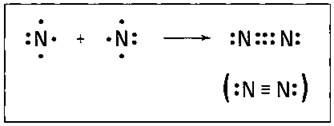
How many bonds is a triple bond?
three covalent bondsTriple bonds consist of three covalent bonds between two atoms, where each bond shares two electron pairs, making a total of six electrons being shared. A covalent bond is when two electrons (an electron pair) are shared between two atoms.
What makes a triple bond?
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order of three.
Is a triple bond 3 covalent bonds?
noun Chemistry. a chemical linkage consisting of three covalent bonds between two atoms of a molecule, represented in chemical formulas by three lines or six dots, as CH≡CH or CH⋮⋮CH.
Do triple bonds count as one bond?
Double and triple bonds still count as being only bonded to one atom.
What is a triple bond called?
Alkynes are hydrocarbons which contain carbon-carbon triple bonds. Their general formula is CnH2n-2 for molecules with one triple bond (and no rings).
What does triple bond mean?
triple bond, in chemistry, a covalent linkage in which two atoms share three pairs of electrons, as in the nitrogen molecule, N2, or acetylene, C2H2.
What is the difference between 3 single bonds and a triple bond?
The number of shared electrons is the major distinction between single double and triple bonds. A single bond is formed when two atoms share one pair of electrons, whereas a double bond is formed when two atoms share two pairs (four electrons). Three pairs of electrons (six atoms) are shared to form triple bonds.
What is an example of a triple bond?
Some atoms form triple bonds with one another by sharing three pairs of electrons. For example, nitrogen form a triple covalent bond, by sharing three pairs of electrons with another.
Can covalent bonds have 3 atoms?
However, the carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms can bond to more than one atom. The number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. The valence of a given atom is the same in most stable neutral organic compounds....Covalent Bonds.AtomValenceSulfur2Nitrogen3Carbon46 more rows
Does 2 have a triple bond?
In the O2 molecule both the oxygen atoms attain stabilization by forming two covalent bonds with each other. There is no necessity to share more electrons to form a triple bond. So is O2 a triple bond, No, O2 is not a triple bond.
Does double bonds count as one bond?
carbon (CO2)—three bonds (double bond counts as one bond), no lone pairs; trigonal planar.
How do you know if it's a triple or double bond?
If the shared number is one pair of electrons, the bond will be a single bond, whereas if two atoms bonded by two pairs (four electrons), it will form a double bond. Triple bonds are formed by sharing three pairs (six atoms) of electrons.
How do you identify a triple bond?
A triple bond is denoted by three parallel dashes between two atoms; ex: C≡C. Some examples of compounds with triple bonds include nitrogen gas (N≡N), cyanide ion (C≡N), acetylene (CH≡CH) and carbon monoxide (C≡O).
How do you know if something has a triple bond?
The number of shared electrons is the major distinction between single double and triple bonds. A single bond is formed when two atoms share one pair of electrons, whereas a double bond is formed when two atoms share two pairs (four electrons). Three pairs of electrons (six atoms) are shared to form triple bonds.
How do you know if a bond is double or triple?
If the shared number is one pair of electrons, the bond will be a single bond, whereas if two atoms bonded by two pairs (four electrons), it will form a double bond. Triple bonds are formed by sharing three pairs (six atoms) of electrons.
How many electrons make a triple bond?
Hence, when a triple bond is formed between two atoms, three electron pairs, i.e., six electrons are shared between the two atoms.
How many covalent bonds does carbon have?
As per the Valence Bond Theory, carbon should produce two covalent bonds by resulting in a CH2 due to the reason it has two unpaired electrons in its electronic configuration. However, some experiments have already shown that CH2 is highly reactive and it cannot exist outside of a reaction. Thus, this does not explain how the CH4 can exist. To produce four bonds, the carbon’s configuration must contain four unpaired electrons.
How many orbitals are there in acetylene?
The bonding types may be explained in terms of orbital hybridization. In the acetylene case, every carbon atom contains two p-orbitals and two sp-orbitals. The two p-orbitals are perpendicular on both the y-axis and z-axis. At the same time, the two sp-orbitals lie linear with 180° angles and occupy the x-axis (cartesian coordinate system). When the carbon atoms approach each other, the sp orbitals overlap to make an sp-sp sigma bond. The Pz-orbitals, at the same time, approach, and together, they produce a Pz-Pz pi-bond. Similarly, the other pair of Py-orbitals produce a Py-Py pi-bond. The result is the formation of one sigma-bond and two pi-bonds.
What is SP3 hybridization?
In it, both the 2s orbitals and all the three of 2p orbitals hybridize to make four sp3 orbitals, each consisting of 75% of p character and 25% of s character. And, the frontal lobes align themselves in a manner as represented below. In this particular structure, electron repulsion is minimized.
What are double bonds and triple bonds?
Answer: Both the double bonds and triple bonds are composed of sigma bonds between the hybridized orbitals and pi-bonds between the unhybridized p-orbitals. These double and triple bonds offer an added stability to the compounds and restrict any rotation across the bond axis.
How many SP3 orbitals are there?
The s-orbital’s hybridization with all the three p orbitals (Px, Py, and Pz) results in four sp3 hybrid orbitals. And, the sp3 hybrid orbitals are oriented at a bond angle of 109.5° from each other. This particular 109.5° arrangement gives the tetrahedral geometry as figured above.
Why do atoms form chemical bonds?
Answer: Atoms form chemical bonds because they make their outer electron cells more stable. An ionic bond, where one atom importantly donates an electron to another and forms when one atom becomes stable by losing its outer electron. In contrast, the other atom becomes stable (generally, by feeling its valence shell) by gaining the electron.
What is triple bond?
In chemistry, a triple bond is defined as a covalent linkage, where two atoms share three pairs of electrons, as in the nitrogen molecule, acetylene, C2H2, or N2. One of the main electron pairs exists in a sigma bond, which is concentrated in the region along the line joining the two nuclei; the remaining two pairs are available in pi bonds, each of which occupies the two parallel regions of space on the opposite sides of the line that is determined by the two atoms.
What is the difference between a pi and a sigma bond?
Sigma bond is head on overlap of the two orbitals whereas pi is sideways overlap of two orbitals. The thumb rule is two atoms participating in a bond formation can have only 1 sigma.
How many sigma bonds are there in a compound?
Usually, all bonds between atoms in most organic compounds contain one sigma bond each. If it is a single bond, it contains only sigma bond. Multiple bonds (double and triple), however, contains sigma and pi bonds. Double bonds have one each, and triple bonds have one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
How is a sigma bond formed?
Beacuse sigma bond is formed by head-on overlapping of atomic orbitals. And in any type of bond only one head-on overlapping is possible. So the rest are pi bond. So simple…. Isn't it??
How many orbitals does acetylene have?
In the case of acetylene each carbon atom has two sp orbitals (hybridised) and two p-orbitals (pure).The two sp orbitals are linear with 180° angles and occupy the x-axis (cartesian coordinate system). The p-orbitals are perpendicular on the y-axis and the z-axis.
What is the second pi bond?
A second pi bond (the third bond in a triple bond, or a second double bond to another atom) is always perpendicular (orthogonal) to the first one. In other words, if the sigma bond is on the x axis, one pi bond will form between orbitals on the y axis and another will form between orbitals on the z axis.
What is a triple bond?
A single bond is a sigma bond. A double bond is a sigma bond plus a pi bond. A triple bond is one sigma and two pi bonds.
Which is stronger, the sigma bond or the pi bond?
The sigma bond is stronger than the pi bond because, in the sigma bond there is a direct overlap of the orbitals
Bonding
Example of A Triple Bond Formation
- Formation of Triple bond in Carbon One of the perfect triple bond examples representing the value of hybrid orbitals is Carbon. The ground state configuration of Carbon is given as follows: Imagewillbeuploadedsoon As per the Valence Bond Theory, carbon should produce two covalent bonds by resulting in a CH2due to the reason it has two unpaired electrons in its electronic confi…
Sp3hybridization
- sp3hybridization may explain the tetrahedral structure of the molecules. In it, both the 2s orbitals and all the three of 2p orbitals hybridize to make four sp3orbitals, each consisting of 75% of p character and 25% of s character. And, the frontal lobes align themselves in a manner as represented below. In this particular structure, electron repulsion is minimized. Energy changes …
Stability of Triple Bond Compared to A Single Bond
- In the case of covalent molecules, more is the sharing of electrons between the atoms; stronger is: a single bond 2 electrons are shared, in a manner, 4 in double bond and 6 in a triple bond. Therefore, a triple bond is the strongest and most difficult to break. Now, the stronger the bond between the two atoms, the stabler (or more stable) the mole...
Rotation of A Triple Bond
- Yes, the rotation of a triple bond takes place. Only a single p-orbital is involved in the sp hybridization in acetylene. The other two mutually perpendicular P-orbitals, say Pz, Py can rotate, replacing each other's axis (on rotation, Pz becomes Py and Py becomes Pz). However, practically it is meaningless and merely detected because there is no formation of a new compound and th…