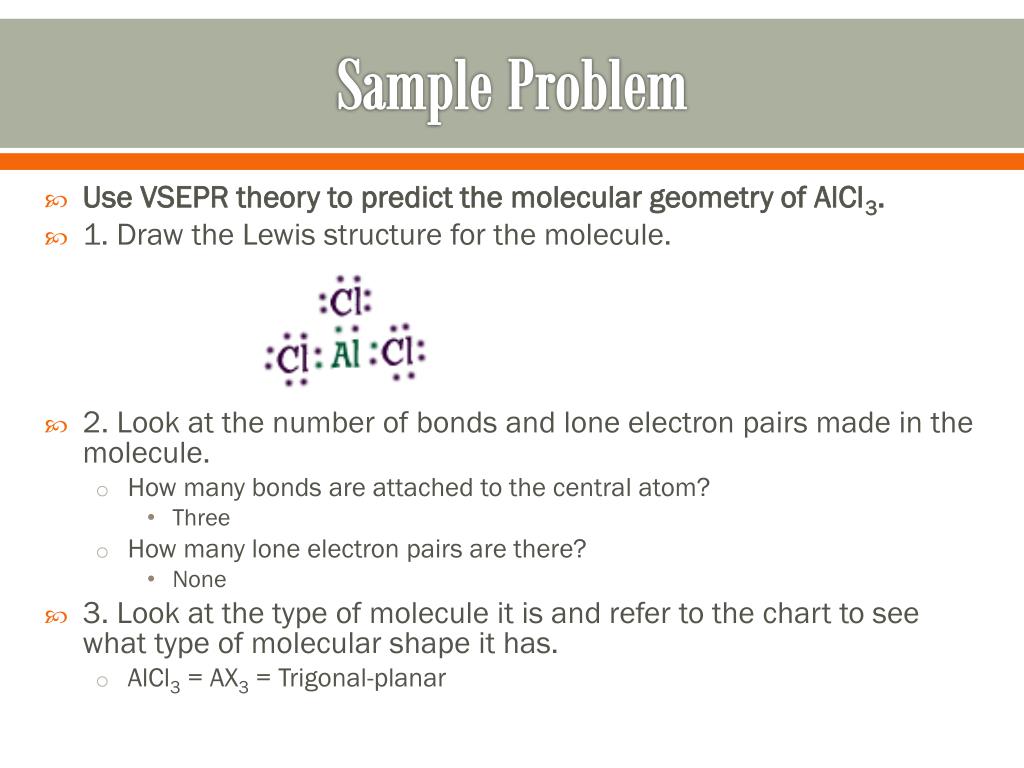
Octahedral molecules have six atoms bonded to the central atom and no lone electron pairs, making the steric number equal to six. The formation of the surrounding atoms give octahedral molecules their overall shape of eight connected triangles. All of the bond angles formed within an octahedral molecule are 90 degrees.
| Number of Electron Groups | Electron-Group Geometry | Ideal Bond Angles |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | trigonal-bipyramidal | 180° |
| 6 | octahedral | 90° |
| 90° | ||
| 90° |
What are the characteristics of octahedral molecules?
Octahedral molecules have six atoms bonded to the central atom and no lone electron pairs, making the steric number equal to six. The formation of the surrounding atoms give octahedral molecules their overall shape of eight connected triangles. All of the bond angles formed within an octahedral molecule are 90 degrees.
What is an example of an octahedron?
The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group O h. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF 6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo (CO) 6.
How many faces does an octahedron have?
The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group O h.
What is the concept of octahedral coordination geometry?
The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred Werner to explain the stoichiometries and isomerism in coordination compounds. His insight allowed chemists to rationalize the number of isomers of coordination compounds.
How many angles are present in octahedral?
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa.
How many 90 degree angles are there in SF6?
The no of 90° angles in sulphur hexafluoride molecule is Twelve (12). - The shape of Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) molecule is octahedral in which there is a central sulphur atom which is connected to 6 fluorine atoms.
How many 90 angles are there?
four 90 degree anglesExample 2: How many 90 degree angles are there in full rotation? Solution: There are four 90 degree angles in full rotation. A full rotation is equal to 360 degrees.
How many bond angles are in 90 degrees?
sp3d2 hybridization leads for octahedral geometry having 3 bonds at 1800 and 12 bonds at 900. which has a maximum number of 90o angle.
Does SF6 have 90 degree angle?
Sulfur hexafluoride has 6 regions of electron density around the central sulfur atom (6 bonds, no lone pairs). The resulting shape is an octahedron with 90° F-S-F bond angles.
How many 90 degree angles are there in SF4?
The SF4 molecule's geometry (defined by the atoms' arrangement) is a “see-saw.” Three of the single bonds would be at 90 degrees if the lone pair were in one of the axial orientations.
How do you find a 90-degree angle?
With a bit of mathematical ability, this formula (a^2 + b^2 = c^2) can be manipulated and used to determine a right angle. Using a ruler, measure the sides of the angle as well as the distance between the angle's open endpoints. If these values plug into the formula correctly, then the angle is a 90-degree angle.
What is a 90 angle called?
Angles that are 90 degrees (θ = 90°) are right angles. • Angles that are 180 degrees (θ = 180°) are known as straight angles.
What shape is a 90-degree angle?
What shapes have right angles? Squares, rectangles and right triangles all have right angles.
What are the angles of octahedral shape?
What is the angle of octahedral shape? The angle between the two vertex atoms in the octahedral molecule is 180 degrees. The angle between any other pair of atoms in the octahedral molecule is 90 degrees.
What are the bond angles for octahedral structure?
McCord - Octahedral - 6 regions. If there are no lone pairs then the molecular geometry matches the electronic and is octahedral. The base bond angles are 180° and 90°.
How many 90 degree angles are in a PCl5?
PCl5 will have 2 right angles.
How many bond angles are there in SF6?
90oHybridization of SF6 (Sulfur Hexafluoride)Name of the MoleculeSulphur HexafluorideMolecular FormulaSF6Hybridization Typesp3d2Bond Angle90oGeometryOctahedral
How many 180 degree angles are there in SF6?
one 180 degree angleSF6 is octahedral, so there are six 90-degree bond angles between sulfur and fluorine, and each fluorine has 90-degree angles between it and its nearest four neighbors, and a 180-degree angle between it and its opposite fluorine. SO ,there is only one 180 degree angle in SF6 .
How many 90 degree angles are in a PCl5?
PCl5 will have 2 right angles.
Which among the following is the geometry of SF6?
The molecular geometry of SF6 is octahedral.
What is the angle of octahedral shape?
The angle between the two vertex atoms in the octahedral molecule is 180 degrees. The angle between any other pair of atoms in the octahedral molec...
What does an octahedral molecule look like?
An octahedron is composed of two square-based pyramids joined at their bases, i.e. a pyramid joined to an inverted pyramid. The central atom is at...
Is octahedral molecule planar?
No, an octahedral molecule has two planes: an equatorial plane and an axial plane. The central atom and four of the terminal atoms lie in the equat...
How many sides does an octahedral have?
Octahedral Shape. We know that an octagon is a polygon with eight sides and an octuplet is a group of eight. After all, the prefix 'octa-' means eight. So you may be wondering why a molecule with six bonds is called an octahedral.
How many atoms are in an octahedral molecule?
An octahedral molecule consists of a central atom bonded to six atoms, with no lone electron pairs. According to the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR), electron pairs repel each other whether they are bonded or in lone pairs.
How to determine the shape of a molecule?
When identifying the shape of a molecule, we need to first know the number of bonds and lone electron pairs with the molecule. The lone electron pairs are the electrons that surround the central atom but are not bonded to another atom. The total number of bonds and lone electron pairs determines the steric number of the molecule.
What is the geometry of molecules?
They're usually drawn this way for simplicity. However, many molecules have a three-dimensional structure. Molecular geometry is a type of geometry used to describe the shape of a molecule.
Is sulfur hexafluoride an octahedral molecule?
Sulfur hexafluoride is a common example of an octahedral molecule. The central sulfur atom is bonded to six fluoride atoms. In molybdenum hexacarbonyl, a central molybdenum atom is bonded to six carbonyl groups. A carbonyl group is a carbon atom triple-bonded to an oxygen atom.
Is carbonyl an octahedral molecule?
A carbonyl group is a carbon atom triple-bonded to an oxygen atom. At first glance it may not appear that this molecule fits the definition of an octahedral because of the additional oxygen atoms. However, the molybdenum atom is only bonded to the six carbon atoms, so this molecule still meets the criteria.
How many faces does an octahedron have?
The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules ...
Who developed the octahedral geometry?
The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred Werner to explain the stoichiometries and isomerism in coordination compounds. His insight allowed chemists to rationalize the number of isomers of coordination compounds.
How many isomers are there in an octahedral complex?
The number of possible isomers can reach 30 for an octahedral complex with six different ligands (in contrast, only two stereoisomers are possible for a tetrahedral complex with four different ligands). The following table lists all possible combinations for monodentate ligands: Formula. Number of isomers.
What are some examples of octahedral compounds?
Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF 6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo (CO) 6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, [Co (NH.
What is a monocapped octahedron?
The specific geometry is known as a monocapped octahedron, since it is derived from the octahedron by placing the lone pair over the centre of one triangular face of the octahedron as a "cap" (and shifting the positions of the other six atoms to accommodate it). These both represent a divergence from the geometry predicted by VSEPR, which for AX 6 E 1 predicts a pentagonal pyramidal shape.
How many isomers are there for ML a#N#4?
For ML a#N#4 L b#N#2, two isomers exist. These isomers of ML a#N#4 L b#N#2 are cis, if the L b ligands are mutually adjacent, and trans, if the L b groups are situated 180° to each other. It was the analysis of such complexes that led Alfred Werner to the 1913 Nobel Prize–winning postulation of octahedral complexes.
What is the alternative to octahedral geometry?
For compounds with the formula MX 6, the chief alternative to octahedral geometry is a trigonal prismatic geometry , which has symmetry D 3h. In this geometry, the six ligands are also equivalent. There are also distorted trigonal prisms, with C 3v symmetry; a prominent example is W (CH#N#3)#N#6. The interconversion of Δ - and Λ -complexes, which is usually slow, is proposed to proceed via a trigonal prismatic intermediate, a process called the " Bailar twist ". An alternative pathway for the racemization of these same complexes is the Ray–Dutt twist .
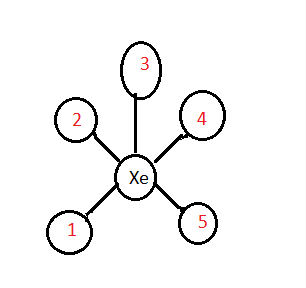
Why are bond angles in IF 5 less than this?
The bond angles in IF 5 are less than this because of the stronger repulsion by the lone pair of electrons in the axial position.
How many pairs of electrons are in a molecule?
There are five pairs of outer electrons around the central atom in each of these molecules. These pairs of electrons repel each other. In terms of the relative strength of repulsion: