
How many members of Congress does the NRA own?
- Mark Amodei (R-NV)- $4,000
- Larry Bucshon (R-IN)- $4,000
- Ben Chandler (Blue Dog-KY)- $4,000
- Howard Coble (R-NC)- $4,000
- Tim Griffin (R-AR)- $4,000
- Jeff Miller (R-FL)- $4,000
- Kevin Yoder (R-KS)- $4,000
- Morgan Griffith (R-VA)- $4,150
- Marsha Blackburn (R-TN)- $4,500
- Lamar Smith (R-TX)- $4,500
What did the Continental Congresses do?
The Continental Congress was the governing body by which the American colonial governments coordinated their resistance to British rule during the first two years of the American Revolution. The Congress balanced the interests of the different colonies and also established itself as the official colonial liaison to Great Britain.
What was the First Continental Congress called?
The First Continental Congress was called to address grievances against the British government. The Second Continental Congress was initially called for the same reason, but once it voted to declare independence it acted as the defacto government of an independent nation.
How many times did the Continental Congress meet?
The Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from each of the thirteen American colonies. These delegates served as the government during the Revolutionary War. Secondly, why did the Second Continental Congress meet and what did they decide? In May 1775, with Redcoats once again storming Boston, the Second Continental Congress convened in
Was there a 3rd Continental Congress?
Hosted by the political interest group Freedom Watch, the Third Continental Congress featured several well-known figures in the American conservative movement, including Freedom Watch founder Larry Klayman, former Maricopa County Sheriff Joe Arpaio, and former Reagan administration official Alan Keyes.
How many Continental Congresses did the colonists setup?
During the Revolutionary War, the Continental Congress became America's de facto government. During the Revolutionary War, the Continental Congress became America's de facto government.
What were the First and Second Continental Congresses?
The First Continental Congress, comprised of delegates from the colonies, met in 1774 in reaction to the Intolerable Acts, a series of measures imposed by the British government after the colonies resisted new taxes. In 1775, the Second Continental Congress convened after the Revolutionary War had already begun.
Did the First and Second Continental Congresses take?
The First Continental Congress organized a boycott of British goods. The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain.
Were there 12 or 13 original colonies?
The United States of America initially consisted of 13 states that had been British colonies until their independence was declared in 1776 and verified by the Treaty of Paris in 1783: New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, ...
What were 3 successes of the Continental Congress?
The First Continental Congress had a series of successes; however, the three most important were (1) colonial unity, (2) non-importation and exportation act, and (3) laying the basis for a future meeting.
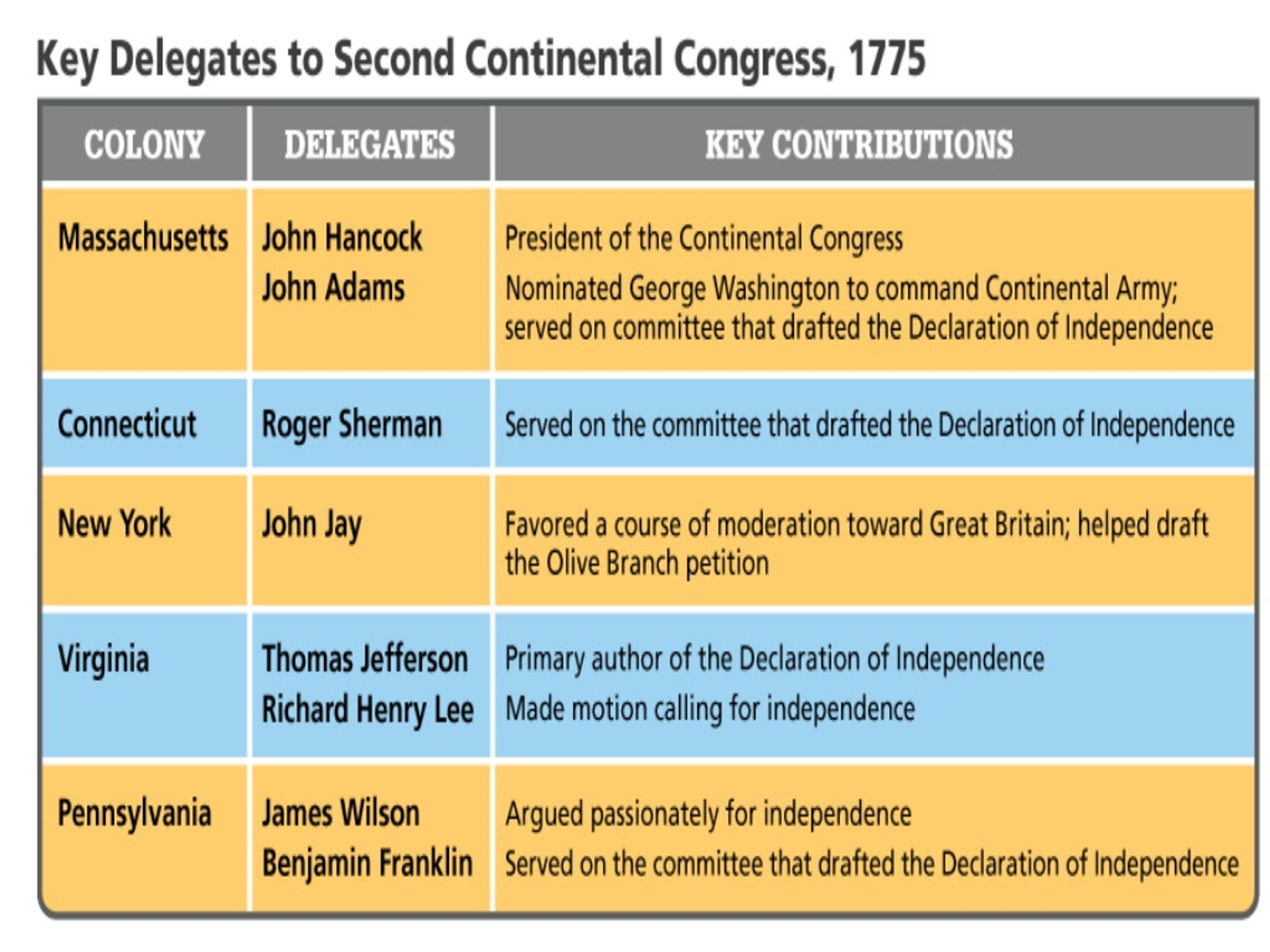
Who attended the 2nd Continental Congress?
New members of the Second Congress included Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson. John Hancock and John Jay were among those who served as president.
Why was it called the Continental Army?
The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the Colonies in their war for independence against the British, who sought to keep their American lands under control....Continental ArmyFounderSecond Continental CongressCommander-in-ChiefGeorge WashingtonDates of operationJune 14, 1775 – 17837 more rows
When was the 2nd Continental Congress?
May 1775The Second Continental Congress met inside Independence Hall beginning in May 1775. It was just a month after shots had been fired at Lexington and Concord in Massachusetts, and the Congress was preparing for war.
Was the shot heard round the world?
DeCosta July 29, 1775. The first shots were fired just after dawn in Lexington, Massachusetts the morning of the 19th, the "Shot Heard Round the World." The colonial militia, a band of 500 men, were outnumbered and initially forced to retreat.
Who ruled America in 1776?
The Second Continental Congress issued the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. Under the leadership of General George Washington, the Continental Army and Navy defeated the British military securing the independence of the thirteen colonies.
Why are they called Minutemen?
Minutemen were members of the organized New England colonial militia companies trained in weaponry, tactics, and military strategies, comprising the American colonial partisan militia during the American Revolutionary War. They were known for being ready at a minute's notice, hence the name.
When was the 2nd Continental Congress?
May 1775The Second Continental Congress met inside Independence Hall beginning in May 1775. It was just a month after shots had been fired at Lexington and Concord in Massachusetts, and the Congress was preparing for war.
What did the 2nd Continental Congress do?
The Second Continental Congress assumed the normal functions of a government, appointing ambassadors, issuing paper currency, raising the Continental Army through conscription, and appointing generals to lead the army.
Who attended the 2nd Continental Congress?
New members of the Second Congress included Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson. John Hancock and John Jay were among those who served as president.
In which colony were the 1st shots of the Revolutionary War fired?
April 19, 2020 marked the 245th anniversary of the first shot of the Revolutionary War – later called the “shot heard round the world” by American poet Ralph Waldo Emerson – at the Old North Bridge in Concord, Massachusetts.
Why did the Continental Congress meet?
The First Continental Congress, which was comprised of delegates from the colonies, met in 1774 in reaction to the Coercive Acts, a series of measures imposed by the British government on the colonies in response to their resistance to new taxes. In 1775, the Second Continental Congress convened after the American Revolutionary War (1775-83) ...
What was the purpose of the first Continental Congress?
On September 5, 1774, delegates from each of the 13 colonies except for Georgia (which was fighting a Native American uprising and was dependent on the British for military supplies) met in Philadelphia as the First Continental Congress to organize colonial resistance to Parliament’s Coercive Acts.
What was the Continental Congress's role in the war against Great Britain?
Declaring Independence. For over a year, the Continental Congress supervised a war against a country to which it proclaimed its loyalty. In fact, both the Congress and the people it represented were divided on the question of independence even after a year of open warfare against Great Britain.
What was the first direct tax imposed on the colonies?
Americans throughout the 13 colonies united in opposition to the new system of imperial taxation initiated by the British government in 1765. The Stamp Act of that year–the first direct, internal tax imposed on the colonists by the British Parliament–inspired concerted resistance within the colonies.
What was the only political institution that united the colonies?
Throughout most of colonial history, the British Crown was the only political institution that united the American colonies. The Imperial Crisis of the 1760s and 1770s, however, drove the colonies toward increasingly greater unity.
What was the purpose of the Congress?
The Congress was structured with emphasis on the equality of participants, and to promote free debate. After much discussion, the Congress issued a Declaration of Rights, affirming its loyalty to the British Crown but disputing the British Parliament’s right to tax it.
When did the American Revolution begin?
As promised, Congress reconvened in Philadelphia as the Second Continental Congress on May 10, 1775 –and by then the American Revolution had already begun. The British army in Boston had met with armed resistance on the morning of April 19, 1775, when it marched out to the towns of Lexington and Concord to seize a cache of weapons held by colonial Patriots who had ceased to recognize the authority of the royal government of Massachusetts. The Patriots drove the British expedition back to Boston and laid siege to the town. The Revolutionary War had begun.
How many delegates were there in the first Continental Congress?
In response, the Committees of Congress called for a meeting of delegates. On September 5, 1774, 56 delegates met in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This First Continental Congress represented all the 13 colonies, except Georgia. It included some of the finest leaders in the land, including George Washington, Patrick Henry, John Adams, Samuel Adams, ...
What was the Continental Congress?
Encyclopedic Entry. Vocabulary. The Continental Congress was a group of delegates who worked together to act on behalf of the North American colonies in the 1770s. Beginning with the Sugar Act in 1764, the British Parliament passed a series of laws that were unpopular with many colonists in the North American colonies.
Why did the Continental Congress meet in the 1770s?
In the 1770s, the Continental Congress, composed of many of the United States' eventual founders, met to respond to a series of laws passed by the British Parliament that were unpopular with many of the colonists.
What rights did the colonies have?
At this meeting, the Congress adopted a Declaration of Rights and Grievances. They declared that their rights as Englishmen included life, liberty, property, and trial by jury .
Which group drafted the Articles of Confederation?
The Congress drafted the Articles of Confederation, the first constitution of the United States, which went into effect in 1781. Under this government, the Continental Congress gave way to the Confederation Congress, which included many of the same delegates. This group continued to provide leadership to the new country until a new Congress, ...
Where did the British and American colonies meet?
By the time this Second Continental Congress convened, hostilities had already broken out between British troops and its American colonists at Lexington, Massachusetts, and Concord, Massachusetts.
What was the Continental Congress?
The Continental Congress was an itinerant legislature, often moving to escape British forces during the Revolutionary War. All told, Delegates met in nine different locations between 1774 and 1789.
When did the first Continental Congress convene?
When the First Continental Congress convened in Philadelphia on September 5, 1774 , the Delegates elected a presiding officer to oversee the revolutionary legislature’s sessions.
What was the legacies of the Continental and Confederation Congresses?
One of the legacies of the Continental and Confederation Congresses was the convening of the Federal Convention of 1787.
What was the purpose of the first Continental Congress?
From 1774 to 1781, Delegates from the 13 colonies located along the eastern seaboard of British North America met in the First Continental Congress (1774) and the Second Continental Congress (1775–1781) to declare their independence from England, manage the Revolutionary War , and set the groundwork for what would become a new nation.
Why did the Delegates meet in the Confederation Congress?
Following the ratification of the Articles of Confederation, which created a limited central governing structure, Delegates from the states met in the Confederation Congress (1781–1789) to chart a path forward with their newfound freedom.
When did the Articles of Confederation become a law?
When the Articles of Confederation proved unable to meet the needs of the young country, states sent Delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in the summer of 1787 to draft a new, stronger governing document, creating the United States of America and its federal legislature, including the House of Representatives.
How many members of the Continental Congress were there?
The First Continental Congress gave the patriot cause greater breadth, depth, and force. Its 56 members, representing all of the colonies except Georgia, were lawyers, country gentlemen, and merchants, respectable and responsible men, and America followed them. They made it clear that…
When did the Continental Congress meet?
When the Continental Congress met in 1774, members did not have to debate procedure (except on voting); they already knew it. Finally, the Congress’s authority was rooted in traditions of legitimacy. The old election laws were used. Voters could transfer their allegiance with minimal difficulty from the…
What was the purpose of the first Continental Congress?
To provide unity, delegates gave one vote to each state regardless of its size. The First Continental Congress included Patrick Henry, George Washington, John and Samuel Adams, John Jay, and John Dickinson. Meeting in secret session, the body rejected a plan for reconciling British authority with colonial freedom. Instead, it adopted a declaration of personal rights, including life, liberty, property, assembly, and trial by jury. The declaration also denounced taxation without representation and the maintenance of the British army in the colonies without their consent. Parliamentary regulation of American commerce, however, was willingly accepted.
Who were the members of the Second Congress?
New members of the Second Congress included Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson. John Hancock and John Jay were among those who served as president. The Congress “adopted” the New England military forces that had converged upon Boston and appointed Washington commander in chief of the American army on June 15, 1775.
When was the Declaration of Independence signed?
The members of the Continental Congress signed the Declaration of Independence in Philadelphia on July 4, 1776. Architect of the Capitol. The Articles placed Congress on a constitutional basis, legalizing the powers it had exercised since 1775.
How long did the Continental Congress last?
Over a period of 15 years, from 1774 to 1789, the Continental Congress underwent a profound evolution. Starting out as a temporary group that met to address American colonists’ issues with British rule, it morphed into the de facto government of the 13 colonies, and ultimately into an official governing body of the United States.
What was the purpose of the Continental Congress?
It focused mainly on how to respond to the British Parliament’s passage of the Intolerable Acts—also known as the Coercive Acts —a series of repressive acts designed to restore order to Boston after the Tea Party and punish the colonists for their bold insurrection. During its short meeting time, the Continental Congress compiled a list of grievances that it sent to Britain’s then-ruler, King George III. It also adopted the Articles of Association, which initiated a boycott of British goods by the colonies.
What powers did the Confederation Congress have?
Congress we have today. The Confederation Congress couldn’t tax Americans and , in many cases, needed nine of the 13 states to approve legislation before a bill could pass.
What was the first Continental Congress' most important accomplishment?
The Articles of Association stand as the First Continental Congress’s most important accomplishment, says Benjamin H. Irvin, a history professor at Indiana University Bloomington and author of Clothed in Robes of Sovereignty: The Continental Congress and the People Out of Doors. In addition to the boycott, the document authorized the creation of local committees to help with the transfer of power between Britain and the colonies.
What was the most important accomplishment of the Second Continental Congress?
The Second Continental Congress’s most significant achievement? The adoption of the Declaration of Independence, which it ratified on July 4, 1776.
When was the Declaration of Independence signed?
The signing of the Declaration of Independence in Philadelphia on July 4th, 1776.
Who were the members of the Confederation?
Members who served terms on the Confederation Congress included James Madison and Alexander Hamilton, who were also two of the 55 delegates that attended the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. The members of that convention drafted a new constitution that, when it became law in 1789, replaced the Articles of Confederation and disbanded the Confederation Congress, replacing it with the U.S. Congress.
How many delegates were there in the Continental Congress?
Altogether, The Biographical Directory of the United States Congress lists 343 men who served as delegates to the Continental Congress in three incarnations from 1774 to 1789; also listed are another 90 persons who were elected as delegates but never served.
What was the Continental Congress?
The Continental Congress was initially a convention of delegates from several British American colonies at the height of the American Revolution era, who spoke and acted collectively for the people of the Thirteen colonies that ultimately became the United States of America. The term mostly refers to the First Continental Congress ...
Why did the British organize the First Continental Congress?
They organized an economic boycott of Great Britain in protest and petitioned the king for a redress of grievances. They also resolved to reconvene in May 1775 if necessary.
What was the unicameral Congress?
The unicameral Congress of the Confederation, officially styled "The United States in Congress Assembled," was composed of delegates elected by the legislature of the various states. The Confederation Congress was the immediate successor to the Second Continental Congress; and delegates to it were similarly chosen.
How many votes does each state have?
In determining questions in the United States in Congress assembled, each State shall have one vote.
How many people were elected to Congress?
The following table lists the 90 people who were elected to Congress: 1st Continental, 2nd Continental, or Confederation, between 1774 and 1789, but who did not participate, as well as the year (s) of their election.
When did the Articles of Confederation come into force?
When the Articles of Confederation came into force on March 1, 1781, after being ratified by all 13 states, the Continental Congress became the Congress of the Confederation, which helped guide the new nation through the final stages of the Revolutionary War.
Who was the first president of the Continental Congress?
The first president of the Continental Congress was Virginia Delegate Peyton Randolph, who had previously served as speaker of the Virginia house of burgesses. 1. Following the creation of the Articles of Confederation, the Confederation Congress convened on March 2, 1781. Like the Continental Congress, the Confederation Congress elected ...
When did the Confederation Congress meet?
Sep. 28, 1779–Mar. 1, 1781 8. Following the creation of the Articles of Confederation, the Confederation Congress convened on March 2, 1781. Like the Continental Congress, the Confederation Congress elected a president to preside over its debates. On the whole, however, the Confederation Congress president had far fewer responsibilities, ...
What was the role of the presiding officer in the first Continental Congress?
When the First Continental Congress convened in Philadelphia on September 5, 1774, the Delegates elected a presiding officer to oversee the revolutionary legislature’s sessions. Given the title of “president,” this officer’s responsibilities included ruling on parliamentary issues, managing official correspondence, ...
Why did Samuel Johnston resign from the Continental Congress?
8 JCC, 1774–1789, vol. 15: 1114; JCC, 1774–1789, vol. 19: 223; JCC, 1774–1789, vol. 20: 724. Resigned due to “ill state of health.” Delegate Samuel Johnston of North Carolina was elected president on July 9, but “declined to accept the office of President,” on July 10; JCC, 1774–1789, vol. 20: 732–733. On March 1, 1781, the Continental Congress ratified the Articles of Confederation and became known as the Confederation Congress.

Taxation Without Representation
The First Continental Congress
The Revolutionary War
Fighting For Reconciliation
Declaring Independence
Waging The War
The Articles of Confederation
- Congress’s inability to raise revenue would bedevil it for its entire existence, even after it created a constitution–the Articles of Confederation–to define its powers. Drafted and adopted by the Congress in 1777 but not ratified until 1781, it effectively established the U.S. as a collection of 13 sovereign states, each of which had an equal voic...