What is intubation and how does it work?
Intubation is a process where a healthcare provider inserts a tube through a person’s mouth or nose, then down into their trachea (airway/windpipe). The tube keeps the trachea open so that air can get through. The tube can connect to a machine that delivers air or oxygen. Intubation is also called tracheal intubation or endotracheal intubation.
What is a nasotracheal intubation?
In some cases, if the mouth or throat is being operated upon or has been injured, the breathing tube is threaded through the nose instead of the mouth, which is called a nasal intubation. The nasotracheal tube (NT) goes into the nose, down the back of the throat, and into the upper airway.
How long can a breathing tube stay in a patient?
If a breathing tube/endotracheal tube stays in for >14 days, there are usually unusual circumstances requiring the breathing tube/endotracheal tube stay in for longer than clinically recommended such as. Extubation(=removal of the breathing tube) is close and only a few more days away.
Is intubation the same for adults and children?
Pediatric Intubation The process of intubation is the same with adults and children, aside from the size of the equipment that is used during the process. A small child requires a much smaller tube than an adult, and placing the tube may require a higher degree of precision because the airway is so much smaller.

How far down does intubation tube go?
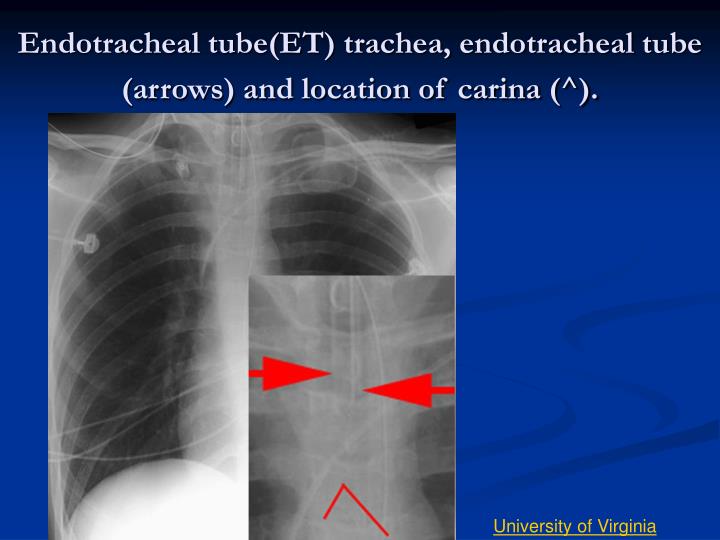
Most of the anaesthesia textbooks recommend depth of placement of ET to be 21 cm and 23 cm in adult females and males, respectively, from central incisors. [5,6] It is suggested that the tip of ET should be at least 4 cm from the carina, or the proximal part of the cuff should be 1.5 to 2.5 cm from the vocal cords.
What is the size of intubation?
SIZES. The size of an ETT signifies the inner diameter of its lumen in millimeters. Available sizes range from 2.0 to 12.0 mm in 0.5 mm increments. For oral intubations, a 7.0-7.5 ETT is generally appropriate for an average woman and a 7.5-8.5 ETT for an average man.
Is being intubated the same as being on a ventilator?
Being intubated and being on a ventilator are related, but they're not exactly the same. Intubation is the process of inserting an endotracheal tube (ETT) into the airway (windpipe). The tube is then hooked up to a device that delivers air.
How long can a person safely be intubated?
Some people can be intubated for a day or two; others can be intubated for weeks, but “less time is better,” says Dr. Casciari. The longer a person is intubated, the higher the risk of complications, like airway narrowing or the lungs becoming more reliant on oxygen supplementation.
Why are patients intubated during surgery?
Why You Might Need It. The drugs that put you to “sleep” during surgery (general anesthesia) may also hold down your breathing. Intubation lets a machine breathe for you. That's why your anesthesiologist (the doctor who puts you to sleep for surgery) might intubate you.
How are intubation tubes measured?
Find the size marking on the ET tube. The outside diameter (OD) and internal diameter (ID) of an ET tube should be marked on the side of the tube. Typical ID sizes range from 3.5 mm for small infants to 8.5 mm for adult males.
Is intubation considered life support?
Tracheal intubation (TI) is commonly performed in the setting of respiratory failure and shock, and is one of the most commonly performed procedures in the intensive care unit (ICU). It is an essential life-saving intervention; however, complications during airway management in such patients may precipitate a crisis.
Is it painful to be intubated?
Conclusion: Being intubated can be painful and traumatic despite administration of sedatives and analgesics. Sedation may mask uncontrolled pain for intubated patients and prevent them from communicating this condition to a nurse.
How does it feel to be intubated?
The main findings of this study showed that undergoing awake intubation was an acceptable experience for most patients, whereas others experienced it as being painful and terrifying. The application of local anaesthetic evoked feelings of discomfort, coughing, and suffocation.
What are the side effects of being intubated?
Potential side effects of intubation include:damage to the vocal cords.bleeding.infection.tearing or puncturing of tissue in the chest cavity that can lead to lung collapse.injury to throat or trachea.damage to dental work or injury to teeth.fluid buildup.aspiration.
Can intubated patients be awake?
Awake Endotracheal Intubation. Intubation may be attempted in an awake patient who is not in respiratory distress. The awake patient has the ability to protect his or her airway against pulmonary aspiration and maintain spontaneous ventilations.
How long does it take for throat to heal after intubation?
Answer: Intubation It is not uncommon for patients to have a mild sore throat for a day or two after surgery due to the breathing tube used during the procedure. Some patients experience no soreness at all. It is usually relieved with simple home remedies such as hot tea and honey or water.
How do you calculate ETT size?
Pediatric Endotracheal Tube SizeUncuffed endotracheal tube size (mm ID) = (age in years/4) + 4.Cuffed endotracheal tube size (mm ID) = (age in years/4) + 3.
What are the two types of intubation?
Orotracheal intubation- This is a type of intubation in which the tube goes in through the oral cavity to the trachea. Nasotracheal intubation- This is a type of intubation in which the tube goes in through the nasal cavity to the trachea.
What are three types of intubation tubes?
Types of endotracheal tubes include oral or nasal, cuffed or uncuffed, preformed (e.g. RAE (Ring, Adair, and Elwyn) tube), reinforced tubes, and double-lumen endobronchial tubes.
What equipment is needed to intubate a patient?
Equipment includes suction, appropriate-sized bag and mask, oxygen source, appropriate size endotracheal tubes including a size larger and one size smaller, laryngoscope and appropriate-sized laryngoscope blades (including one size smaller and one size larger), endotracheal tube-securing equipment (tape or other), ...
What happens during endotracheal intubation?
Most intubation procedures happen in the hospital. Sometimes emergency medical services (EMS) personnel intubate people outside the hospital setting.
How is the tracheal tube removed during extubation?
When the healthcare providers decide it is safe to remove the tube, they will remove it. This is a simple process called extubation. They will:
What are the risks of intubation?
Intubation is a common and generally safe procedure that can help save a person’s life. Most people recover from it in a few hours or days, but some rare complications can occur:
Why would a person need to be intubated?
Intubation is necessary when your airway is blocked or damaged or you can’t breathe spontaneously. Some common conditions that can lead to intubation include:
What is the difference between endotracheal intubation and nasotracheal intub?
Endotracheal intubation is typically used in emergencies but also supports breathing in people with severe breathing problems due to disease or trauma. Nasotracheal intubation is more commonly used to deliver anes thesia but can also protect the airways if there is a risk of obstruction.
What are the risks of intubation?
While most surgery is very low risk, and intubation is equally low risk, there are some potential issues that can arise particularly when a patient must remain on the ventilator for an extended period of time. Common risks include: 1 Trauma to the teeth, mouth, tongue, and/or larynx 2 Accidental intubation in the esophagus (food tube) instead of the trachea (air tube) 3 Trauma to the trachea 4 Bleeding 5 Inability to be weaned from the ventilator, requiring tracheostomy. 6 Aspirating (inhaling) vomit, saliva or other fluids while intubated 7 Pneumonia, if aspiration occurs 8 Sore throat 9 Hoarseness 10 Erosion of soft tissue (with prolonged intubation)
How long after intubation can you feed a ventilator patient?
If a patient is expected to be ventilator-dependent for two or more days, feeding will typically be started a day or two after intubation. 6 .
Why is it so hard to intubate a baby?
Newborns can be especially difficult to intubate, not only because of their smaller size but because their tongues are proportionally larger and the passage into the windpipe is proportionately longer and less flexible. Because of this, it often takes several attempts before intubation is successful. 6
What are the risks of a tracheostomy?
Common risks include: Trauma to the teeth, mouth, tongue, and/or larynx. Accidental intubation in the esophagus (food tube) instead of the trachea (air tube) Trauma to the trachea. Bleeding. Inability to be weaned from the ventilator, requiring tracheostomy.
Why do people need to be intubated?
Intubation is done because the patient cannot maintain their airway, cannot breathe on their own without assistance, or both. They may be going under anesthesia and will be unable to breathe on their own during surgery, or they may be too sick or injured to provide enough oxygen to the body without assistance.
Why do we need to intubate?
Intubation is the process of inserting a tube into the mouth or nose and then into the airway to help move air in and out of the lungs. There are several reasons why it may be performed, but it is mainly used to support breathing. 1
What is the procedure called when you can't breathe?
Intubation is a procedure that's used when you can't breathe on your own. Your doctor puts a tube down your throat and into your windpipe to make it easier to get air into and out of your lungs. A machine called a ventilator pumps in air with extra oxygen.
What happens when you blow up a tube?
This seals off much of your airway from your stomach and keeps food from getting into your lungs. But air can still flow through the tube.
Why do doctors intubate you?
A doctor may intubate you if you need emergency surgery that calls for general anesthesia.
Can an intubation cause a chest X-ray?
Complications. It's rare for intubation to cause problems, but it can happen. The scope can damage your teeth or cut the inside of your mouth.
Can food from your stomach get into your lungs?
Food from your stomach could get into your lungs (aspiration) if you vomit, or if it flows backward from your stomach. To keep this from happening, the tube has an air bladder that balloons up to seal off your airway from your stomach.
Can you knock out a tube before it's put in?
What to Expect. Except in rare cases, your doctor will give you drugs to partly or completely knock you out before they put the tube in. They also typically give you a drug to paralyze your airway. This is so your body doesn’t fight against the insertion by gagging or other reflexes.
Can a scope hurt your teeth?
If you've just eaten, there's a risk that the food can be pulled into your lungs. There's a greater chance that the scope will damage your teeth if they're in poor shape. If you smoke, have a lung disease such as COPD, have a neck or spine injury, or you're overweight, it can make intubation and recovery harder.
What is the process of intubation?
This process is carried out when a person is given under anesthesia while performing surgery or in time of emergencies like if a person is severely ill or wounded and faces difficultly breathing.
How long does it take for hoarseness to go away?
Transient hoarseness is a popular illness that transpires in one-third of the intubated patients. But it gets resolved automatically within 1 week. Whereas persistent hoarseness is a rare condition and is produced by granuloma inside your vocal cord. Its risk factors require a longer span of intubation for older age groups, and female patients. For females, the use of smaller-sized tubes is recommended to lessen the frequency of persistent hoarseness.
Why do we need to intubate?
Are you aware what is the purpose of intubation? Intubation is performed because the patient won’t be able to sustain their breath on their own without support or help. For that reason, they need to go through anesthesia during surgery or illness, or pregnancy. Lack of oxygen in their body causes breathing problems.
Why do people sleep during surgery?
A patient needs to sleep during surgery so they’re given anesthesia as it holds down your breath. In intubation, a machine is placed for breathing. During an injury or sickness, it’s difficult to breathe. Through breathing every cell of your body gets oxygen. If you don’t get adequate oxygen then you can pass out. It can also lead to brain injury. Also, ventilation helps you to gently blow out.
How long is an extended intubation?
The extended intubation period refers to surpassing 7 days. From clinical studies, it has been reported that lengthened intubation is a danger for many complexities. Also, keep in mind that anesthesia drugs aim at paralyzing the muscles of your body which includes the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the portion that makes it difficult to grab a breath in the absence of a ventilator.
What is fiber optic intubation?
Fiber-optic intubation: In this process, the physician injects a tube into your throat. It inspects your throat or assists endotracheal intubation when the patient is unable to extend or move their head.
How long does it take to ventilate a patient?
Prolonged ventilation is expensive but it is required for 14 to 21 days depending on the patient’s condition. After that, the discharge timing is dependent on the patient’s psychological and social balance.
What happens if a critically ill person is requiring ongoing mechanical ventilation?
Usually what happens if your critically ill loved one is requiring ongoing mechanical ventilation and it is foreseeable that Extubation or removal of the breathing tube is not on the horizon due to the critical illness of your loved one , normally a formation of a Tracheostomy is the next step.
How long does a breathing tube stay in the throat?
Now, as a rule of thumb, a Breathing Tube or an endotracheal tube is usually staying in your loved one’s throat or Larynx for up to two weeks at the most, unless there are special and rare circumstances. I’ll come to that later.
What happens if you are ventilated and on a tube?
If your loved one is mechanically ventilated and on a breathing tube/endotracheal tube they will also be in an induced coma.
What is the name of the swelling in the upper airway?
Upper airway swelling is present also known as laryngeal oedema. It basically means that the throat/larynx is swollen and if the breathing tube or endotracheal tube would be removed it would cause a stridor and your loved one wouldn’t be able to breathe.
Where is a tracheostomy tube inserted?
A Tracheostomy is another tube that is permanently or temporarily inserted into your loved one’s neck into the windpipe going directly into the lungs. This Tracheostomy tube is making it a lot easier for your loved one to be. mechanically ventilated as the tube is no longer in the mouth.
Is a tracheostomy tube safer than a breathing tube?
generally looked after, as a Tracheostomy is much easier for your loved one to tolerate and is also less risky than a breathing tube or an endotracheal tube. Furthermore, a Tracheostomy tube can stay in infinitely and in fact some People have a life long Tracheostomy tube in place and they can live with it independently.
Do critically ill patients need ventilation?
The reality is that most critically ill Patients in Intensive Care only require mechanical ventilation with Ventilators (Breathing Machine) with a Breathing Tube or an endotracheal tube for a limited period of time. Most mechanically ventilated Patients in Intensive Care only require ventilation with a breathing tube or an endotracheal tube ...
What is the process of inserting a tube called?
The process of inserting the tube is called endotracheal intubation . There are many reasons why an endotracheal tube may be placed, including surgery with a general anesthetic, trauma, or serious illness. Learn about the procedure, potential risks and complications, and what you might expect. Sister Sarah / Getty Images.
What is the endotracheal tube?
Updated on January 03, 2020. An endotracheal tube is a flexible plastic tube that is placed through the mouth into the trachea (windpipe) to help a patient breathe. The endotracheal tube is then connected to a ventilator, which delivers oxygen to the lungs.
What is the best way to support breathing?
To support breathing: If someone is having difficulty breathing due to pneumonia, a pneumothorax (collapse of a lung), respiratory failure or impending respiratory failure, heart failure, or unconsciousness due to an overdose, stroke, or brain injury, an endotracheal tube may be placed to support breathing.
Why is an endotracheal tube placed?
An endotracheal tube is placed when a patient is unable to breathe on their own, when it is necessary to sedate and "rest" someone who is very ill, or to protect the airway. The tube maintains the airway so that air can pass into and out of the lungs.
What size tube do you need for a newborn?
Newborns often require a 3.0 mm to 3.5 mm tube, with a 2.5 to 3.0 mm tube used for premature infants. In an emergency, doctors often guess at the right size, while in the operating room the size is often chosen based on age and body weight.
How many intubations are there in dental injuries?
Dental injuries (particularly to the upper incisors) occur in around one in 3000 intubations. Pneumothorax (collapse of a lung): If the endotracheal tube is advanced too far such that it only enters one bronchus (and thus ventilates only one lung), inadequate ventilation may occur or collapse of one lung.
How long should you wait to eat before a piercing?
People should not eat or drink before surgery for at least six hours to reduce the risk of aspiration during intubation.
How Is the Tube Removed?
Once the doctor is sure that it’s safe to remove the ETT, it's quite simple to take it out.
Why do you need an ETT tube?
The drugs that put you to sleep during surgery ( general anesthesia) may also hold down your breathing. That’s why you sometimes need the ETT in the first place. But the tube is uncomfortable, and you don't need it if you can breathe on your own. This typically happens as you start to wake up.
What is the process of getting air out of your lungs called?
This helps to get air into and out of your lungs. The process is called intubation. Extubation is taking that tube out.
How long does an ETT stay in place?
If you have an ETT because you're sick or hurt, it may be in place for as long as a couple of weeks. You may be awake as you use it.
Why can't you breathe on your own?
That’s because there can be serious results if you can’t breathe on your own, including brain damage and death.
What happens when you wake up and cough?
This typically happens as you start to wake up. If you're alert, can cough strongly, and don't have a lot of mucus in your lungs, your doctor will plan for extubation. If needed, they'll give you a drug to reverse the effects of any drugs they used to paralyze your muscles.
