How many hydrogen atoms are present in propane?
there are 8 hydrogen atoms present in propane. There is 8 hydrogen atoms in propane, Each carbon has a valency of 4, 4 bonds with other atoms. Hydrogen has valency of 1. the general formula for alkanes is CnH2n +2 (n means number of that atom.) so to find how many hydrogens there with, say, 50 carbons you would do CnH2n + 2= C50H102.
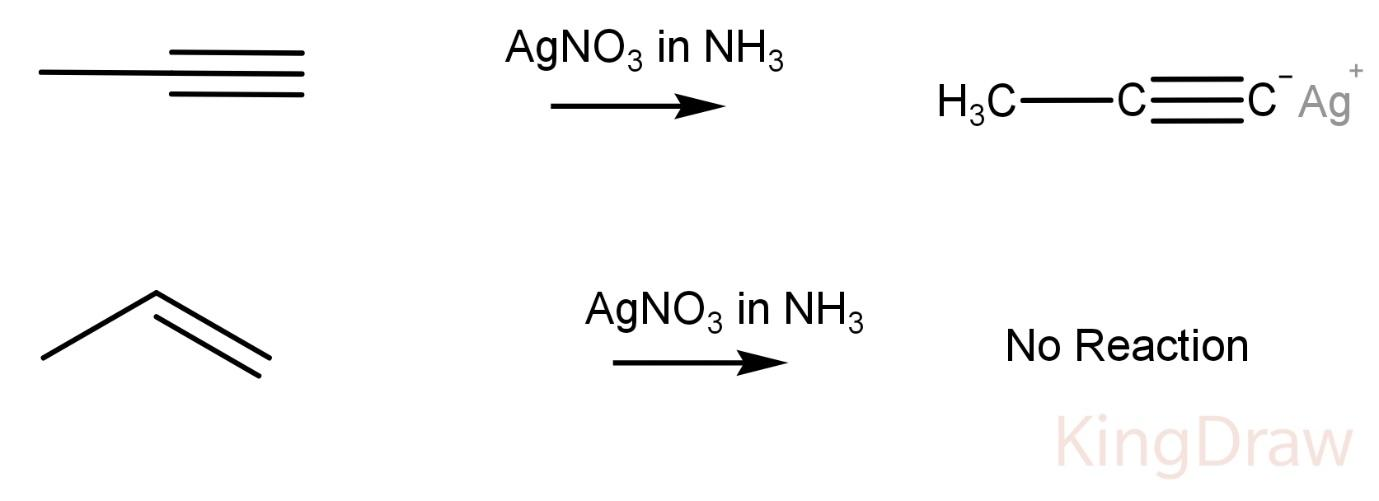
What type of compound is propyne?
Propyne is an alkyne, a terminal acetylenic compound and a gas molecular entity. PubChem compound Propyne
What are the chemical properties of propane?
not present Gas Properties: Hydrogen Methane Propane Chemical Formula H2 CH4 C3H8 Molecular Weight 2.016 16.04 44.097 Gas Density (kg/m3) @ STP 0.0808 0.643 1.767 Diffusivity (m2/sec) x 105 6.11 1.60 1.00 15 more rows ...
Is prop-1-yne an alkyne?
Propyne is an alkyne, a terminal acetylenic compound and a gas molecular entity. prop-1-yne Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) InChI=1S/C3H4/c1-3-2/h1H,2H3 Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) MWWATHDPGQKSAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) CC#C
How much propyne is in the air?
How many people are exposed to 1-propyne?
What is the reaction of 1-propyne?
What is the rate constant of a vapor phase reaction of 1-propyne?
What is propane used for?
Is gas heavier than air?
Is 1-propyne a liquefied gas?
See 4 more
About this website

How many hydrogens does propyne have 1 point?
- The structure of the propyne is as follows. - Propyne contains three carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms in the above structure.
Does propyne have 4 carbon atoms?
Therefore, propyne is a hydrocarbon containing 3 carbons and a triple bond.
How many carbon atoms are in propyne?
Propyne is a convenient three-carbon building block for organic synthesis.
Is propyne a single or double bond?
Explanation: The molecular formula of propyne, C3H4 , specifies 2 degrees of unsaturation; two double bonds as required.
What is 4 hydrogen called?
List of isotopesNuclideZNote3H (T)1Tritium4 H15 H17 more rows
What is structure of propyne?
C3H4Propyne / Formula
Is propyne an alkyne?
Propyne is an alkyne, a terminal acetylenic compound and a gas molecular entity.
What is the shape of propyne?
a dartPropyne is shaped like a dart; it has a pointed end and a feathered end.
How many covalent bond are in propyne?
Bonds formed between the hydrogen and carbon atom and carbon-carbon atoms are covalent bonds. Hence, there are ten covalent bonds in propane as shown in the image. Q. Propane has ___ covalent bonds.
Is propyne saturated or unsaturated?
unsaturated hydrocarbonsTherefore, only i.e. propene and propyne are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Is propyne polar or nonpolar?
Propyne is propyne no “1″ is necessary. Since the terminal H is acidic the molecule is slightly polar as are most terminal alkynes except acetylene which is still acidic but has no dipole moment because of symmetry. Propyne has a dipole moment of 0.78 Debye, which is on the more polar end of hydrocarbons.
How many double bonds are there in propene?
It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons.
How many covalent bonds are present in propyne molecule?
8 covalent bondsA molecule of Propyne has 8 covalent bonds. 4 C-H bonds, 2 C-C sigma bonds and 2 C-C pi bonds.
What type of compound is propyne?
alkynePropyne is an alkyne, a terminal acetylenic compound and a gas molecular entity.
What is the geometry of propyne?
Propyne is shaped like a dart; it has a pointed end and a feathered end. Other molecules have more complicated shapes.
Is propyne saturated or unsaturated?
unsaturated hydrocarbonsTherefore, only i.e. propene and propyne are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Propyne - Wikipedia
Propyne (IUPAC name: methylacetylene) is an alkyne with the chemical formula CH 3 C≡CH.It is a component of MAPD gas—along with its isomer propadiene (allene), which was commonly used in gas welding.Unlike acetylene, propyne can be safely condensed.
Where is hydrogen produced?
foods. Most of this hydrogen is produced in just three states: California, Louisiana, and Texas (www.eia.doe.gov). Almost all of the hydrogen used is “captive,” that is, consumed at the refinery or chemical plant where it is produced. Nevertheless, a safe and reliable hydrogen distribution network has been developed over the years, consisting of liquid hydrogen delivery trucks, gaseous hydrogen tube trailers, and dedicated gaseous hydrogen pipelines. Worldwide, there are over 800 km of hydrogen pipelines, including 225 km in the Ruhr Valley of Germany that have operated safely since 1938, and over 200 km of hydrogen pipeline in the United States, primarily in the Texas Gulf Coast area. Both liquid and gaseous hydrogen are distributed throughout the United States in hundreds of tanker trucks and tube trailers. (www.hydrogensociety.net)
What happens if hydrogen leaks?
If there is a brief leak, hydrogen, being more buoyant, will rise more rapidly than either propane or methane vapor and will quickly disperse. A rapid dispersion rate is probably hydrogen’s greatest safety asset in an outdoor environment, although wind and the escape velocity from a high-pressure tank may have more influence on the size of a flammable hydrogen cloud. Indoors, high dispersion rates can be both an asset, in the sense that a small leak will rapidly mix with air and stay below the lean flammability limit, and a potential liability — in a larger leak the expanding gas cloud is more likely to reach ignition sources.
Is propane safe to use?
and propane have long histories of being used as fuel. Both fuels can be used safely if their physical, chemical, and thermal properties are understood and if appropriate codes, standards, and guidelines are followed. Although the properties of hydrogen have been compared to those of propane and methane, these comparisons were made to facilitate appreciation of the physical and chemical differences and similarities among these fuels. It is not possible to rank these fuels according to safety because plausible accident scenarios can be formulated in which any one of the fuels can be considered the safest or the most hazardous.
How much propyne is in the air?
1-Propyne has been detected in the human respiratory air at 0.81 ug/hr in a non-smoker and at 1.1 and 2.3 ug/hr in two smokers (1).
How many people are exposed to 1-propyne?
NIOSH (NOES Survey 1981-1983) has statistically estimated that 119 workers (6 of these are female) are potentially exposed to 1-propyne in the US (1). Occupational exposure to 1-propyne may occur through inhalation of this compound at workplaces where 1-propyne is produced or used (SRC). The most likely pathway by which the general public is exposed to 1-propyne is by inhalation due to the release of this substance from combustion fuels, biomass emissions and cigarette smoke (SRC).
What is the reaction of 1-propyne?
Gas-phase 1-propyne will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 2.7 days. 1-Propyne does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, 1-propyne is expected to have high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 77. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 0.011 atm-cu m/mole. If released into water, 1-propyne is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Estimated volatilization half-lives for a model river and model lake are 41 min and 2.5 days, respectively. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Alkynes are generally resistant to hydrolysis; therefore, 1-propyne is not expected to hydrolyze in the environment. Occupational exposure to 1-propyne may occur through inhalation with this compound at workplaces where 1-propyne is produced or used. The most likely pathway by which the general public is exposed to 1-propyne is by inhalation due to the release of this substance from combustion fuels, biomass emissions and cigarette smoke. (SRC)
What is the rate constant of a vapor phase reaction of 1-propyne?
The rate constant for the vapor-phase reaction of 1-propyne with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals has been estimated as 5.9X10-12 cu cm/molecule- sec at 25 °C (1). This corresponds to an atmospheric half-life of about 2.7 days at an atmospheric concentration of 5X10+5 hydroxyl radicals per cu cm (1). Alkynes are generally resistant to hydrolysis (2); therefore, 1-propyne is not expected to hydrolyze in the environment (SRC). 1-Propyne does not absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight (2). The rate constant for the vapor-phase reaction of 1-propyne with ozone has been estimated as 1.43X10-20 cu cm/molecule-sec at 25 °C (SRC) that was derived using a structure estimation method (1). This corresponds to an atmospheric half-life of about 800 days at an atmospheric concentration of 7X10+11 ozone molecules per cu cm (3).
What is propane used for?
1-Propyne's production and use as a synthetic intermediate, specialty and welding torch fuel (1,2) as well as its emission as a byproduct of automobile and turbine engine combustion (3) result in its release to the environment through various waste streams (SRC).
Is gas heavier than air?
The gas is heavier than air and may travel along the ground; distant ignition possible. As a result of flow, agitation, etc., electrostatic charges can be generated.
Is 1-propyne a liquefied gas?
1-propyne appears as a colorless liquefied gas with a sweet odor. mp: -104°C, bp: -23.1°C. Insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, chloroform and benzene. Moderately toxic by inhalation. Used as a specialty fuel.
