Why are there so many faults in California?
Since the formation of the San Andreas Fault system 25-30 million years ago, the juxtaposition of the Pacific and North American plates has formed many faults in California that accommodate lateral motion between the plates. North and east of California, the Basin and Range province between the Wasatch Mountains in Utah and the Sierra Nevada Mountains in eastern California is actively spreading and stretching westward.
What are famous fault line in California?
What is the biggest fault line in the world?
- This fault is one of the largest faults in the world, running more than 800 miles from the Salton Sea to Cape Mendocino.
- See Your Local Earthquake Risk.
- Scientist project the San Andreas fault line could cause a devastating earthquake in California by 2030.
What are California's major faults?
These 5 fault lines are directly below Los Angeles and have the potential to inflict more devastation than a San Andreas quake Santa Monica Fault. New maps made of the Santa Monica Fault in the past year not only show the potential of a more powerful quake, but also a longer fault ... Palos Verdes Fault. ... Newport-Inglewood Fault. ... Puente Hills Thrust. ... Hollywood Fault. ...
What fault line is located in California?
What part of California is on the fault line? The San Andreas Fault System, which crosses California from the Salton Sea in the south to Cape Mendocino in the north, is the boundary between the Pacific Plate (that includes the Pacific Ocean) and North American Plate (that includes North America).
How far away from faults do most Californians live?
What would happen if a large earthquake hit the coast?
How were the mountains and valleys formed?
What fault is the longest in California?
Which fault system is the major boundary between the North American and Pacific tectonic plates?
What is the Cascadia subduction zone?
What is the landscape of Southern California?
See 4 more
About this website

How do I find the nearest fault to a property or specific location ...
If you are looking for faults in California use: How Close to a Fault Do You Live? (Bay Area Earthquake Alliance) For faults in California and the rest of the United States (as well as the latest earthquakes) use the Latest Earthquakes Map: click on the "Basemaps and Overlays" icon in the upper right corner of the map. check the box for "U.S. Faults".
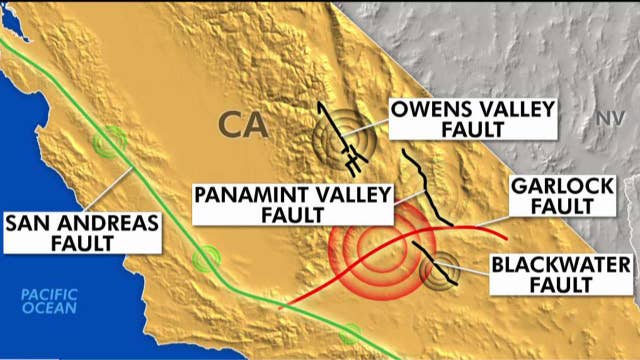
Major Fault Lines In California Map
Major Fault Lines In California Map. CEA’s inexpensive earthquake coverage guidelines Permit you select the protection that fits your funds. Our insurance plan fees, depending on the most up-to-date science and analysis, are based on numerous aspects like your house’s age, place near a fault, foundation variety, building variety, and roof sort.
What are the signs of an active geologic area?
Another sign of an active geologic area is the number of hot springs and volcanoes. Lassen Peak had a series of major eruptions in the 1910s and remains dormant for now. Some recent studies have placed the Mammoth Lakes area, Lassen, and Mt. Shasta zones as potentially active volcanic regions again in the future.
Where are faults found in Tahoe?
Recently, many faults have been discovered in the Sierra and Southern Cascades. This area on the eastside of the Sierra and Lake Tahoe has been active with many smaller earthquakes and swarms over the last 150 years.
Where does the San Andreas earthquake occur?
There is, however, another area that has a lot of past earthquake activity and potential for more in the future. The San Andreas begins near the Salton Sea and moves north though Southern California and Los Angeles.
Where is the Transverse Range?
Near Ventura County and Santa Barbara, the fault makes a slight deviation with a more east and west angle near the mountains in Santa Barbara, sometimes called the Transverse Range because of its different orientation from the north and south Coastal Range and Sierra Nevada. That deviation before the San Andreas continues in a more north ...
Is San Andreas a pressure point?
That deviation before the San Andreas continues in a more north and south direction is a pressure point. At the junction where it deviates, there have been a number of recent earthquakes, in Ridgecrest and a large earthquake many years ago on the Garlock Fault .
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is the point on a fault where rupture initiates?
The point on a fault where rupture initiates is referred to as the focus or hypocenter of an earthquake. The hypocenter is described by its depth in kilometers, its map location in latitude and longitude, its date and time of occurrence, and its magnitude (a measure of the amount of energy radiated as seismic waves).
How does an earthquake happen?
Earthquakes occur when the two sides of a fault slip suddenly against each other. In California, the Pacific and North American plates creep past each other in opposite directions, about 1.5 inches per year. Friction between the plates causes some parts to snag, then break free in sudden, jerking movements. Those movements emit waves of energy that travel through the ground, causing the shaking you feel.
How are earthquake probabilities calculated?
Earthquake probabilities are calculated by projecting earthquake rates based on earthquake history and fault slip rates. The result is expressed as the probability that an earthquake of a specified magnitude will occur on a fault or within an area.
What is the California Geological Survey?
The California Geological Survey studies earthquakes to help Californians plan and build earthquake resistant communities. We record the strong ground motion from earthquakes, study the distribution of historic earthquakes and evaluate faults that are the source of earthquakes. We combine that information to prepare maps showing ...
How is the strength of an earthquake expressed?
The strength of an earthquake is generally expressed in two ways: magnitude and intensity. The magnitude is a measure that depends on the seismic energy radiated by the earthquake as recorded on seismographs. An earthquake's magnitude is expressed in whole numbers and decimals (e.g., 6.8).
How much energy does a magnitude 6.0 earthquake release?
A magnitude 6.0 quake releases approximately as much energy as 6,270 tons of TNT , a magnitude 7.0 199,000 tons, a magnitude 8.0 6.27 million tons and a magnitude 9.0 99 million tons. Of course, all that energy is not focused in one particular spot, but spreads out in waves.
What is a fault in the crust?
A fault is a fracture in the crust along which one side has moved relative to the other side. Faults can be very small or hundreds of miles long. The earth's crust is composed of huge plates that are in slow but nearly constant motion. Part of California is on the Pacific Plate, and part is on the North American Plate. The San Andreas Fault, which runs from the Salton Sea in Imperial County to Cape Mendocino in Humboldt County, is the boundary between these plates. Sometimes one block of the crust moves up while the other moves down, sometimes they move horizontally in opposite directions (that's what's happening with the San Andreas Fault; Los Angeles is creeping closer to San Francisco). Some faults are well known and easy to spot, such as the San Andreas. Others are underground, with nothing on the surface revealing their presence (a blind thrust fault). The 1994 Northridge earthquake was caused by a blind thrust fault.
How far away from faults do most Californians live?
Most Californians live within 30 miles of an active fault. 15,700. Known faults in California (and scientists continue to discover new ones) Select your county from the dropdown menu above to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you. *The probability is based on a 30-year period, beginning in 2014.
What would happen if a large earthquake hit the coast?
Very large earthquakes occurring close to the coast could cause damaging levels of ground shaking and tsunami waves.
How were the mountains and valleys formed?
Many of the mountains, and some of the valleys, in Southern California were formed by movement within the San Andreas fault system —the tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates.
What fault is the longest in California?
The San Andreas fault is the primary feature of the system and the longest fault in California, slicing through Los Angeles County along the north side of the San Gabriel Mountains. It can cause powerful earthquakes—as big as magnitude 8.
Which fault system is the major boundary between the North American and Pacific tectonic plates?
The greater San Francisco Bay Area has a high likelihood of future damaging earthquakes as it straddles the San Andreas fault system —the major geologic boundary between the North American and Pacific tectonic plates.
What is the Cascadia subduction zone?
The Cascadia Subduction Zone stretches underneath the Humboldt-Del Norte county region, extending from Cape Mendocino all the way up through the Pacific Northwest. This zone is capable of generating an earthquake of a magnitude 9 or larger, occurring—on average—once every 500 years.
What is the landscape of Southern California?
Inland Southern California has scenic mountains, valleys, and deserts. Tremendous geologic forces within the San Andreas fault system —the tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates—created this spectacular landscape and continue today, reminding us often that we live in earthquake country.
