How many amino acids are typically found in a polypeptide?
ferent amino acids are commonly found in polypep- tides, and they can be joined in any number and in any order. Because the number of amino acids in a polypeptide usually ranges from 100 to 1000, an enor - mous number of polypeptide chains differing in amino acid sequence can be formed.
What role does amino acids play in making polypeptides?
Proteins are made up of a sequence of 20 amino acids. These amino acids link together to form a polypeptide chain, and then folds into a three dimensional structure. This conformation is vital, because the protein cannot function until it is a certain shape. Their shapes determine their function.
Which foods contain all amino acids?
What foods contain all 20 amino acids?
- Red meat.
- Chicken.
- Fish.
- Seafood.
- Eggs.
- Milk.
- Cheese.
- Yogurt.
What are the names of the 23 amino acids?
The full list of the 23 amino acids is:
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartic acid
- Cysteine
- Cystine
- Glutamine
- Glutamic acid
- Glycine
- Histidine
How do you determine the number of amino acids in a polypeptide chain?
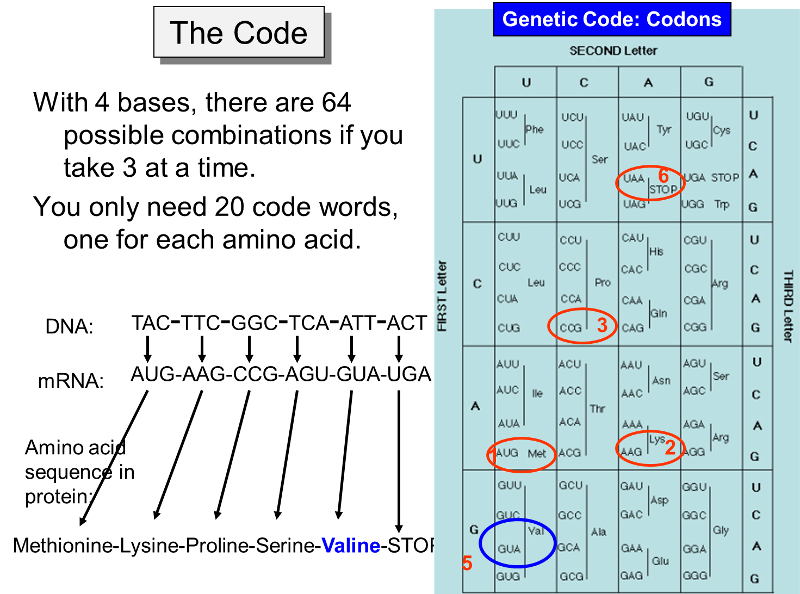
2:506:48How to find a number of Amino acids in protein chain? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo our formula would be simple number of nucleotides divided by 3.MoreSo our formula would be simple number of nucleotides divided by 3.
How many amino acids are there in the α polypeptide chain?
141 amino acid residuesLike all proteins, it is made up of small molecules called amino acids. A hemoglobin molecule is made up of four polypeptide chains, two alpha chains of 141 amino acid residues each and two beta chains of 146 amino acid residues each.
Are there 20 or 22 amino acids?
Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 (selenocysteine and pyrrolysine) that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
How many polypeptide sequences can form from 4 amino acids?
Since each of the 20 amino acids is chemically distinct and each can, in principle, occur at any position in a protein chain, there are 20 × 20 × 20 × 20 = 160,000 different possible polypeptide chains four amino acids long, or 20n different possible polypeptide chains n amino acids long.
What 3 amino acids are in a polypeptide chain?
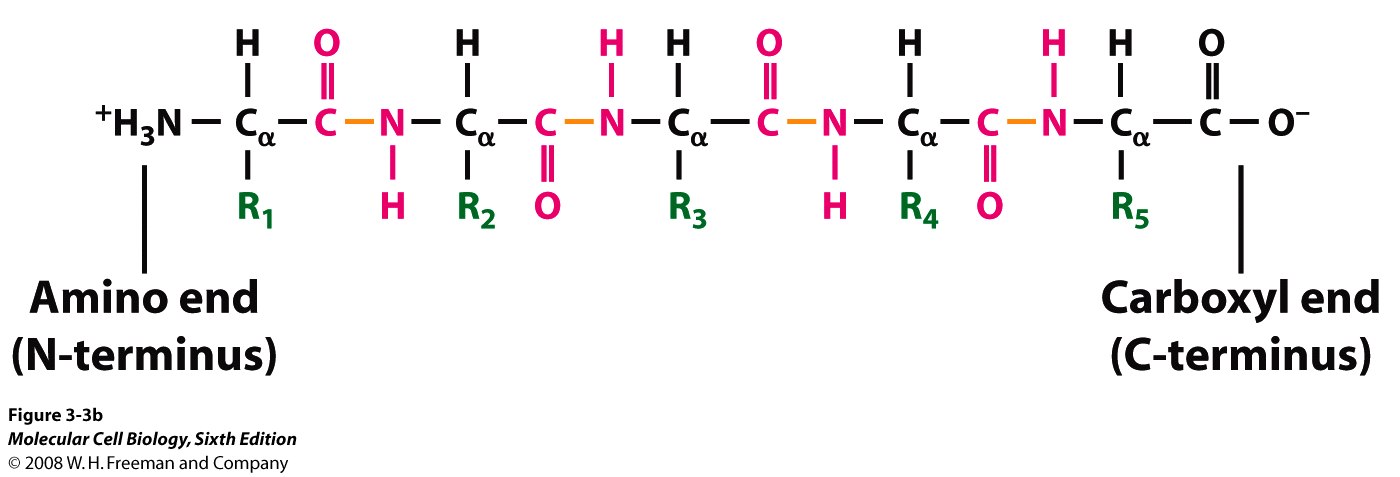
The amino acids which make up polypeptides contain an alkali amino group (-NH2), an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH), and an R group (side chain). The R group is variable in its components and is unique to every amino acid. Each amino acid molecule contains a carbon atom (α-carbon).
What is a chain of more than 50 amino acids called?
The general term peptide refers to an amino acid chain of unspecified length. However, chains of about 50 amino acids or more are usually called proteins or polypeptides. In its physiologically active form, a protein may be composed of one or more polypeptide chains.
What are 20 amino acids?
The essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. The nonessential amino acids are alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and serine.
What amino acids are found at turns in a polypeptide chain?
Gratifyingly, the turn propensities of amino acids at different positions of various protein β-turn types obtained through statistical analysis by directed evolution and phage-display correlate well with work on model peptides in showing glycine, proline, asparagine, and aspartic acid to be the most common β-turn- ...
How many different amino acids are there?
Amino acids are the small molecules that are put together to make proteins. And so there are 20 different amino acids. You can think of it as different flavors that get linked together like beads on a string to make long chains that we call polypeptides, and those are the building blocks of proteins. And the really neat thing about the amino acids ...
What are amino acids?
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. =. Amino acids are a set of 20 different molecules used to build proteins. Proteins consist of one or more chains of amino acids called polypeptides. The sequence of the amino acid chain causes the polypeptide to fold into a shape that is biologically active. The amino acid sequences of proteins are encoded in the genes.
What happens when amino acids are linked together?
And the really neat thing about the amino acids is that when they're linked together, they fold to make the final shape of the protein. And it's the shape of the protein that really dictates what it can do in the cell.
How many amino acids are in a polypeptide?
The polypeptide definition describes a chain of more than twenty and less than fifty amino acids bound together via covalent peptide bonds. Singular amino acids are the building blocks of life and can be linked to form oligopeptides, polypeptides, and proteins inside the cell. This occurs during a process called protein synthesis.
What is a Polypeptide?
To know what a polypeptide is, it is best to break it down into its smallest components – amino acids. Singular amino acid monomers link together to make more complex polymer chains.
How does a ribosome form a peptide bond?
To form a peptide bond, the ribosome helps to push the carboxyl group of one amino acid closer to the amino group of the next. The formation of a peptide bond requires energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What type of bond is formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the other?
Peptide Bonds. A ribosome links two amino acids by way of peptide bonds. These are covalent chemical bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the other. When these two residues attach, they release a single molecule of water – a dehydration synthesis reaction.
What is the primary structure of a peptide chain?
Primary structure refers to the amino acid order of a simple peptide chain. Secondary structures – commonly alpha-helix, beta-strand, or beta-sheet – create spirals, coils, or sheet forms from a single polypeptide chain by way of hydrogen bonds.
What is a singular amino acid?
A singular amino acid is just that – an amino acid. The moment it bonds with another amino acid it becomes a peptide. No matter how many amino acids are linked together and no matter what the structure, joined amino acids are all peptides. Peptides are further categorized according to length.
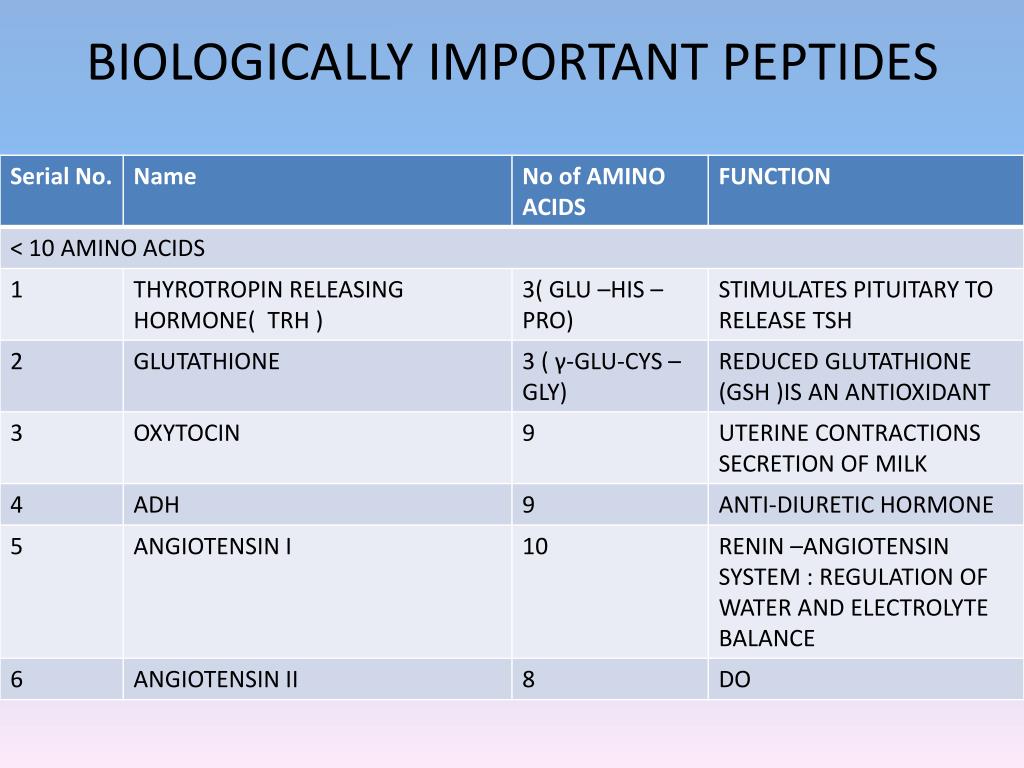
What is synthetic polypeptide?
A synthetic polypeptide example covers the chemicals produced to research, design, and prepare novel enzymes, drugs, and vaccines. As peptide synthesis in smaller laboratories is a time-consuming task, industrial-sized companies produce specific peptides on a massive scale. The first peptides to be synthesized were the hormones oxytocin and insulin. Current technology allows companies to produce less reactive polypeptides that provide lower levels of undesired reactions with other molecules. This is done through the addition of temporary or permanent protecting chemicals (benzyl or tert-butyl groups) during synthetic polypeptide synthesis.