
Assuming that the chromosomes have replicated there should be ten centromeres. Centromeres are the point at which two replicated sister chromatids are attached and only appear when DNA replication occurs. Meaning that the normal number of chromosomes in the cell should be 10 and there should normally be 5 chromosome pairs.
How does a centrosome help a cell?
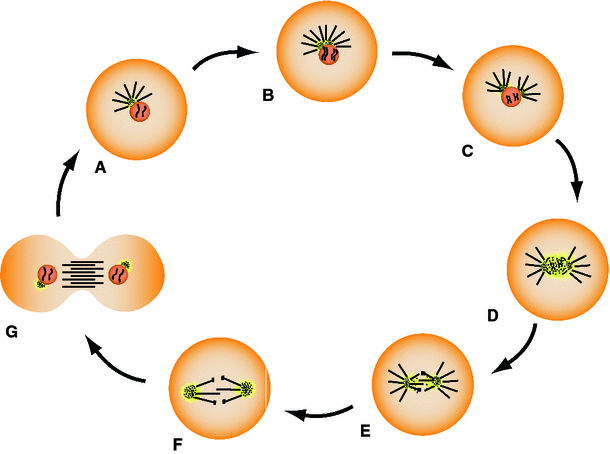
Centrosomes help regulate mitosis, the process by which one cell separates into two identical copies of the original.There are four phases in the cell cycle. In G1 phase, the cell grows and prepares to replicate chromosomes.In S-phase, DNA is replicated. In G2, further preparations are made for the last phase, called M-phase, in which mitosis occurs.
How many chromosomes move to each pole of the cell?
homologous chromosomes are pulled apart and move towards opposite ends of the cell. Do not confuse this with the pulling apart of sister chromatids! This is the point in which reduction occurs with 23 chromosomes moving to each pole. All possible combinations of genetic material are created from the independent assortment.
How many centrioles are present in a dividing cell?
So a dividing cell will have 2 pairs of centrioles, for a total of Four centrioles. Hope that answered the question. Prior to cell division the replicating cell contains two centrioles. As the cell divides, the centrioles divide too so that after cell division the mother and daughter cells will each have two centrioles.
What does cell have a centrosome?
The centrosome is an organelle present in an animal cell that acts as the microtubule-organizing centre of the cell. It also regulates the cell cycle. What is the main function of a centrosome?

How many centrosomes are there in a cell?
two centrosomesCentrosome duplication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, and by the time a cell enters mitosis, it contains two centrosomes, which will form the poles of the bipolar mitotic spindle.
Is there only one centrosome in a cell?
The centrosome is copied only once per cell cycle, so that each daughter cell inherits one centrosome, containing two structures called centrioles. The centrosome replicates during the S phase of the cell cycle.
How many centrosomes do humans have?
Before cell division, the centrosome duplicates and then, as division begins, the two centrosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. Proteins called microtubules assemble into a spindle between the two centrosomes and help separate the replicated chromosomes into the daughter cells.
How many centrosomes are in mitosis?
two centrosomesThe mitotic spindle also begins to develop during prophase. As the cell's two centrosomes move toward opposite poles, microtubules gradually assemble between them, forming the network that will later pull the duplicated chromosomes apart.
How many centrosomes are in G2?
two centrosomesDisassembly of the GGT occurs in G2, when the two centrosomes (each comprised of a pair of engaged centrioles) separate in preparation for assembly of the mitotic spindle.
Do all cells have centrosome?
The centrosome acts as the main microtubule-nucleating organelle in animal cells and plays a critical role in mitotic spindle orientation and in genome stability. Yet, despite its central role in cell biology, the centrosome is not present in all multicellular organisms or in all cells of a given organism.
Is centrosome and centriole same?
Within the cell, a centrosome is a structure that organizes microtubules during cell division. Each centrosome contains “paired barrel-shaped organelles” called centrioles and a “cloud” of proteins referred to as the pericentriolar material, or PCM.
What happens if there are too many centrosomes?
Hence, the presence of extra centrosomes appears to interfere with the spindle orientation and asymmetric division important for early development.
How many centrioles usually a centrosome contains?
two centriolesThe centrosome is a cellular organelle that is composed of two centrioles surrounded by pericentriolar material and is involved in diverse cellular processes including sensory reception, locomotion, and embryogenesis (Clift & Schuh, 2013).
How many centrosomes are in g1 phase?
G1 phase cells possess a single centrosome containing two centrioles (Fig. 2). In a normal somatic cell cycle centrosome duplication is first visible during early S-phase, when a new procentriole assembles next to the proximal end of each parental centriole.
Why are there two copies of the centrosomes?
Since spindle polarity in higher animal cells is usually dependent upon the number of centrosomes present, the cell must have exactly two centrosomes by the onset of mitosis or else mitotic defects will occur that can have disastrous consequences for the organism (reviewed in Brinkley, 2001; Rieder et al., 2001).
Do centrosomes duplicate?
Centrosome duplication Centrosomes are only supposed to replicate once in each cell cycle and are therefore highly regulated. The centrosome cycle has been found to be regulated by multiple things, including reversible phosphorylation and proteolysis.
How many centrioles are in a centrosome?
The centrosome is copied only once per cell cycle, so that each daughter cell inherits one centrosome, containing two structures called centrioles. The centrosome replicates during the S phase of the cell cycle. During the prophase in the process of cell division called mitosis, the centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
What are centrosomes associated with?
Functions. Centrosomes are associated with the nuclear membrane during the prophase stage of the cell cycle. During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the centrosome-nucleated microtubules can interact with the chromosomes to build the mitotic spindle . The mother centriole, the older of the two in the centriole pair, ...
How is centrosome doubling similar to DNA replication?
Doubling of a centrosome is similar to DNA replication in two respects: the semiconservative nature of the process and the action of CDK2 as a regulator of the process. But the processes are essentially different in that centrosome doubling does not occur by template reading and assembly.
Why do centrosomes have a function?
The function of centrosomes in this context is hypothesized to ensure the fidelity of cell division, because it greatly increases the efficacy. Some cell types arrest in the following cell cycle when centrosomes are absent. This is not a universal phenomenon.
What are the proteins in the PCM?
The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring — including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based on a nine-triplet microtubule assembled in a cartwheel structure, and contains centrin, cenexin and tektin.
What is replaced by the centrosome?
In many cell types, the centrosome is replaced by a cilium during cellular differentiation. However, once the cell starts to divide, the cilium is replaced again by the centrosome.
What is the centrosome?
The structure of the centrosome. The generalized structure and molecular components of a cell. In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (also called cytocenter) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression.
How many chromosomes are in a human cell?
Learn more. In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differ between males and females.
How many copies of chromosomes do females have?
Females have two copies of the X chromosome, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. The 22 autosomes are numbered by size. The other two chromosomes, X and Y, are the sex chromosomes. This picture of the human chromosomes lined up in pairs is called a karyotype. Credit: U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Where is the centromere located?
When you look at the chromosomes, there's a part that is not always right in the middle, but it's somewhere between one-third and two-thirds of the way down the chromosome. It's called the centromere. That's the part where the cell's chromosomes are constricted, and they're a little bit tighter, and it almost looks like a little ball in ...
What is the centromere in cytogenetics?
And these P and Q arms are a part of what we use when we do cytogenetics to say how many chromosomes are present in a cell and what chromosome number they are.
Why are chromosomes held together during cell division?
During cell division, this is the place where the chromosomes, when they're undergoing replication, that they're held together so that the chromosomes don't lose their sister chromatid during the cell division process . Julie A. Segre, Ph.D.
What is the name of the region of a chromosome that separates into a short arm and
Centromere. A centromere is a constricted region of a chromosome that separates it into a short arm (p) and a long arm (q). During cell division, the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Overview
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (also called cytocenter ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants la…
History
The centrosome was discovered jointly by Walther Flemming in 1875 and Edouard Van Beneden in 1876, and later described and named in 1888 by Theodor Boveri.
Functions
Centrosomes are associated with the nuclear membrane during the prophase stage of the cell cycle. During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the centrosome-nucleated microtubules can interact with the chromosomes to build the mitotic spindle.
The mother centriole, the older of the two in the centriole pair, also has a centr…
Centrosome alterations in cancer cells
Theodor Boveri, in 1914, described centrosome aberrations in cancer cells. This initial observation was subsequently extended to many types of human tumors. Centrosome alterations in cancer can be divided in two subgroups — i.e., structural or numeric aberrations — yet both can be found simultaneously in a tumor.
Usually, structural aberrations appear due to uncontrolled expression of centrosome component…
Evolution
The evolutionary history of the centrosome and the centriole has been traced for some of the signature genes — e.g., the centrins. Centrins participate in calcium signaling and are required for centriole duplication. There exist two main subfamilies of centrins, both of which are present in the early-branching eukaryote Giardia intestinalis. Centrins have therefore been present in the common ancestor of eukaryotes. Conversely, they have no recognizable homologs in archea and b…
Associated nucleotides
Research in 2006 indicated that centrosomes from Atlantic surf clam eggs contain RNA sequences. The sequences identified were found in "few to no" other places in the cell, and do not appear in existing genome databases. One identified RNA sequence contains a putative RNA polymerase, leading to the hypothesis of an RNA-based genome within the centrosome. However, subsequent research has shown that centrosome do not contain their own DNA-based genomes. While it wa…