
See more

How many stations does BART have?
50 stationsSystemwide, there are 33.5 miles of aerial track; 65.1 miles of track at grade and 32.8 miles of subway track. 50 stations comprise 19 surface, 15 elevated and 16 subway stations.
Where does the BART run in San Francisco?
Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) connects the San Francisco Peninsula with communities in the East Bay and South Bay. BART service currently extends as far as Millbrae, Richmond, Antioch, Dublin/Pleasanton, and Berryessa/North San José.
What is the busiest BART station?
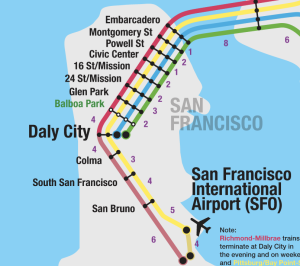
BART Ridership Quick Facts During peak commute hours, nearly 25,000 people ride through the Transbay Tube into Downtown San Francisco. BART's Pittsburg/Bay Point (yellow) line carries the largest number of people. The busiest stations in the BART system are Embarcadero and Montgomery.
What BART station is downtown San Francisco?
Civic Center/UN Plaza Station is served by San Francisco Muni and Golden Gate Transit. This station doesn't have restrooms however free attended Pit Stop bathrooms are available at street level. View the map.
Does BART go directly to San Francisco airport?
The Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) rail system provides direct service from the San Francisco International Airport (SFO) to downtown San Francisco, the East Bay and Peninsula cities. Avoid traffic, parking hassles and the high cost of taxis, rental cars and shuttles by taking BART from the airport to your destination.
Does BART run from SFO to downtown San Francisco?
BART trains connect SFO with downtown San Francisco, downtown Oakland and many other Bay Area destinations. BART is the best way to avoid sitting in Bay Area traffic. Trains depart from the SFO International Terminal, and it's just 30 minutes to downtown San Francisco. Plan your trip with the Trip Planner.
How much does a BART janitor make?
The estimated total pay for a Janitor at Bart is $39,683 per year.
What are the safest BART stations?
The safest BART stations were Pittsburg and West Dublin, which had no reported thefts in 2019, Millbrae, with one, and North Concord and South San Francisco, which each had two.
How much do BART employees make?
The average Bay Area Rapid Transit salary ranges from approximately $80,353 per year for CAD Drafter to $160,257 per year for Regulatory Affairs Manager. Average Bay Area Rapid Transit hourly pay ranges from approximately $28.08 per hour for Ambassador to $60.40 per hour for Police Sergeant.
Which BART stop for Fisherman's Wharf?
the EmbarcaderoTake BART to the Embarcadero and connect to an outbound F-Line streetcar to the Wharf. You can catch the F-Line directly in front of the Ferry Building.
How long is the BART ride from Union City to San Francisco?
The best way to get from Union City to San Francisco without a car is to BART which takes 46 min and costs $4 - $7. How long does it take to get from Union City to San Francisco? The BART from Union City to Civic Center / UN Plaza takes 46 min including transfers and departs every 30 minutes.
What is the best way to get around San Francisco?
The best ways to get around San Francisco are on foot and by using public transportation. Most of the popular attractions are within walking distance of the city center, and the large municipal transportation system (called the Muni) operates bus and streetcar lines, leaving little need for your own set of wheels.
How do you ride BART in San Francisco?
You'll need to purchase a ticket at the station before riding BART. Your ticket can cover a single ride or multiple rides. Each person must have his or her own ticket, except children age 4 and under, who ride free and do not need a ticket. Be sure to keep your ticket.
Which BART stop for Fisherman's Wharf?
the EmbarcaderoTake BART to the Embarcadero and connect to an outbound F-Line streetcar to the Wharf. You can catch the F-Line directly in front of the Ferry Building.
Does BART run under the Bay Bridge?
The Transbay Tube is an underwater rail tunnel that carries Bay Area Rapid Transit's four transbay lines under San Francisco Bay between the cities of San Francisco and Oakland in California.
Where are BART stations?
Stations12th St. Oakland City Center.16th St. Mission (SF)19th St. Oakland.24th St. Mission (SF)Antioch.Ashby (Berkeley)Balboa Park (SF)Bay Fair (San Leandro)More items...
How many subway stations are there in San Francisco?
50 stations comprise 19 surface, 15 elevated and 16 subway stations. Four of these are a combination of BART and MUNI Metro stations in downtown San Francisco (Embarcadero, Montgomery St, Powell St, and Civic Center). One station is a combination of BART and Caltrain in Millbrae.
What is a clipper?
Clipper#N#The Clipper fare payment system is a Bay Area regional project managed the Metropolitan Transportation Commission. Clipper provides Bay Area transit customers a single fare payment medium for all their transit trips, through use of electronic "smart card" technology.
What is the BART vision?
BART's vision is to support a sustainable and prosperous Bay Area by connecting communities with seamless mobility.
What is OCC in computer?
Operations Control Center (OCC) The current Operations Control Center (OCC) replaced the old "central control room," which made history when the system first opened in 1972, with what was considered the largest monitor display board of its kind in the country.
Where are the addfare machines located?
Addfare machines are located in the paid area of the stations , and are intended for use by customers who need to add value to their BART ticket in order to exit the system. Addfare machines accept cash only. In some stations, Addfare machines also serve for parking validation/payment.
When will the fleet of the future train be delivered?
The first Fleet of the Future train carried passengers in January 2018. The size of BART's fleet will be dynamic while new trains are put into service and old trains are retired. The current forecast indicates the balance of new train cars will be delivered by Spring 2022.
How many stations does BART have?
BART has 50 passenger stations, of which 47 are high-platform rapid transit stations. Oakland International Airport is served by the Oakland Airport Connector, which uses cable-hauled automated guideway transit (AGT) rolling stock; Coliseum has separate platforms for rapid transit trains and AGT trains. Antioch and Pittsburg Center have low platforms for use with the diesel multiple unit (DMU) trains used on that section of the line. A transfer platform east of Pittsburg/Bay Point, which does not have street access and is not designated as a unique station, provides cross-platform transfers between the rapid transit and DMU sections of the line.
What is the BART system?
BART is administered by the Bay Area Rapid Transit District, a special district government agency formed by Alameda, Contra Costa, and San Francisco counties. Mondays through Saturdays, BART trains run on five principal routes; four are transbay routes connecting San Francisco to Oakland and various destinations in the East Bay, while the fifth, ...
When was the San Mateo County line extended?
The San Mateo County line was extended south from Colma to San Francisco International Airport and Millbrae in 2003. BART passengers can reach Oakland International Airport on BART's new automated guideway transit (AGT) system, the Coliseum–Oakland International Airport line.
What is a transfer platform east of Pittsburg?
A transfer platform east of Pittsburg/Bay Point , which does not have street access and is not designated as a unique station, provides cross-platform transfers between the rapid transit and DMU sections of the line.
When was the first BART line built?
The original system was completed in September 1974 when trains first carried passengers through the underwater Transbay Tube. BART's three routes then were Concord–Daly City, Fremont—Daly City and Richmond–Fremont. The Concord-Daly City line was extended to North Concord/Martinez in 1995 and to Colma and Pittsburg/Bay Point in 1996.
When will the Silicon Valley BART station open?
The four-station Phase II of the Silicon Valley BART extension will add underground stations at 28th Street/Little Portugal, Downtown San José, and Diridon in San José, plus the surface-level Santa Clara station; it is planned to open in 2029 or 2030.
When will the Richmond-Fremont and Fremont-Daly City lines be extended?
The Richmond-Fremont and Fremont-Daly City lines were later extended to Warm Springs/South Fremont in 2017, and then further to Berryessa/North San José in 2020. An extension of BART using diesel multiple unit technology, called BART to Antioch but also known during construction as eBART, opened to Antioch in 2018.
What is the Bay Area Rapid Transit System?
Some of the Bay Area Rapid Transit system's current coverage area was once served by an electrified streetcar and suburban train system called the Key System. This early 20th-century system once had regular transbay traffic across the lower deck of the Bay Bridge, but the system was dismantled in the 1950s, with its last transbay crossing in 1958, and was superseded by highway travel. A 1950s study of traffic problems in the Bay Area concluded the most cost-effective solution for the Bay Area's traffic woes would be to form a transit district charged with the construction and operation of a new, high-speed rapid transit system linking the cities and suburbs. Marvin E. Lewis, a San Francisco trial attorney and member of the city's board of supervisors spearheaded a grassroots movement to advance the idea of an alternative bay crossing and the possibility of regional transit network.
What county is San Francisco in?
The San Francisco Bay Area Rapid Transit District is a special district consisting of Alameda County, Contra Costa County, and the City and County of San Francisco. San Mateo County, which hosts six BART stations, and Santa Clara County, which hosts two, are not part of the BART District.
What is the BART system?
BART was one of the first U.S. rail transit systems of any size to be substantially automated. Routing and dispatching of trains, and adjustments for schedule recovery are controlled by a combination of computer and human supervision at BART's Operations Control Center (OCC) and headquarters at the Kaiser Center in Downtown Oakland. Station-to-station train movement, including speed control and maintenance of separation between successive trains, is entirely automatic under normal operation, the operator's routine responsibilities being issuing announcements, closing the doors after station stops, and monitoring the track ahead for hazards. In unusual circumstances the operator controls the train manually at reduced speed.
How many passengers does BART have?
With an average of 411,000 weekday passengers and 118 million annual passengers in fiscal year 2019, BART is the fifth-busiest heavy rail rapid transit system in the United States and is operated by the Bay Area Rapid Transit District which formed in 1957. The initial system opened in stages from 1972 to 1974.
How many stations does BART have?
The entirety of the system runs in exclusive, grade-separated right-of-way. BART's rapid transit revenue routes cover about 120 miles (190 km) with 50 stations. On the main lines, approximately 28 miles (45 km) of lines run through underground sections with 32 miles (51 km) on elevated tracks.
What are the major airports in the Bay Area?
BART also runs directly to two of the three major Bay Area airports: San Francisco International Airport and Oakland International Airport .
Is the fare on the BART higher than the subway?
Fares on BART are comparable to those of commuter rail systems and are higher than those of most subways, especially for long trips. The fare is based on a formula that takes into account both the length of the trip and the counties passed through. A surcharge is added for trips traveling through the Transbay Tube, to Oakland International Airport, to San Francisco International Airport, and/or through San Mateo County, a county that is not a member of the San Francisco Bay Area Rapid Transit District .
Overview
Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) is a heavy rail rapid transit system in the San Francisco Bay Area in California, United States. With average weekday ridership around 405,000 passengers in February 2020, BART is the fifth busiest rapid transit system in the United States. BART is administered by the Bay Area Rapid Transit District, a special district government agency formed by Alameda, Contra Costa, and San Francisco counties.
Services
History
Rolling stock
Fares
Ridership levels
Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) is a rapid transit system serving the San Francisco Bay Area in California. BART serves 50 stations along six routes on 131 miles (211 kilometers) of rapid transit lines, including a 10-mile (16 km) spur line in eastern Contra Costa County which uses diesel multiple-unit trains and a 3.2-mile (5.1 km) automated guideway transit line to the Oakland International Airport. W…
Infrastructure
BART serves large portions of its three member counties – San Francisco, Alameda, and Contra Costa – as well as smaller portions of San Mateo County and Santa Clara counties. The system has 50 stations: 22 in Alameda County, 12 in Contra Costa County, 8 in San Francisco, 6 in San Mateo County, and 2 in Santa Clara County. BART operates five named heavy rail services plus one se…
Organization and management
Some of the Bay Area Rapid Transit system's current coverage area was once served by an electrified streetcar and suburban train system called the Key System. This early 20th-century system once had regular transbay traffic across the lower deck of the Bay Bridge, but the system was dismantled in the 1950s, with its last transbay crossing in 1958, and was superseded by highway travel. A 1950s study of traffic problems in the Bay Area concluded the most cost-effec…