In 500 BC, Rome was a minor city-state on the Italian peninsula. By 200 BC, the Roman Republic had conquered Italy, and over the following two centuries it conquered Greece and Spain, the North African coast, much of the Middle East, modern-day France, and even the remote island of Britain. What countries were controlled by the Romans?
How many countries did Rome conquer in modern times?
Related Questions More Answers Below. Rome conquered the following countries in modern times in this order with their general: (Romulus)Italy, (Iulus) Switzerland (Scipio) Balkan states (Scipio Africanus) North Africa, Spain, and Portugal (Caesar)France, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Lichtenstein, Monaco, Papal States,...
How many countries were part of the Roman Empire?
These are the countries that were partially or wholly part of the Roman Empire. The Roman Empire wiped out at least about 50 countries. Including Carthage, Macedonia, Bendu Kingdom, Seleucid Empire, Ptolemy Egypt, Gauls, Germans, Britons, Greek city-states.
How many countries did the Roman Empire wipe out?
The Roman Empire wiped out at least about 50 countries. Including Carthage, Macedonia, Bendu Kingdom, Seleucid Empire, Ptolemy Egypt, Gauls, Germans, Britons, Greek city-states.
How did Rome become a large country?
When Rome was founded, it was still a small country. Since the beginning of the 5th century BC, it has defeated some cities in the Latin League and the neighbors such as the Etruscans, and conquered the indigenous and Greek city-states in the southern part of the Italian peninsula and became a large country in the western Mediterranean.
See more
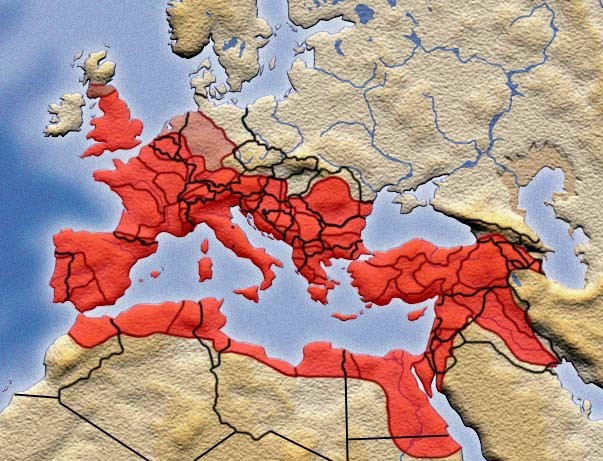
Which countries were part of the Roman Empire?
It also included territory in the Middle East and Africa that later became Syria, Iraq, Cyprus, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco. The Roman Empire also annexed some outlying areas.
When did the Roman Empire begin?
The empire began in 27 B.C. when the Roman Senate formally granted Octavian, Julius Caesar's adopted son, greater power and the new title Augustus, effectively ending the Roman Republic. It reached its height in the year A.D. 117.
How did Diocletian stem the decline of the Roman Empire?
Emperor Diocletian was able to stem the empire's decline somewhat, partially by refusing absolute power and splitting the empire first in half and then into four regions between A.D. 286 and 293.
