What are the different types of bases found in RNA?
What are the names of the 4 nitrogen bases in DNA?
- Adenine, abbreviated 'A,' has a 2-ring structure, so that makes it a purine.
- Thymine, abbreviated 'T,' is a pyrimidine, which means it has a 1-ring structure.
- Uracil, abbreviated 'U,' is found in RNA.
- Guanine, abbreviated 'G,' is part of both DNA and RNA, where it bonds with cytosine.
What are base pairs match up in RNA?
The base pairing of guanine (G) and cytosine (C) is just the same in DNA and RNA. So in RNA the important base pairs are: adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U); guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C). Transcription Transcription is the name given to the process where the information in a gene in a DNA strand is transferred to an RNA molecule.
What are the complementary bases of RNA?
noun Genetics.either of the nucleotide baseslinked by a hydrogen bond on opposite strands of DNA or double-stranded RNA: guanine is the complementary baseof cytosine, and adenine is the complementary baseof thymine in DNA and of uracil in RNA.
How does base pairing differ in RNA, compared to DNA?
- The base composition varies from one species to another.
- In a dsDNA and RNA, the no. of guanine is equal to the no. of cytosine.
- In a DNA the no. of adenine is equal to the no. Of thymine but in RNA the no. of adenine is equal to the no. of uracil

Is there base pairing in RNA?
Bases pair off together in a double helix structure, these pairs being A and T, and C and G. RNA doesn't contain thymine bases, replacing them with uracil bases (U), which pair to adenine1.
How many bases does DNA and RNA have?
four nitrogenousDNA and RNA molecules both contain four nitrogenous bases. Three of these (adenine, cytosine, and guanine) are found in both types of nucleic acid.
What are the base pairs in DNA and RNA?
In DNA Adenine-Thymine and Guanine-Cytosine pair together due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between the two bases. In RNA the base Thymine is not present, instead the base Uracil is present which has a very similar structure to Thymine.
What are the different base pairs of RNA?
In DNA/RNA base pairing, adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G).
What are the bases in RNA?
An RNA molecule has a backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and the sugar ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) or guanine (G).
How many base pairs are in DNA?
The four bases in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C).
What is difference RNA and DNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its own.
How are the bases in DNA and RNA different?
DNA and RNA base pairing is slightly different since DNA uses the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine; RNA uses adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Uracil differs from thymine in that it lacks a methyl group on its ring.
How do you find the number of base pairs?
Here it is given that, the length of the E.coli DNA is 1.36mm.We know the length of the DNA can be calculated by multiplying the number of base pairs into the distance between the basepairs.Thus, from this we can get, Number of base pairs = Length of DNA/ Distance between the base pairs.
Which base is only in RNA?
UracilExplanation: Uracil is a nitrogenous base that is only found in single-stranded RNA—it is not found in DNA. Thymine pairs with adenine in DNA, whereas in RNA, uracil pairs with adenine.
What are the 3 bases of tRNA called?
Roughly in the middle of the tRNA molecule is a sequence of three bases called the anticodon. These three bases are hydrogen bonded to a complementary sequence in an RNA molecule— called messenger RNA, mRNA— during protein synthesis. All tRNA molecules have the same basic L-shaped tertiary structures (Figure 30.20).
What are the 4 types of base pairs?
There are four nucleotides, or bases, in DNA: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C).
How are DNA and RNA different?
There are two differences that distinguish DNA from RNA: (a) RNA contains the sugar ribose, while DNA contains the slightly different sugar deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom), and (b) RNA has the nucleobase uracil while DNA contains thymine.
What are the 5 differences between DNA and RNA?
One of the primary differences between DNA and RNA is that DNA is double-stranded while RNA is single-stranded....Differences Between DNA and RNA.DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)RNA (Ribonucleic acid)Sugar portionIt has 2-deoxyribose.It has Ribose.Function11 more rows
Does DNA and RNA have thymine?
Figure 3: DNA (top) includes thymine (red); in RNA (bottom), thymine is replaced with uracil (yellow). Three of the four nitrogenous bases that make up RNA — adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) — are also found in DNA.
What is difference between RNA and DNA?
DNA and RNA perform different functions in humans. DNA is responsible for storing and transferring genetic information, while RNA directly codes for amino acids and acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins.
What are the base pairs of DNA?
The base pairs in DNA are adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine. In RNA, they are adenine to uracil and guanine to cytosine. A base pair is made of two nucleotides. The nucleotides, located on opposite strands of DNA or RNA, are drawn to each other in a hydrogen bond.
What is the name of the DNA base pair?
Every nucleotide in the coding strand has a complementary nucleotide in the other strand, called the template strand. The Watson-Crick pairs are the standard DNA and RNA base pairs.
What holds a strand together in a double helix?
These bonds are what hold the strand together in a double helix formation. The double structure is a redundancy that acts as a backup system to store genetic information. Base pairs facilitate transcription, which is the process whereby genetic information encoded in DNA is transferred to RNA.
Is uracil the same as thymine?
Uracil and thymine molecules are very similar in shape, allowing them to form the same kinds of hydrogen bonds with adenine. There are, however, some alternate bond pairs which result from other hydrogen bonds.
How many base pairs does a gene have?
We also count DNA and the amount of DNA, or the length of DNA by using units of base pairs, so if we're discussing a gene and we want to describe how big is a gene, we might say that the gene is a thousand base pairs long.
What is a base pair?
Base Pair. =. A base pair is two chemical bases bonded to one another forming a "rung of the DNA ladder.". The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), ...
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
So each DNA molecule is made up of two strands, and there are four nucleotides present in DNA: A, C, T, and G. And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other side of the strand, and this makes up the double helix.
How are adenine and cytosine held together?
The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine forming a base pair with thymine, and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine.
What are the three bases that make up RNA?
RNA contains the nucleotides adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil (U). When three continuous nucleotide bases code for an amino acid or signal the beginning or end of protein synthesis, the set is known as a codon. These triplet sets provide the instructions for the production of amino acids.
How many codons are there in RNA?
Any of the four nucleotides in RNA may occupy one of three possible codon positions. Therefore, there are 64 possible codon combinations. Sixty-one codons specify amino acids and three (UAA, UAG, UGA) serve as stop signals to designate the end of protein synthesis.
How does RNA translation work?
During translation, each RNA codon is read and the appropriate amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain by transfer RNA. The mRNA molecule will continue to be translated until a termination or stop codon is reached.
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is a sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA and RNA that code for the production of specific amino acids. Amino acids are linked together to form proteins.
What is the genetic code of a protein?
Updated November 05, 2019. The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotide bases in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) that code for amino acid chains in proteins. DNA consists of the four nucleotide bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). RNA contains the nucleotides adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil (U).
What are the four bases that are stored in DNA?
Genetic information is stored as long, complex sequences of the four different bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ( C). Triplets of these bases are interpreted by the genetic machinery as instructions to add a certain amino acid to a protein.
What is the name of the enzyme that transcribes DNA into a single stranded RNA poly?
Certain proteins called transcription factors unwind the DNA strand and allow the enzyme RNA polymerase to transcribe only a single strand of DNA into a single stranded RNA polymer called messenger RNA (mRNA). When RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA, guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with uracil.
Overview
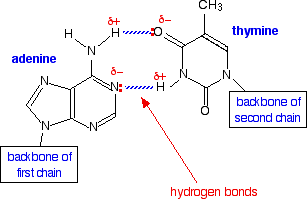
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and
Hydrogen bonding and stability
Hydrogen bonding is the chemical interaction that underlies the base-pairing rules described above. Appropriate geometrical correspondence of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors allows only the "right" pairs to form stably. DNA with high GC-content is more stable than DNA with low GC-content. But, contrary to popular belief, the hydrogen bonds do not stabilize the DNA significantly; stabilization is mainly due to stacking interactions.
Base analogs and intercalators
Chemical analogs of nucleotides can take the place of proper nucleotides and establish non-canonical base-pairing, leading to errors (mostly point mutations) in DNA replication and DNA transcription. This is due to their isosteric chemistry. One common mutagenic base analog is 5-bromouracil, which resembles thymine but can base-pair to guanine in its enol form.
Other chemicals, known as DNA intercalators, fit into the gap between adjacent bases on a singl…
Mismatch repair
Mismatched base pairs can be generated by errors of DNA replication and as intermediates during homologous recombination. The process of mismatch repair ordinarily must recognize and correctly repair a small number of base mispairs within a long sequence of normal DNA base pairs. To repair mismatches formed during DNA replication, several distinctive repair processes have evolved to distinguish between the template strand and the newly formed strand so that on…
Unnatural base pair (UBP)
An unnatural base pair (UBP) is a designed subunit (or nucleobase) of DNA which is created in a laboratory and does not occur in nature. DNA sequences have been described which use newly created nucleobases to form a third base pair, in addition to the two base pairs found in nature, A-T (adenine – thymine) and G-C (guanine – cytosine). A few research groups have been searching for a third base pair for DNA, including teams led by Steven A. Benner, Philippe Marliere, Floyd E. …
Non-canonical base pairing
In addition to the canonical pairing, some conditions can also favour base-pairing with alternative base orientation, and number and geometry of hydrogen bonds. These pairings are accompanied by alterations to the local backbone shape.
The most common of these is the wobble base pairing that occurs between tRN…
Length measurements
The following abbreviations are commonly used to describe the length of a D/RNA molecule:
• bp = base pair—one bp corresponds to approximately 3.4 Å (340 pm) of length along the strand, and to roughly 618 or 643 daltons for DNA and RNA respectively.
• kb (= kbp) = kilo–base-pair = 1,000 bp
See also
• List of Y-DNA single-nucleotide polymorphisms
• Non-canonical base pairing
• Chargaff's rules