific nerve or a bundle of nerves. The medication prevents the nerves’ impulses from reaching ...
What happens to a nerve block?
In a permanent nerve block, the nerve itself is completely destroyed either by deliberating cutting the nerve, removing it , or damaging it with small electrical currents, alcohol, phenol, or cryogenic freezing. However, not all permanent nerve destruction procedures actually end up being permanent.
How long does it take for a nerve to come back after surgery?
In some cases, your doctor may use a nerve catheter to continuously provide numbing medication to the nerve over the course of two to three days following a surgery. A small tube is placed below the skin near the nerve.
Why do doctors use nerve blocks?
Nerve blocks are most commonly used to prevent or control pain. A nerve block is more effective than medications given through an intravenous (IV) line. Your doctor may want to use a nerve block to manage the following types of pain: pain from labor and childbirth. pain before, during, and after a surgery, such as a joint or knee replacement.
