How long can you Live Without vitamin D?
The half-life of vitamin D is 2–3 months so after that time, people tend to get an infection as seen in seasonal flu due to the lack of sunlight in the winter. People who don’t get an infection will become hypercalcemia witin a few years due to unresponsive parathyroid glands resulting in bone dissolution.
How long does excess vitamin D stay in your system?
Vitamin D has a half-life of around 15 days. This means that in about two weeks your circulating levels of vitamin D should drop significantly. Then, over the course of the following 2 weeks, you’ll see them continue to drop.
How long does it take to absorb natural vitamin D?
defficiency of vitamin d is due to excess output of semen 1 drop of sperm contain 50 percent calcium rest of the vitamin d absorb and drain out through urine and other metabolism activitiy absorption of vitamin d is 30 days × 500 mg for regular in...
How long to vitamin D results take to come back?
Your doctor will check your blood work to determine the right course of action. How long it takes for you to feel the effects of your vitamin D supplement depends on the severity of your deficiency. It may take weeks or months. Your doctor will monitor your blood levels of vitamin D and adjust your dose accordingly.
See more
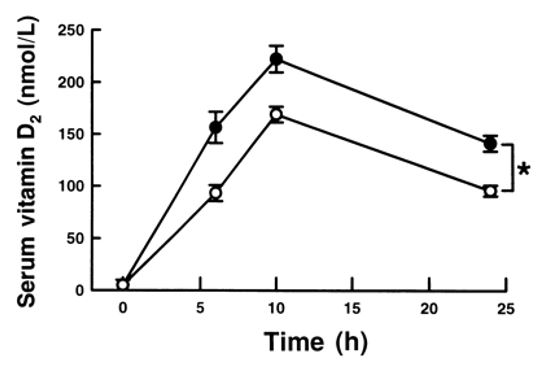
How long vitamin D is stored in the body?
Vitamin D undergoes two hydroxylations in the body for activation. Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3), the active form of vitamin D, has a half-life of about 15 h, while calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3) has a half-life of about 15 days. [63] Vitamin D binds to receptors located throughout the body.
Does vitamin D get stored in the body?
Absolutely not. That's a misconception. Vitamin D is stored in fat. So, if you're a small person and getting large doses, you have less available storage, which means vitamin D goes into your blood and you may absorb too much calcium, creating a toxic situation.
Do you pee out excess vitamin D?
All fat-soluble vitamins can be stored in the fatty tissues of your body if you get more than you need, unlike water-soluble vitamins, which wash out in urine. Excess vitamin D accumulates in the fat and liver, providing you with a vitamin D source to draw on if your stores run low.
How do you flush vitamin D out of your system?
There's no quick fix to flush vitamin D out of your system, but staying hydrated and staying away from more vitamin D and calcium can help lower your levels. Call your doctor right away if you experience confusion, vomiting, dizziness, or other symptoms of a vitamin D overdose.
What does the body do with excess vitamin D?
The main consequence of vitamin D toxicity is a buildup of calcium in your blood (hypercalcemia), which can cause nausea and vomiting, weakness, and frequent urination. Vitamin D toxicity might progress to bone pain and kidney problems, such as the formation of calcium stones.
Is it better to take vitamin D every day or once a week?
Conclusion. Daily vitamin D was more effective than weekly, and monthly administration was the least effective.
How much vitamin D can the body absorb in a day?
4,000 IU per dayThe safe upper limit of intake is set at 4,000 IU per day. Intake in the range of 40,000–100,000 IU per day (10–25 times the recommended upper limit) has been linked with toxicity in humans.
How Long Will Vitamin D Last in Your Body?
Because the previously listed factors affect vitamin D metabolization and any excess amounts are stored in fatty tissue, it's difficult to make broad statements about how long a seasonal dose will last in the body.
Where is vitamin D stored?
Unlike water-soluble vitamins that your body regularly excretes out in urine, vitamin D can be stored in fatty tissue. This means sufficient vitamin D production during part of the year can bank up your levels for when options for sunlight become slim.
How Quickly Will Vitamin D Levels Drop After the Summer?
Often referred to as the “Sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D can be best utilized by your body when it is metabolized by direct exposure to sunlight. While the family of D vitamins ranges from D1 to D5, the most important for you metabolically are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 ( cholecalciferol ).
What Affects Your Vitamin D Levels?
The best way to boost your vitamin D levels is through sunlight. According to Harvard Health, your body can produce as much as 20,000 IU of vitamin D3 during thirty minutes of whole-body sun exposure, depending on the strength of the light in question. Numerous factors affect its metabolism, including the following:
What is the most important vitamin for bone health?
While the family of D vitamins ranges from D1 to D5, the most important for you metabolically are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 ( cholecalciferol ). Vitamin D is integral for many physiological functions, including calcium absorption and bone health. A deficiency in vitamin D can put you at risk for bone diseases, ...
How much vitamin D is needed for skin?
Sunscreen and covered skin will affect vitamin D production rates by as much as 95% , so it's necessary to ensure your skin is uncovered for maximum absorption. If ample sunlight isn't available, 5000 IU per day is considered safe and effective.
How long does it take for vitamin D to increase?
Research from the University of Pennsylvania found that light-skinned participants could experience as much as a 50-fold increase in their blood's vitamin D levels within eight hours of exposure to sunlight, while it took darker-skinned participants over 40 hours to achieve a 30-fold increase in their amounts.
How long does vitamin D stay in the body?
According to a 2010 journal article published by "Pediatric Nephrology," vitamin D-2 and vitamin D-3 circulate in the blood for about 24 hours. Afterward, these vitamins are stored in the fat tissue for approximately two months. When the body needs more vitamins, vitamin D-2 and vitamin D-3 are converted to their active form called 25-hydroxyvitamin D. The active vitamin is then released into the blood. The released 25-hydroxyvitamin D can circulate in the body for approximately three weeks. After the body is replenished, the biologically active form is stored in fat tissues for months; 25-hydroxyvitamin D is released from the storage irregularly depending on the body's need. By the time the physician detects your vitamin D deficiency, your serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D is less than 20ng/ml. At this point, your vitamin D stores have been depleted.
What is the vitamin D in the body?
Foods such as fish oil, various plants and egg yolk also contain vitamin D. Vitamin D-2, or ergosterol, is the form of vitamin D you get from plants.
How does the body make vitamin D?
The ultraviolet B radiations of the sun convert 7-dehydrocholesterol -- a compound found in your skin's epidermis -- to previtamin D-3. The body then converts previtamin D-3 to vitamin D-3 in a process that consumes heat.
What happens if you take too much vitamin D?
Too much supplemental vitamin D can cause weight loss, nausea, weakness, vomiting, constipation and poor appetite. An overdose of the vitamin also raises the level of serum calcium and can cause anomalies in heart rhythms and mental confusion.
What is the purpose of vitamin D?
Image Credit: Siriwachara/iStock/Getty Images. Vitamin D is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that helps the body to metabolize calcium. Humans synthesize vitamin D by exposing the skin to the sun's ultraviolet-B radiations, or by obtaining it from the diet.
What is the serum concentration of 25 hydroxyvitamin D?
By the time the physician detects your vitamin D deficiency, your serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D is less than 20ng/ml. At this point, your vitamin D stores have been depleted. Advertisement.
Where are fat soluble vitamins stored?
Unlike water-soluble vitamins, excess fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the liver and fatty tissue. Most healthy people do not need vitamin D supplements. Moreover, those who may require supplemental amounts of vitamin D should note that too much of it could be toxic.
How long does it take for vitamin D to leave the body?
There is no simple answer as to the amount of time it takes vitamin D to leave the body. However, with the knowledge that calcidiol provides the best indication of vitamin D levels, it can be asserted that in a time period of 15 days, your body will deplete half of its supply of serum vitamin D.
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin present in very few foods and most reliably obtained through sun exposure. When vitamin D is consumed or manufactured through sun exposure, it must be converted into its active form, known as calcitriol.
What is the best vitamin D supplement?
The best dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish, such as salmon, swordfish and tuna, and cod liver oil. Some foods are fortified with vitamin D, including orange juice and milk. According to the National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements, sun exposure for between five and 30 minutes, twice a week, during peak sun hours -- 10 a.m to 2 p.m. -- typically leads to sufficient vitamin D synthesis. Pharmacist Christine Gonzalez notes in "U.S. Pharmacist" magazine that vitamin D3 is the best supplemental form of vitamin D for raising serum levels.
Which vitamin is the best for raising serum levels?
Pharmacist Christine Gonzalez notes in "U.S. Pharmacist" magazine that vitamin D3 is the best supplemental form of vitamin D for raising serum levels.
Does vitamin D decrease with fat?
This does not, however, take into account the body's stored vitamin D. Because vitamin D is very fat-soluble, it is stored throughout the body's fat tissues. Serum levels of the active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, are carefully regulated by the body and do not usually decrease until vitamin D is severely deficient, ...
How does the body make vitamin D?
Your body also makes vitamin D when direct sunlight converts a chemical in your skin into an active form of the vitamin (calciferol). The amount of vitamin D your skin makes depends on many factors, including the time of day, season, latitude and your skin pigmentation.
What are the benefits of vitamin D?
However, more studies are needed to determine the benefits of vitamin D supplementation for cognitive health. Inherited bone disorders. Vitamin D supplements can be used to help treat inherited disorders resulting from an inability to absorb or process vitamin D, such as familial hypophosphatemia. Multiple sclerosis.
What happens if you don't get enough vitamin D?
If you don't get enough vitamin D through sunlight or dietary sources, you might need vitamin D supplements.
Why is vitamin D important for bone?
That's because your body can only absorb calcium, the primary component of bone, when vitamin D is present. Vitamin D also regulates many other cellular functions in your body. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective properties support immune health, muscle function and brain cell activity.
Does vitamin D help with osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis. Studies suggest that people who get enough vitamin D and calcium in their diets can slow bone mineral loss, help prevent osteoporosis and reduce bone fractures. Ask your doctor if you need a calcium and vitamin D supplement to prevent or treat osteoporosis. Psoriasis.
Does Orlistat help with vitamin D?
Orlistat (Xenical, Alli). Taking this weight-loss drug can reduce your absorption of vitamin D.
Is it safe to take vitamin D?
Taken in appropriate doses, vitamin D is generally considered safe. However, taking too much vitamin D in the form of supplements can be harmful. Children age 9 years and older, adults, and pregnant and breastfeeding women who take more than 4,000 IU a day of vitamin D might experience: Nausea and vomiting.
What is the importance of vitamin D?
(The skin actually produces a precursor that is converted into the active form of the vitamin by the liver and kidneys.) Vitamin D is best known for its vital role in bone health. Without this "sunshine vitamin," the body can't absorb the calcium it ingests, so it steals calcium from bones, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Vitamin D also helps maintain normal blood levels of phosphorus, another bone-building mineral.
How much sun do you need for vitamin D?
Under the right circumstances, 10 to 15 minutes of sun on the arms and legs a few times a week can generate nearly all the vitamin D we need. Unfortunately, the "right circumstances" are elusive: the season, the time of day, where you live, cloud cover, and even pollution affect the amount of UVB that reaches your skin.
How many people are in a large randomized trial of vitamin D?
In fact, a large-scale randomized trial that would include 20,000 U.S. women and men has been proposed by Harvard researchers and will be considered for funding by the National Institutes of Health.
How much sun does your body need?
Under the right circumstances, 10 to 15 minutes of sun on the arms and legs a few times a week can generate nearly all the vitamin D we need. Unfortunately, the "right circumstances" are elusive: the season, the time of day, where you live, cloud cover, and even pollution affect the amount of UVB that reaches your skin. What's more, your skin's production of vitamin D is influenced by age (people ages 65 and over generate only one-fourth as much as people in their 20s do), skin color (African Americans have, on average, about half as much vitamin D in their blood as white Americans), and sunscreen use (though experts don't all agree on the extent to which sunscreen interferes with sun-related vitamin D production).
Can you get enough vitamin D from diet?
People who have trouble absorbing dietary fat — such as those with Crohn's disease or celiac disease — can't get enough vitamin D from diet no matter how much they eat (vitamin D requires some dietary fat in the gut for absorption).
Is vitamin D bad for breast cancer?
At a scientific meeting in May 2008, Canadian researchers reported that vitamin D deficiency was linked to poorer outcomes in women with breast cancer.
Is vitamin D good for you?
Vitamin D would be essential if it did nothing else. But researchers have discovered that it's active in many tissues and cells besides bone and controls an enormous number of genes, including some associated with cancers, autoimmune disease, and infection. Hardly a month goes by without news about the risks of vitamin D deficiency or about a potential role for the vitamin in warding off diseases, including breast cancer, multiple sclerosis, and even schizophrenia. In June 2008, a study published in the Archives of Internal Medicine found that low blood levels of vitamin D were associated with a doubled risk of death overall and from cardiovascular causes in women and men (average age 62) referred to a cardiac center for coronary angiography. At a scientific meeting in May 2008, Canadian researchers reported that vitamin D deficiency was linked to poorer outcomes in women with breast cancer. And a large study of aging in the Netherlands published in the May 2008 issue of Archives of General Psychiatry found a relationship between vitamin D deficiency and depression in women and men ages 65 to 95.
How much vitamin D should I take daily?
There are no concerns about toxicity with this dose of supplemental vitamin D (the body will make 10,000 to 20,000 IU per day with moderate exposure to the summer sun).
Why is vitamin D not enough?
Most adults are not getting enough vitamin D, which we need for bone health and, more and more research suggests, for protection against a number of diseases including many types of cancer. We get vitamin D from fortified milk and cereals as well as from eggs, salmon, tuna, mackerel and sardines, and our bodies make it with exposure ...
How much sun exposure is needed for vitamin D?
Holick, whose book, The UV Advantage (iBooks, 2003), provides tables showing how much sun exposure you need for adequate vitamin D synthesis, depending on your skin type, the season of the year, time of day, and where you live . For example, if you’re African-American and live in Boston, New York or San Francisco, adequate exposure equals 25 to 35 minutes a day in the sun between the hours of 11 a.m. and 3 p.m., from June through August. After that time, apply sunscreen.
Does vitamin D work in the winter?
Fortunately, if you get enough sun exposure in the summer, your body will make and store enough D to get you through the winter. This doesn’t work as well if you’re obese because body fat holds onto vitamin D tenaciously and doesn’t release it efficiently,says Michael Holick, Ph.D., M.D., an expert at Boston University.
Does dark skin help with vitamin D?
As you probably know, darkly pigmented skin isn’t efficient at inducing the synthesis of vitamin D. This isn’t a problem in Africa where there’s plenty of sun, but it often translates into vitamin D deficiency in areas of the world where sunshine is more limited. Fortunately, if you get enough sun exposure in the summer, your body will make and store enough D to get you through the winter. This doesn’t work as well if you’re obese because body fat holds onto vitamin D tenaciously and doesn’t release it efficiently,says Michael Holick, Ph.D., M.D., an expert at Boston University.
How long does it take to get enough vitamin D?
Official Answer. It varies. It could take weeks or months, depending on where your levels are now . Vitamin D deficiency and the impact of getting enough or too much of the nutrient have been the topic of numerous studies. That includes variations in how much vitamin D people should take or doctors should prescribe and for how long.
How long does it take for vitamin D to come up?
Therefore, it may take up to 2 to 3 months to bring levels of vitamin D up, depending on how deficient you are. Yet, the recommended daily allowance of vitamin D in the United States is 600 IUs for adults up to age 70 and 800 IUs after age 70.
How to increase vitamin D2 intake?
In addition to taking supplements of vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) or D3 (cholecalciferol), you can increase your vitamin intake by eating a small number of foods that naturally contain it, eating fortified foods or through sunlight. Consuming vitamin D with food that contains fat aids in absorption of the nutrient.
What is the effect of vitamin D on the body?
Foods that naturally contain vitamin D are: Foods commonly fortified with vitamin D include: Excess amounts of vitamin D can be toxic, result ing in renal failure, calcification of soft tissues, cardiac arrhythmias and death.
Why is calcium important for the body?
The nutrient is considered to be important for a variety of health reasons, including: Maintaining strong bones. Helping the body absorb calcium. Helping nerves carry messages between the brain and body parts. Reducing inflammation.
Do people with vitamin D deficiency need more?
People at high risk of vitamin D deficiency may need more, but how much and for how long can be determined by your doctor. The National Institutes of Health acknowledges that even with these guidelines, there is no international agreement on vitamin D intake, and some professional organizations also disagree.
Is vitamin D bad for you?
Excess amounts of vitamin D can be toxic, resulting in renal failure, calcification of soft tissues, cardiac arrhythmias and death.