Different enzymes present in Lysosomes [40]
| Sr. No | Enzymes | Substrate |
| 1 | Phosphates | |
| A- Acid phosphatase | Most phosphomonoesters | |
| B- Acid phosphodiesterase | Oligonucleotides and phosphodiesterase | |
| 2 | Nucleases |
What enzymes are used in lysosomes?
To accomplish the tasks associated with digestion, the lysosomes use some 40 different types of lysosomal enzymes, such as glycosidases, protease, acid phosphatases, sulfatases and lipases. Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and modified in the Golgi apparatus.
What is the structure of a lysosome?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes, such as glycosidases, proteases and sulfatases.
Why can't lysosomal enzymes be incorporated into the cytoplasm?
The result is a general failure of lysosomal enzymes to be incorporated into lysosomes. All of the lysosomal enzymes are acid hydrolases, which are active at the acidic pH (about 5) that is maintained within lysosomes but not at the neutral pH (about 7.2) characteristic of the rest of the cytoplasm (Figure 9.35).
What is the pH of lysosomal enzymes?
All of the lysosomal enzymesare acid hydrolases, which are active at the acidic pH (about 5) that is maintained within lysosomes but not at the neutral pH (about 7.2) characteristic of the rest of the cytoplasm (Figure 9.35).
Which enzymes are present in lysosomes?
Lysosomes filled with hydrolytic enzymes are used for the controlled intracellular digestion of macromolecules. They contain about 40 types of hydrolytic enzymes, including proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, lipases, phospholipases, phosphatases, and sulfatases.
How many lysosomes are there?
There are 50 to 1,000 lysosomes per mammalian cell, but a single large or multilobed lysosome called the vacuole in fungi and plants.
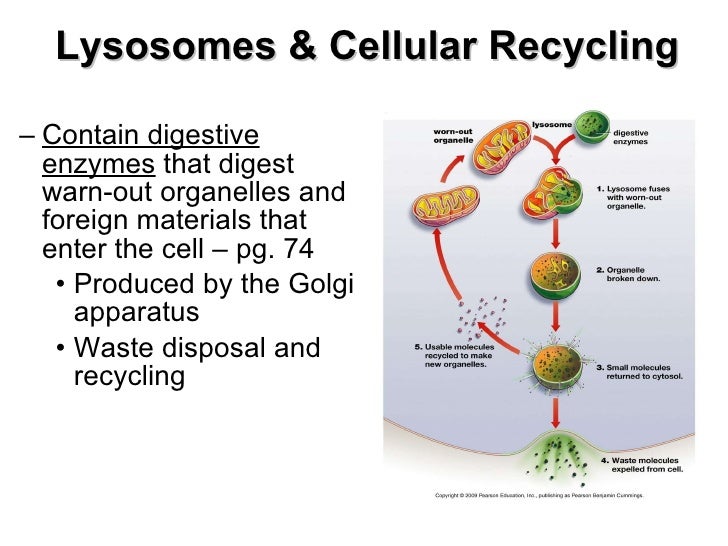
What are 3 lysosomes functions?
A lysosome has three main functions: the breakdown/digestion of macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), cell membrane repairs, and responses against foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses and other antigens.
What is a lysosomal enzyme?
Lysosomal enzyme: an enzyme in an organelle called the lysosome within the cell. Lysosomal enzymes degrade macromolecules and other materials that have been taken up by the cell during the process of endocytosis.
What are the four types of lysosome?
There are four types of lysosomes depending on their morphology and function.Primary Lysosomes. They have newly pinched-off vesicles from the Golgi apparatus. ... Secondary Lysosomes. ... Residual Bodies(Residual or Tertiary Lysosomes). ... Autophagic Vacuoles( Autophagosome,Autolysosomes).
What is the size of lysosomes?
0.2–0.3 μmLysosomes are typically 0.2–0.3 μm in diameter. They originate from the trans face of the Golgi stack and are formed first as primary lysosomes.
Who discovered lysosome?
Christian de DuveChristian de Duve, whose laboratory in Louvain discovered lysosomes in 1955 and defined peroxisomes in 1965, died at his home in Nethen, Belgium at the age of 95, on May 4, 2013.
Why are lysosomes acidic?
Lysosomes are hydrolytic enzymes. They need an acidic environment for proper functioning, they are referred to as acid hydrolases. These enzymes help in the disintegration of polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, etc. These enzymes require low pH compared to the cytoplasm to stay active.
What are the 5 functions of lysosomes?
Following are the functions of Lysosomes:Immune system - It destroys viruses and bacteria that attack the cell.Demolition squads - It is destroys worn out cellular organelles and organic debris. ( ... Suicide Bags - When a cell becomes old or is damaged, lysosomes burst and enzymes digest their own cells.More items...
What do lysosomes contain?
Lysosomes contain about 50 different degradative enzymes that can hydrolyze proteins, DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, and lipids.
Is lysozyme an enzyme?
Lysozyme is a naturally occurring enzyme found in bodily secretions such as tears, saliva, and milk. It functions as an antimicrobial by enzymatically cleaving a glycosidic linkage of bacterial cell walls peptidoglycan, which leads to cell death [4].
What are different types of lysosomes?
There are two types of lysosomes; secretory lysosomes and conventional ones. Conventional lysosomes are involved in the dismantling and re-cycling of various substrates presented to them through endocytocis, phagocytosis and by autophagosomes. They are responsible for returning many amino acids to the system.
What are the 5 functions of lysosomes?
Following are the functions of Lysosomes:Immune system - It destroys viruses and bacteria that attack the cell.Demolition squads - It is destroys worn out cellular organelles and organic debris. ( ... Suicide Bags - When a cell becomes old or is damaged, lysosomes burst and enzymes digest their own cells.More items...
Where lysosomes are found?
Lysosomes are found in all animal cells, but are most numerous in disease-fighting cells, such as white blood cells. This is because white blood cells must digest more material than most other types of cells in their quest to battle bacteria, viruses, and other foreign intruders.
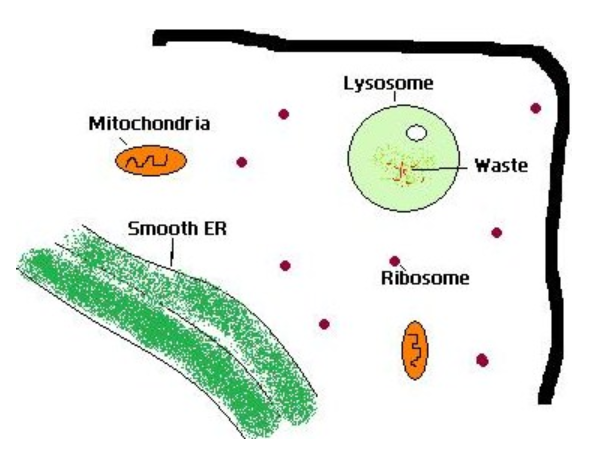
What are the lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
What are lysosomes Class 11?
“Lysosomes are sphere-shaped sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes that have the capability to break down many types of biomolecules.” In other words, lysosomes are membranous organelles whose specific function is to breakdown cellular wastes and debris by engulfing it with hydrolytic enzymes.
Where are lysosomal enzymes synthesized?
Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), are transported to the Golgi apparatus, and are tagged for lysosomes by the addition of mannose-6-phosphate label. Malfunction of lysosomal enzymes can result in lysosomal storage diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Pompe's disease.
What are the functions of lysosomes?
In addition, lysosomes destroy targeted organelles, such as mitochondria, and injured cells via autolysis. Autolysis plays a central role in many apoptotic cascades. Lysosomal functions are dependent on lysosomes fusing with target vacuoles and release of digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are also responsible for digesting protein from the cell surface presented via endocytosis.
What is lysosomal enzyme?
Enzymes. Other Enzymes Products Center. Lysosomal Enzymes. Lysosomal Enzymes-enzyme. Lysosomal enzyme: an enzymein an organelle called the lysosome within the cell. Lysosomal enzymes degrade macromolecules and other materials that have been taken up by the cell during the process of endocytosis.
What enzymes are used in digestion?
To accomplish the tasks associated with digestion, the lysosomes use some 40 different types of lysosomal enzymes, such as glycosidases, protease, acid phosphatases, sulfatases and lipases. Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and modified in the Golgi apparatus.
Is lysosomal enzymes involved in cancer?
Lysosomal enzymes are also known to be involved in cancer processes. Sino Biological offers a comprehensive set of tools for research on lysosomal enzymes, including recombinant proteins, antibodies (rabbit mAbs, mouse mAbs, and rabbit pAbs), ELISA kits, and ORF cDNA clones. Lysosomal Enzymes list. ARSA.
What are Lysosomes?
The name Lysosome is derived from the Greek word where “lyso” means digestive and “soma” means body.
Where does the word "lysosome" come from?
The name Lysosome is derived from the Greek word where “lyso” means digestive and “soma” means body.
Which lysosome contains the full complement of acid hydrolases?
Only in the secondary lysosome, there is the presence of the full complement of acid hydrolases.
What is the function of the lysosome in the ovum?
In the cells like the sperms, the lysosome helps in extracellular digestion. The membrane of the ovum is digested which aids in the penetration of the sperms in the ovum.
