
How long was the transatlantic cable in miles?
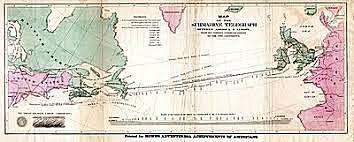
On July 29, 1858, two steam-powered battleships met in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. There, they connected two ends of a 4,000 kilometer (2,500 mile) long, 1.5 centimeter (0.6 inch) wide cable, linking for the first time the European and North American continents by telegraph.
What is a transatlantic telegraph cable?
Transatlantic telegraph cable. A transatlantic telegraph cable is an undersea cable running under the Atlantic Ocean used for telegraph communications.
What was the transatlantic cable made out of?
May 14: The U.S.S. Niagara, assigned to assist H.M.S. Agamemnon in laying the transatlantic cable, arrives in England. The cable is made of 340,500 miles of copper and iron wire, insulated with 300 tons of gutta-percha, and stretches 2,500 nautical miles.
Who invented the first transatlantic cable?
Cyrus West Field and the Atlantic Telegraph Company were the major implementors of the first transatlantic telegraph cable. The project began in 1854 and was completed in 1858. The cable functioned for only three weeks, but was the first such project to yield practical results.
Is the transatlantic cable still used today?
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is now an obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and data are still carried on other transatlantic telecommunications cables.
How long is the transatlantic telegraph cable?
By August 5, the cable had been successfully laid, stretching nearly 2,000 miles across the Atlantic at a depth often of more than two miles. On August 16, President James Buchanan and Queen Victoria exchanged formal introductory and complimentary messages.
Do transatlantic cables sit on ocean floor?
The previously used small diameter fiberoptic cables were damaged by fishing boats. To reduce the risk of damaging, modern day underwater cables are buried in the ocean floor with the facilitation of special under sea ploughs.
How long does it take to lay a transatlantic cable?
between three to four weeksThe coiling of hundreds of miles of cable in the cargo hold is a process that can take between three to four weeks to complete.
Why did the transatlantic cable fail?
The failure of the 1858 Atlantic Telegraph occurred because the insulation resistance was first impaired and then the insulation failed, creating short circuits. These took the electrical signals sent down the cable to sea earth at the short.
Do cables run under the ocean?
Though we live in an increasingly wireless world, that connectivity depends on wires under the ocean. Subsea or submarine cables are fiber optic cables that connect countries across the world via cables laid on the ocean floor.
Are transatlantic cables buried?
Yes, cables go all the way down. Nearer to the shore cables are buried under the seabed for protection, which explains why you don't see cables when you go the beach, but in the deep sea they are laid directly on the the ocean floor.
What is the deepest undersea cable?
SAPEI, is a high-voltage direct current power transmission system that connects Sardinia with the Italian mainland. The submarine cable from Fiume Santo to Latina runs at 1,600 metres (5,200 ft) below sea level in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the deepest submarine power cable in the world.
Who owns undersea cable?
BSNL owns its first international submarine cable connecting India and Sri Lanka (BLCS) and its cable landing station in Tuticorin.
Who paid for the transatlantic cable?
The British government helped Field out with a subsidy of £1,400 per year, which works out as about £150,000 today, and the financier managed to get the US congress to help out, too, despite fierce opposition from Anglophobe senators. Field also supplied a quarter of the funds for the cable himself.
What is the longest submarine cable in the world?
At 45,000 km and circling the African continent, the subsea cable is the longest fiber optic cable in the world and will connect three continents: Africa, Asia, and Europe, and 33 countries across 46 landing points.
How thick are undersea cables?
Undersea cables have been used since the 1850s. Today, they've evolved into technological marvels. Laid by slow-moving ships, they are typically between two and seven inches thick and have a lifespan of approximately 25 years.
How far can a telegraph go?
The equipment's guaranteed working range was 250 miles, but communications could be maintained for up to 400 miles during daylight and up to 2000 miles at night.
How many transatlantic cables are there?
How many cables are there? As of 2022, we track 530 active and planned submarine cables.
Is there a cable from UK to US?
The Yellow cable system (also known as Atlantic Crossing 2, AC-2) is a 6,400 km trans-Atlantic submarine cable system linking the USA and the UK. The AC-2 was put into service in September 2000, with an initial design capacity of 320 Gbps on 4 fiber pairs.
How long did it take for the first transatlantic telegraph to send?
It wasn't exactly instant messaging: The queen's 98-word greeting of goodwill took almost 16 hours to send through the 3,200-kilometer cable. Still, compared to packet steamships, which could take 10 days to cross the Atlantic, the cable promised a tremendous improvement in speed for urgent communications.
How did the transatlantic cable work?
The transatlantic cable reduced communication time considerably, allowing a message and a response in the same day.
Who landed the Transatlantic Telegraph Cable?
Landing of the Transatlantic telegraph cable of 1866 at Heart's Content, Newfoundland, by Robert Charles Dudley, 1866.
What was the problem with the 1858 cable?
He had no formal training in physics; all his knowledge was gained through practical experience. The two clashed even before the project began when Whitehouse disputed Thomson's law of squares when the latter presented it to a British Association meeting in 1855. Thomson's law predicted that transmission speed on the cable would be very slow due to an effect called retardation. To test the theory, Bright gave Whitehouse overnight access to the Magnetic Telegraph Company's long underground lines. Whitehouse joined several lines together to a distance similar to the transatlantic route and declared that there would be no problem. Morse was also present at this test and supported Whitehouse. Thomson believed Whitehouse's measurements were flawed and that underground and underwater cables were not fully comparable. Thomson believed a larger cable was needed to mitigate the retardation problem. In mid-1857, on his own initiative, he examined samples of copper core of alleged identical specification and found variations in resistance up to a factor of two. But cable manufacture was already underway and Whitehouse supported use of a thinner cable, so Field went with the cheaper option.
What is the transatlantic telegraph?
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean used for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is now an obsolete form of communication and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and data are still carried on other transatlantic telecommunications cables.
What were the causes of the failure of the 1858 cable?
The operation of the 1858 cable was plagued by conflict between two of the senior members of the project, Thomson and Whitehouse. The points of disagreement were highly relevant to the ultimate causes of the cable failure. Whitehouse was a medical doctor by training but had taken an enthusiastic interest in the new electrical technology and had given up his medical practice to follow a new career. He had no formal training in physics; all his knowledge had been gained through practical experience. The two clashed even before the project had started when Whitehouse disputed Thomson's law of squares when he presented it to a British Association meeting in 1855. Thomson's law predicted that transmission speed on the cable would be very slow due to an effect called retardation. To put this to the test, Bright gave Whitehouse overnight access to the Magnetic Telegraph Company's long underground lines. He joined several lines together to a distance similar to the transatlantic route and declared that there would be no problem. Morse was also present at this test and supported Whitehouse. Thomson believed that Whitehouse's measurements were flawed and that underground and underwater cables were not fully comparable. Thomson believed that a larger cable was needed, which would improve the retardation problem predicted by the law of squares. In mid-1857, on his own initiative, he examined samples of copper core of alleged identical specification and found variations in resistance up to a factor of two. But the cable manufacturing was already underway and Whitehouse supported use of a thinner cable so Field went with the cheaper option.
How much does a cable weigh?
The cable consisted of seven copper wires, each weighing 26 kg/km (107 pounds per nautical mile ), covered with three coats of gutta-percha (as suggested by Jonathan Nash Hearder ), weighing 64 kg/km (261 pounds per nautical mile), and wound with tarred hemp, over which a sheath of 18 strands, each of seven iron wires, was laid in a close helix. It weighed nearly 550 kg/km (1.1 tons per nautical mile), was relatively flexible, and could withstand tension of several tens of kilonewtons (several tons).
How long did the first telegram cable last?
The cable functioned for only three weeks, but it was the first such project to yield practical results. The first official telegram to pass between two continents was a letter of congratulations from Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom to President of the United States James Buchanan on August 16.
When was the first transatlantic cable laid?
The ship's initial attempt to lay the cable, in 1865, ended in failure. In 1866, eight years after the first transatlantic telegram, the Great Eastern successfully laid cable from Valentia, Ireland, to a port in Newfoundland, aptly named Heart's Content, thus performing a feat that had previously required two ships.
What was the Atlantic cable?
The Atlantic cable was unique only for its length . Underwater cables had been investigated since Morse began experimentation in 1852. By 1858 a large number of submarine cables were already in operation over shorter distances. Gulfs, harbors, lakes, and other sizable bodies of water were already spiderweb bed with them.
How many miles of wire is in a gutta percha cable?
A vast amount of gutta percha came to be used in cable making. A cable 2,500 nautical miles in length involved 300 tons of it, in addition to 340,000 miles of wire. In the beginning, the importation of gutta percha led to the destruction of 26 million trees per year in Borneo alone.
What is splicing cable?
Splicing was an involved operation. The cable comprised a stranded copper conductor encased in gutta percha insulation and surrounded by a braided steel cable which also acted as a shield. This in turn was protected by additional layers of insulation and shielding, the number of layers depending on the environment. Over-wrapping usually included a fiat iron ribbon that was a barrier to marine life. All of this constituted a shell that had to be opened before the conductor itself was accessible.
Why did the cable insulation break down?
During the early stages moderate voltages were used. Later, higher voltages were applied in an effort to boost signal strength and the cable insulation broke down and failed. The story of subsequent cable laying involved a ship which was the colossus of its time.
How did the submarine telegraph cable affect communication?
The submarine telegraph cable reduced communication time from days to hours. A world that had seemed infinite was reduced overnight to human proportions. In 1854, Frederic N. Gisborne, a Canadian inventor, traveled to New York to raise money for a project to link Newfoundland to the United States by telegraph.
Why did the ships refuse to give up the cable?
Each time, they had to start over. The refusal to give up the project after repeated failures is a particular tribute to Cyrus Field's tenacity.
What is the fastest cable to cross the Atlantic?
Marea is the highest-capacity subsea cable to cross the Atlantic, with speeds more than 16 million times faster than the average home internet connection, able to stream 71 million HD videos simultaneously.
How far is the cable between Spain and the US?
A cable stretching 4,000 miles between the US and Spain is the key to a high-speed future. 6,000 metres beneath the crashing waves of the Atlantic Ocean, traversing live volcanoes, coral reefs and earthquake zones, lies an unassuming cable around 1.5 times the diameter of a garden hose.
How many minutes of video will cross the internet in 2018?
With nearly 1 million minutes of video estimated to cross the internet every single second by 2018, and the ever-growing importance and scope of big data, Marea has a new open design, with the future firmly in mind.
How fast is Marea?
Dubbed Spanish for “tide”, Marea is capable of transferring data at a staggering 160Tbps. It’s so fast, in fact, that it’s capable of sending eight times the entirety of the US Library of Congress’ collection, in a single second.
When will Marea cable be operational?
The physical work to manufacture and lay the cable has now been completed, and it’s planned to be operational in early 2018.
Does Telxius use bandwidth?
Rafael Arranz, chief operating officer for Telxius, states that, “All of these applications, especially everything that is driven by video, consume a huge amount of bandwidth. So everybody needs to be connected with a high-volume, high-bandwidth infrastructure. With its unique route, this cable is going to be able to absorb and deliver back-and-forth traffic to strengthen communications, not just across the Atlantic, but across the globe.”
When was the transatlantic cable laid?
TRANSATLANTIC CABLE. In 1866 a transatlantic cable was laid along the ocean floor to carry telegraph messages from North America to Europe. But this success had been long-awaited: it followed four failed attempts to lay the wire.
How many telegraph cables were there in 1900?
By 1900 there were fifteen telegraph cables lying on the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, enabling telegrams (called "cables" when they were intercontinental) to be transmitted between the United States or Canada and Europe. The development was a tremendous boom to communication. Prior to the transatlantic telegraph cable (1866), ...
What was the purpose of the submarine telegraph cable?
He became determined to connect America and Europe with a submarine telegraph cable, which would greatly improve communication. Cables laid in 1857 and 1858 broke. A third cable was put down later in 1858 and it successfully carried messages across the Atlantic for a period of four weeks before it broke. A fourth wire was put down between ...
What was the fastest way to send a message across the ocean?
Prior to the transatlantic telegraph cable (1866), the fastest way to send a message across the ocean was aboard a ship. The telephone (invented 1875), which allows voice transmission over electrical wires, gradually replaced the telegraph. But for many decades the two technologies were both in use. See also: AT&T, Alexander Graham Bell, Telegraph. ...
When was the 4th wire put down?
A fourth wire was put down between Newfoundland ( Canada ), and Ireland in 1865, but before the project was completed, it too broke. The following year, aided by a cable developed by British mathematician and physicist William Thomson (1824 – 1907), the project was finally a success.
When did the first transatlantic cable system start?
The first transatlantic submarine cable system, TAT-1, went into service on 25 September 1956. From then on, there have been the TAT series of transatlantic submarine cable systems, until the latest one TAT-14.
How long is the Dunant cable?
The Dunant submarine cable system is a 6,600km submarine cable connecting Virginia Beach in the United States to the French Atlantic coast.
How many fiber pairs does the WASACE 1 system have?
WASACE 1 submarine cable system will provide 8 fiber pairs for a total capacity of 144 Tbps, each pair with an upgradeable initial capacity of 18 Tbps.
How many fiber pairs does Apollo North have?
The Apollo cable system was ready for service in February 2003, with 4 fiber pairs and 3.2Tbps initial design capacity on both Apollo North and Apollo South, for a total of 6.4 Tbps trans-Atlantic capacity. In 2014, the Apollo cable system was upgraded to a system capacity of 25Tbps with Alcatel-Lucent’s 1620 Light Manager (LM) submarine line terminal equipment using coherent transmission at 100 Gbps. In 2015, it achieved the capacity of 8Tbps per fiber pair.
What is the TGN Atlantic?
TGN-Atlantic is a 13,000 km transatlantic submarine cable system linking the United States and the United Kingdom. TGN-Atlantic was ready for service in June 2001.
What is the Yellow Cable?
The Yellow cable system (also known as Atlantic Crossing 2 , AC-2) is a 6,400 km trans-Atlantic submarine cable system linking the USA and the UK.
Where is the GTT cable?
GTT Atlantic (formerly Hibernia Atlantic ) is a 12,200 km private transatlantic submarine cable system in the North Atlantic Ocean, connecting Canada, the United States, Ireland and the United Kingdom. Hibernia Atlantic Submarine Cable System was ready for service on April 8, 2001, with a design capacity of 10.16 Tbps.
What was the name of the steamer that lays cable across the Cabot Strait?
Summer: The steamer Propontis successfully lays cable across the Cabot Strait and the Newfoundland line is completed; now the telegraph has been extended one-third of the distance between New York and Europe. Field returns to England to raise more money.
Who suggested running a cable from Ireland to Newfoundland?
November 8: A bishop in Newfoundland, J. T. Bullock, suggests running a cable from Ireland to Newfoundland rather than Nova Scotia, which is further west, estimating a Newfoundland terminal could speed transmission of messages to America by 48 hours. "I hope the day is not far distant," he writes, "when St. John's will be the first link in the electric chain which will unite the Old World and the New."
Why did the James Adger cable fail?
She meets up with the Bryant, but the attempt to lay the cable fails due to bad weather and the Adger captain's refusal to follow orders. Field returns to New York, determined to try again.
How far apart are the Semaphore stations?
Claude Chappe builds semaphore stations across France. Stationed five to ten miles apart, they use a mast and two crossarms to signal each other. Messages sent through what Chappe dubs the "telegraph" can travel several hundred miles a day.
When is the Great Eastern launched?
January 31: The Great Eastern is finally launched. The day before she is supposed to head to sea, Brunel suffers a stroke. He will die a week later.
Who showed that electricity can be sent long distances down a metal wire?
Sir William Watson shows that electricity can be sent long distances down a metal wire.
Who invented the telegraph?
Inventor Samuel Morse places a wire across New York harbor and sends an electric current through it. In December he sends messages by wire between two committee rooms in the U.S. Capitol, leading Congress to appropriate $30,000 towards construction of a telegraph line.
How many messages did the Transatlantic cable send?
This level of voltage was unnecessary, and damaged the already-damaged transatlantic cable. Although Marsh writes that the cable was able to send a total of 732 messages during the three weeks it was active, it clearly wasn’t working very well even before it died.
Why did the British want to lay another transatlantic cable?
The British government and British investors were still interested in laying another transatlantic cable even after this failure, in part because the British Empire had colonized many islands in the Caribbean Sea. In the United States, the government and investors were less interested, particularly between 1860 and 1865, when the country was in the midst of its Civil War.
What was the name of the ship that was built to lay a cable?
In August 1857, two ships—the HMS Agamemnon and the USS Niagara —set out from Valentia, Ireland in the hopes of laying a cable that went all the way to Heart's Content, Newfoundland.
How many volts did the Atlantic Telegraph use?
Believing that a high voltage was necessary to send the message successfully, Whitehouse pumped up to 2,000 volts into the cable, writes Allison Marsh, a history professor at the University of South Carolina.
How long does it take to get a message across the Atlantic?
But what about a very large body of water? Delivering a message by ship across the Atlantic could take about 10 days. If scientists and engineers could figure out how to connect Europe and North America by cable, the average transatlantic message delivery time could shrink from days to hours.
When was the first cable laid?
After much ado, the US and Britain laid the first successful cable under the ocean in August 1858. It stopped working weeks later.
Who was the first person to attempt to lay the Atlantic Telegraph?
Edward Orange Wildman Whitehouse, the electrician behind the first failed attempt at lay the Atlantic telegraph. His experiments led him to conclude, inaccurately, that messages should be sent over the cable using high voltages and that the conducting wire should have a small diameter.
How long was the cable connecting the continents?
There, they connected two ends of a 4,000 kilometer (2,500 mile) long, 1.5 centimeter (0.6 inch) wide cable, linking for the first time the European and North American continents by telegraph. Just over two weeks later, the UK’s Queen Victoria sent a congratulatory message to then US President James Buchanan, which was followed by a parade ...
How many words did the first cable transmit?
By 1866, new cables were transmitting 6 to 8 words a minute, which would rise to more than 40 words before the end of the century.
How fast is the Marea cable?
In 2018, the Marea cable began operating between Bilbao, Spain, and the US state of Virginia, with transmission speeds of up to 160 terabits per second – 16 million times faster than the average home internet connection.
Why do cable companies have to build trenches?
Depending on the coast, cable companies might also have to build concrete trenches far out to sea, to tuck the cable in to protect it from being bashed against rocks.
What are underwater cables?
Underwater cables are the invisible force driving the modern internet, with many in recent years being funded by internet giants such as Facebook, Google, Microsoft and Amazon. They carry almost all our communications and yet – in a world of wireless networking and smartphones – we are barely aware that they exist.
Where is the Marea cable?
Part of the Marea cable, funded by Microsoft and Facebook, running out to the ocean. The cable runs across the Atlantic between Virginia, US and Bilbao, Spain. A man is arrested during a demonstration against the government of Cuban President Miguel Diaz-Canel in Havana, on July 11, 2021.
When do cable laying ships begin passing out equipment?
Once the route is plotted and checked, and the shore connections are secure, huge cable laying ships begin passing out the equipment.

Overview
Early history
| CABLE NAME | READY FOR SERVICE | CABLE LENGTH (KM) | LATENCY (MS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC-1 | May 1998 | 14,301 km | 65 ms [6] |
| Yellow/AC-2 | September 2000 | 7,001 km | under 100 ms |
| Hibernia Atlantic | April 2001 | 12,200 km | 59 ms [6] |
| FLAG Atlantic | June 2001 | 14,500 km | under 100 ms |
| Tata TGN-Atlantic | June 2001 | 13,000 km | under 100 ms |
| Apollo | February 2003 | 13,000 km | under 100 ms |
| AEConnect (AEC-1) | January 2016 | 5,522 km | 54 ms |
A plan takes shape
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is now an obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and data are still carried on other transatlantic telecommunications cables. The first cable was laid in the 1850s from Valentia Island off the west c…
First transatlantic cable
In the 1840s and 1850s several people proposed or advocated construction of a telegraph cable across the Atlantic, including Edward Thornton and Alonzo Jackman.
As early as 1840 Samuel F. B. Morse proclaimed his faith in the idea of a submarine line across the Atlantic Ocean. By 1850 a cable was run between En…
First contact
In 1854, businessman and financier Cyrus West Field invited Gisborne to his house to discuss the project. From his visitor, Field considered the idea that the cable to Newfoundland might be extended across the Atlantic Ocean.
Field was ignorant of submarine cables and the deep sea. He consulted Morse and Lieutenant Matthew Maury, an authority on oceanography. The charts Maury constructed from soundings in …
Failure of the first cable
The cable consisted of 7 copper wires, each weighing 26 kg/km (107 pounds per nautical mile), covered with three coats of gutta-percha (as suggested by Jonathan Nash Hearder ), weighing 64 kg/km (261 pounds per nautical mile), and wound with tarred hemp, over which a sheath of 18 strands, each of 7 iron wires, was laid in a close helix. It weighed nearly 550 kg/km (1.1 tons per nauti…
Preparing a new attempt
Test messages were sent from Newfoundland beginning 10 August 1858. The first was successfully read at Valentia on 12 August and in Newfoundland on 13 August. Further test and configuration messages followed until 16 August, when the first official message was sent via the cable:
Directors of Atlantic Telegraph Company, Great Britain, to Directors in America…
Great Eastern and the second cable
Operation of the 1858 cable was plagued by conflict between two of the project's senior members – Thomson and Whitehouse. Whitehouse was a medical doctor by training, but had taken an enthusiastic interest in the new electrical technology and given up his medical practice to follow a new career. He had no formal training in physics; all his knowledge was gained through pra…