
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction | |
|---|---|---|
| Time taken | Asexual reproduction is completed in a very short period of time. | Sexual reproduction can take several months to complete. |
| Number of offspring | Two or more | One or more |
What are five organisms that reproduce asexually?
What are five organisms that reproduce asexually?
- Bacteria and Binary Fission. Many single-celled organisms rely on binary fission to reproduce themselves.
- Fragmentation and Blackworms.
- Budding and Hydras.
- Parthenogenesis and Copperheads.
- Vegetative Propagation and Strawberries.
What animals reproduce asexually?
What mammals can reproduce asexually?
- Marbled Crab. Marmorkrebs, which look like shrimp with tusks, are an asexual form of slough crayfish who live in Florida and southern Georgia, but they don’t quite belong there.
- Whiptail Lizard. …
- Komodo Dragon. …
- Captive Sharks. …
- Ageless Hydra. …
- Cloning Wasps.
What are facts about asexual reproduction?
what asexual reproduction in plants?
- Even without partners, female Komodo dragon can produce eggs. ...
- Paramecia reproduce through binary fission with means the macronucleus splits, creating micronuclei which then undergo mitosis. ...
- Jellyfish development is divided in two phases: mobile and stationary. ...
- Once per year all corals in the reef release gametes (reproductive cells) at the same time. ...
What animals are asexual?
The most commonly known animals known to reproduce asexually are invertebrate animals such as aphids, flatworms, hydra, Bdelloid rotifers, ants, bees, parasitic wasps, coral and starfish.
Does asexual reproduce quickly?
Asexual reproduction occurs quickly, but because all of the offspring have the same genetic information, individuals are more susceptible to disease. Budding and fragmentation are not the same thing.
Is asexual reproduction longer or shorter?
Characteristics of Asexual Reproduction This process of reproduction occurs in a very short time. The organisms multiply and grow rapidly. The offspring is genetically similar.
Does asexual reproduction take less time?
Asexual reproduction can be very rapid. This is an advantage for many organisms. It allows them to crowd out other organisms that reproduce more slowly. Bacteria, for example, may divide several times per hour.
How is asexual reproduction done?
Asexual reproduction occurs by cell division during mitosis to produce two or more genetically identical offspring. Sexual reproduction occurs by the release of haploid gametes (e.g., sperm and egg cells) that fuse to produce a zygote with genetic characteristics contributed by both of the parent organisms.
Do Asexuals live longer?
Initially, mean lifespans for asexual and sexual females were similar, but asexual females increased lifespan and fecundity, whereas these traits changed little for sexual females.
What animal is asexual?
Animals that reproduce asexually include planarians, many annelid worms including polychaetes and some oligochaetes, turbellarians and sea stars. Many fungi and plants reproduce asexually.
Why does asexual reproduction happen more quickly?
Both methods have advantages and disadvantages. Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent because the offspring are all clones of the original parent. A single individual can produce offspring asexually and large numbers of offspring can be produced quickly.
Why is asexual propagation faster?
About this Research Topic Asexually reproducing organisms spend fewer resources for the same reproductive output, meaning their populations grow and expand faster than sexually reproducing ones.
What are the pros and cons of asexual?
Advantages and Disadvantages Of Asexual ReproductionAdvantages Of Asexual ReproductionDisadvantages Of Asexual ReproductionAll the positive traits of the species are transferred to future generations.There is a huge competition for food and space among the species.The organisms mature rapidly.They have short lifespans.4 more rows
What is asexual reproduction called?
0:323:43What Is Asexual Reproduction | Genetics | Biology | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou may already know that many plants use asexual reproduction like spider plants. But do you knowMoreYou may already know that many plants use asexual reproduction like spider plants. But do you know that bacteria reproduce asexually in a process called binary fission.
What are 5 types of asexual reproduction?
Common forms of asexual reproduction include: budding, gemmules, fragmentation, regeneration, binary fission, and parthenogenesis.
Which is the simplest type of reproduction?
Asexual reproduction, the simplest and most primitive method of reproduction, involves a single parent and produces a clone, an organism that is genetically identical to the parent. Haploid gametes are not involved in asexual reproduction.
Which is correct about asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction does not involve sex cells or fertilisation . Only one parent is required, unlike sexual reproduction which needs two parents. Since there is only one parent, there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information.
What is an advantage of asexual reproduction?
The advantages of asexual reproduction include: the population can increase rapidly when the conditions are favourable. only one parent is needed. it is more time and energy efficient as you don't need a mate. it is faster than sexual reproduction.
Which is a disadvantage of asexual reproduction?
The disadvantage of asexual reproduction is that it produces identical progeny and does not produce genetic variation. Due to this reason, the population becomes more vulnerable to any disease or environmental stress.
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which only one parent is involved to reproduce offspring. In asexual reproduction, the offsprings...
What is the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction?
Sexual Asexual Two parents take part Single parent Variation occurs in offspring Offspring are genetically identical to each other and to their pa...
How sexual reproduction is advantageous over asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction brings variations in the population. When gametes (reproductive cells) from two individuals meet, genes from two individuals ar...
Justify the statement ‘Vegetative reproduction is also a type of asexual reproduction.
The formation of new plants from the vegetative parts of the plant called vegetative propagules is called vegetative propagation or reproduction....
What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
The advantages of asexual reproduction are following: Rapid Populating: Asexual reproduction gives the ability to produce large quantities of offs...
What is asexual reproduction and give one example?
Asexual reproduction is a type where a single parent is involved in the production of offspring. For example, in yeast, the parent cell produces a...
What are 3 asexual reproduction examples?
The three asexual reproduction examples are budding, fragmentation and fission.
What are the two advantages of asexual reproduction?
The two advantages of asexual reproduction are: 1. A single parent is required. 2. Seedless plants can be produced by vegetative propagation.
What is fission in asexual reproduction?
Fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which unicellular organisms divide into two or more than two, small, nearly equal-sized daughter indiv...
Name some plants that reproduce asexually
The plants that reproduce asexually are potato, onion, rose, ginger, etc.
What is asexual reproduction?
Not to be confused with Asexuality. Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent.
What is the most common form of asexual reproduction?
In vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited.
Why is asexual reproduction beneficial?
Current hypotheses suggest that asexual reproduction may have short term benefits when rapid population growth is important or in stable environments, while sexual reproduction offers a net advantage by allowing more rapid generation of genetic diversity, allowing adaptation to changing environments.
How long has the stick insect been asexual?
Molecular evidence strongly suggests that several species of the stick insect genus Timema have used only asexual (parthenogenetic) reproduction for millions of years, the longest period known for any insect.
How do monogonont rotifers reproduce?
Monogonont rotifers of the genus Brachionus reproduce via cyclical parthenogenesis: at low population densities females produce asexually and at higher densities a chemical cue accumulates and induces the transition to sexual reproduction. Many protists and fungi alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes ( Archaea and Bacteria) reproduce asexually through binary fission, in which the parent organism divides in two to produce two genetically identical daughter organisms. Eukaryotes (such as protists and unicellular fungi) may reproduce in a functionally similar manner by mitosis; most of these are also capable of sexual reproduction.
Which organisms are asexually reproduced?
Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and bacteria.
What is the process of asexual reproduction?
Spore formation. In this method of asexual reproduction, a small body called spores is formed. Usually, this is seen in kingdom fungi and some algae. These are covered by the hard protective coat that protects the cell from unfavourable conditions such as high temperature, drought, etc.
What are the different types of asexual reproduction?
The different modes or types of asexual reproduction in animals include fission, budding, spore formation, regeneration and fragmentation.
What is Vegetative Propagation?
The production of new plants from different vegetative parts of the plant body such as roots, stems, bulbs, leaves, tubers, etc., is called vegetative propagation.
Why is vegetative reproduction beneficial?
Vegetative reproduction is a very ideal way to propagate a greater number of plants.
What is a fission?
Fission. It is a type of asexual reproduction in which unicellular organism divide into two or more than two, small, nearly equal-sized daughter individuals.
How do plants reproduce asexually?
Plants reproduce asexually in many different ways. Even some plants reproduce by spore formation (Ferns and mosses), which is also seen in animals. We will discuss about a special mode of asexual reproduction in plants vegetative propagation.
Which type of reproduction only has DNA from one parent?
An organism that is born through asexual reproduction only has DNA from one parent.
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual Reproduction Definition. Asexual reproduction occurs when an organism makes more of itself without exchanging genetic information with another organism through sex. In sexually reproducing organisms, the genomes of two parents are combined to create offspring with unique genetic profiles. This is beneficial to the population ...
Why is asexual reproduction faster than sexual reproduction?
Only offspring that are genetically identical to the parent can be produced in this way: nurturing the creation of a new organism whose tissue is different from the parents’ tissue takes more time, energy, and resources. This ability to simply split in two is one reason why asexual reproduction is faster than sexual reproduction.
Why is asexual reproduction important?
Asexual reproduction, which can often be accomplished just by having part of the parent organism split off and take on a life of its own, takes fewer resources than nurturing a new baby organism.
How does asexual reproduction promote diversity?
Some organisms that practice asexual reproduction can exchange genetic information to promote diversity using forms of horizontal gene transfer such as bacteria who use plasmids to pass around small bits of DNA. However this method results in fewer unique genotypes than sexual reproduction.
What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction?
Because members of an asexually reproducing population are genetically identical except for rare mutants, they are all susceptible to the same diseases, nutrition deficits, and other types of environmental hardships.
What is the process of reproduction of normally sexual organisms without the need for fertilization?
Agamenogenesis. Agamenogenesis is the reproduction of normally sexual organisms without the need for fertilization. There are several ways in which this can happen. In parthenogenesis, an unfertilized egg begins to develop into a new organism, which by necessity possesses only genes from its mother.
Which is correct: Asexual reproduction or asexual reproduction?
Answer to Question #3. D is correct. Asexual reproduction is the only means of reproduction for prokaryotes, but some eukaryotes, including many plants, many sea creatures, and some land animals are also capable of reproducing asexually.
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is the production of new individuals from a single parent. This type of reproduction is generally observed in single-celled organisms. Here no fusion of gametes is involved and a single parent divides into two or more daughter cells. The offsprings produced are genetically and physically identical to the parent and are known as clones.
What are the characteristics of asexual reproduction?
Following are the important features of asexual reproduction: 1 No formation of gametes or fertilization takes place. 2 Only one parent is involved. 3 The process occurs in very less time. 4 The offsprings produced are exact copies of the parent, there is no variation. 5 The growth of the offspring is rapid.
What type of reproduction is Planaria?
This type of asexual reproduction is exhibited by Planaria. In this, the parent body breaks into several pieces where each piece grows into a new individual. The detachment of the body parts is intentional.
What is binary fission?
Binary Fission. In this type of reproduction, parent cell divides into two equal parts each containing a nucleus. These are called daughter cells. The daughter cells are genetically and physically similar to the parent cell. This type of asexual reproduction can be seen in organisms such as amoeba, bacteria, euglena, etc.
What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction?
Since the offspring is an exact copy of the parent, any negative mutation will also pass on to the offspring. It takes place in various environments. There is limited diversity within life forms. It allows for the survival of species.
How many parents are involved in reproduction?
Only one parent is involved. The process occurs in very less time. The offsprings produced are exact copies of the parent, there is no variation. The growth of the offspring is rapid. Also Read: Reproduction.
Is parthenogenesis asexual or asexual?
Parthenogenesis is considered to be a form of asexual reproduction because the process does not require any male gametes for the production of the offspring. The embryos develop from unfertilized eggs. It can more accurately be termed as an “incomplete form of sexual reproduction. Explore Your Knowledge!
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction in echinoderms usually involves the division of the body into two or more parts ( fragment ation) and the regeneration of missing body parts. Fragmentation is a common method of reproduction used by some species of asteroids, ophiuroids, and holothurians, and in some of these species sexual reproduction is ...
How long does it take for an echinoderm to metamorphose?
Among holothurians, echinoids, and ophiuroids, the larvae may metamorphose as they float, and the young then sink to the seafloor; among crinoids and asteroids, however, the larvae firmly attach to the seafloor prior to metamorphosis. The average life span of echinoderms is about four years, and some species may live as long as eight or 10.
How long are holothurians?
Although most larval stages are small, often less than 1 mm (0.04 inch) in length, some holothurians are known to be 15 mm (0.59 inch) long in the larval stage , and the length of bipinnaria larvae of some starfishes may exceed 25 mm (0.98 inch).
How many arms does an echinoid larva have?
The echinoid larva (echinopluteus) and the ophiuroid larva (ophiopluteus) usually have four pairs of arms but may have fewer or more.
What is the term for the development of an egg?
Development involving an egg, planktonic larval stages, and a juvenile form is termed indirect development. Echinoderm development in which large eggs with abundant yolk transform into juvenile echinoderms without passing through a larval stage is termed direct development.
When do Japanese feather stars spawn?
In the case of one Japanese feather star (Crinoidea), spawning is correlated with phases of the Moon and takes place during early October when the Moon is in the first or last quarter. Many echinoderms aggregate before spawning, thus increasing the probability of fertilization of eggs.
Do asteroids regenerate?
Successful regeneration requires that certain body parts be present in the lost pieces; for example, many asteroids and ophiuroids can regenerate a lost portion only if some part of the disk is present . In sea cucumbers, which divide transversely, considerable reorganization of tissues occurs in both regenerating parts.
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and bacteria. Many plants and fungi sometimes reproduce asexually. Click here to learn more concerning the contents of asexual reproduction amongst various organisms . Head lice are not known to reproduce asexually (or through parthenogenesis ), ...
How Do Lice Reproduce?
As you can imagine, we receive lots of questions about head lice. Recently, we were asked, “Do lice reproduce sexually or asexually?” and it is a great question. So, let’s dive into it!
When Do Lice Lay Eggs?
Lice are most active in all ways, including laying eggs, at night. Head lice are highly light sensitive to help them hide from detection in the hair, and they scatter so quickly when the hair is parted under bright light that you’ll almost never spot an adult louse until the infestation gets pretty advanced. This is also why people with lice tend to experience more itching at night, because the lice are actively crawling and biting most in the dark.
How Quickly Do Lice Lay Eggs?
Lice will mate (successfully) immediately upon moulting their last nymph stage exoskeleton, so an average of 10 days after hatching from an egg. After mating, the female louse lays 3 to 5 eggs almost immediately, within just a few hours of conception.
How Long Until Lice Eggs Hatch?
It takes7-10 days for the nit to hatch after being laid, but it is very important to note that for the first few days, the new nit will be microscopic inside of its clear eggshell, so it is often impossible to see a nit immediately after it is laid. By the time the nits are readily observed on the hair, they are getting closer to being ready to hatch.
How Long Do Head Lice Take To Grow?
These are so similar in appearance that you would probably need a microscope to be able to tell the difference by sight, and honestly, it’s not very important to identify what stage each individual louse is in, since at any given time you’ll probably have lice at most or all stages of life on one head ; the life cycle stage of the few lice you are examining won’t reliably tell you how long ago you caught lice. If you find a louse that is shorter and smaller than the others, it is probably a nymph.
How many eggs can a female lice lay?
An adult female louse can lay about 10 eggs per day. An adult female louse will be in her reproductive life phase for about 1-2 weeks, with an average of 10 days. So how many eggs can lice lay in a lifetime? About 100+ per female louse.
What is the mode of asexual reproduction?
However, there is a mode of asexual reproduction which occurs naturally in a woman’s body which is known as the monozygotic twinning.
How do humans reproduce?
But there are cases where humans reproduce through asexual modes. Asexual reproduction in humans is carried out without the immediate use of fertilization of the male and female sex cells (the sperm and egg). It is carried out by fusing a few parts of human sperm, embryo, the egg or unnatural genes to reproduce a new human fetus which further ...
How many parents can produce one embryo?
The concept is that three parents can be used to produce one single embryo if the mitochondria, which are usually found in the female egg, is replaced by the mitochondria from the third party in case of any defect. Get to know more about asexual reproduction in humans and related topics, by registering at BYJU’S.
How is IVF carried out?
It is carried out by fusing a few parts of human sperm, embryo, the egg or unnatural genes to reproduce a new human fetus which further undergoes maturation and development depending upon the medical procedures. It is usually carried out in case of infertility using the assisted reproductive treatment such as the IVF (Invitro fertilization). ...

Overview
Types of asexual reproduction
Prokaryotes (Archaea and Bacteria) reproduce asexually through binary fission, in which the parent organism divides in two to produce two genetically identical daughter organisms. Eukaryotes (such as protists and unicellular fungi) may reproduce in a functionally similar manner by mitosis; most of these are also capable of sexual reproduction.
Alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction
Some species can alternate between sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as heterogamy, depending on many conditions. Alternation is observed in several rotifer species (cyclical parthenogenesis e.g. in Brachionus species) and a few types of insects.
One example of this is aphids which can engage in heterogony. In this system, females are born pregnant and produce only female offspring. This cycle allows them to reproduce very quickly. H…
Inheritance in asexual species
In the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus asexual reproduction (obligate parthenogenesis) can be inherited by a recessive allele, which leads to loss of sexual reproduction in homozygous offspring. Inheritance of asexual reproduction by a single recessive locus has also been found in the parasitoid wasp Lysiphlebus fabarum.
Examples in animals
Asexual reproduction is found in nearly half of the animal phyla. Parthenogenesis occurs in the hammerhead shark and the blacktip shark. In both cases, the sharks had reached sexual maturity in captivity in the absence of males, and in both cases the offspring were shown to be genetically identical to the mothers. The New Mexico whiptail is another example.
Some reptiles use the ZW sex-determination system, which produces either males (with ZZ sex c…
Adaptive significance of asexual reproduction
A complete lack of sexual reproduction is relatively rare among multicellular organisms, particularly animals. It is not entirely understood why the ability to reproduce sexually is so common among them. Current hypotheses suggest that asexual reproduction may have short term benefits when rapid population growth is important or in stable environments, while sexual reproduction offers a net advantage by allowing more rapid generation of genetic diversity, allowing adaptation to cha…
See also
• Alternation of generations
• Self-fertilization
• Bacterial conjugation
• Biological life cycle
• Biological reproduction, also simply reproduction
Further reading
• Avise, J. (2008). Clonality: The Genetics, Ecology, and Evolution of Sexual Abstinence in Vertebrate Animals. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-536967-0.
• Graham, L.; Graham, J.; Wilcox, L. (2003). Plant Biology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. pp. 258–259. ISBN 978-0-13-030371-4.
Asexual Reproduction Definition
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
Types of Asexual Reproduction
Examples of Asexual Reproduction
- Bacteria
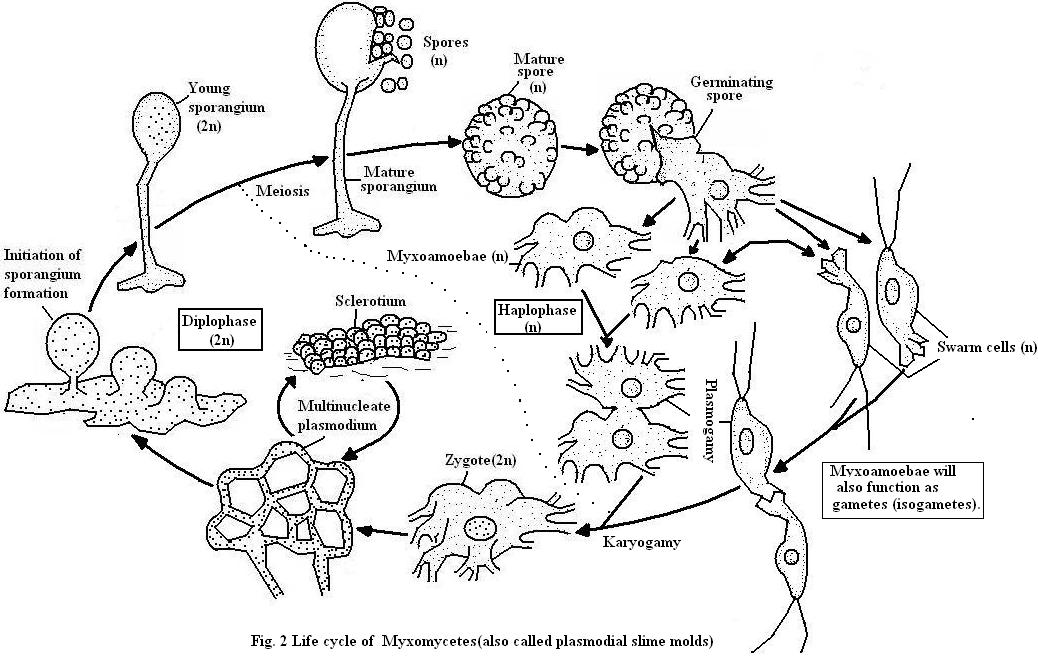
All bacteria reproduce through asexual reproduction, by splitting into two “daughter” cells that are genetically identical to their parents. Some bacteria can undergo horizontal gene transfer – in which genetic material is passed “horizontally” from one organism to another, instead of “vertica… - Slime Molds
Slime molds are a fascinating organism that sometimes behave like a multicellular organism, and sometimes behave like a colony of single-celled organisms. Unlike animals, plants, and fungi, the cells in a slime mold are not bound together in a fixed shape and dependent on each other for su…
Related Biology Terms
Quiz