
What are the functions of the 4 lobes of the brain?
Positions and Functions of the Four Brain Lobes
- The frontal lobe has many functions most of which center on regulating social behavior.
- The parietal lobe has several functions including sensation, perception, and spatial reasoning.
- The temporal lobe.
How many bones surround the brain?
Your brain is protected by several bones. There are eight bones that surround your brain: one frontal bone; two parietal bones, two temporal bones, one occipital bone, one sphenoid bone and one ethmoid bone. These eight bones make up the cranium. Another 14 bones in the face make up the entire skull.
What are the 4 main lobes of the cerebral cortex?
Lobes of the brain
- Frontal lobe. The frontal lobe is separated from the parietal lobe by a space called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by the lateral sulcus.
- Parietal lobe. The parietal lobe is behind the frontal lobe, separated by the central sulcus. ...
- Temporal lobe. ...
- Occipital lobe. ...
What are the four lobes of the brain Quizlet?
What are the four lobes of the brain quizlet?
- What are the 4 lobes of the cerebrum? Frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.
- Frontal lobe. Intergral role in memory formation, emotion, decision making, reasoning, and personality.
- Broca's area.
- Parietal lobe.
- Proprioception.
- Somatosensory association cortex.
- Primary gustatory cortex.
- Occipital lobe.
Does the brain have 4 or 8 lobes?
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 2). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central sulcus. The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language.
Are there 4 or 5 lobes of the brain?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes, four of which have the same name as the bone over them: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe. A fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil, lies deep within the lateral sulcus.
What are all 4 lobes together called?
Each lobe has specific functions, but for most activities, several areas of different lobes in both hemispheres must work together. The frontal lobes are the largest of the four lobes and are responsible for many different functions....Gov't Insurance.•Frontal lobe•Parietal lobe•Occipital lobe•Temporal lobe
What are the 6 major lobes of the brain?
The lobes of the cerebrum are actually divisions of the cerebral cortex based on the locations of the major gyri and sulci. The cerebral cortex is divided into six lobes: the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, insular and limbic lobes.
What do the 4 lobes do?
Each side of your brain contains four lobes. The frontal lobe is important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity. The parietal lobe processes information about temperature, taste, touch and movement, while the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
What are the 4 main functions of the brain?
The brain controls our thoughts, memory and speech, movement of the arms and legs, and the function of many organs within our body.
What part of the brain does love come from?
More specifically, in a 2012 review of the love research literature Lisa Diamond and Janna Dickenson, psychologists at the University of Utah, found romantic love is most consistently associated with activity in two brain regions—the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the caudate nucleus.
What part of the brain controls love?
The hypothalamus is one of the brain regions that makes up the limbic system and is often considered the main control centre of love.
What is the hippocampus?
Hippocampus is a complex brain structure embedded deep into temporal lobe. It has a major role in learning and memory. It is a plastic and vulnerable structure that gets damaged by a variety of stimuli. Studies have shown that it also gets affected in a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Where are the 4 lobes of the brain located?
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 2). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central sulcus . The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language.
Is insula a lobe?
The insula is a lobe that has a triangular shape. It is surrounded by the anterior, superior and medial limiting sulci that are used to distinguish the three parts of the operculum: The frontal operculum.
Who is thalamus?
Your thalamus is your body's information relay station. All information from your body's senses (except smell) must be processed through your thalamus before being sent to your brain's cerebral cortex for interpretation. Your thalamus also plays a role in sleep, wakefulness, consciousness, learning and memory.
What are the major functions of the 5 lobes?
The frontal lobe is important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity. The parietal lobe processes information about temperature, taste, touch and movement, while the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
What are the 5 lobes of the brain quizlet?
Terms in this set (5)Frontal Lobe. Emontional control, self awareness, motivation, judgement, problem solving, talking, movement, and initiation, matured, personality.Parietal Lobe. ... Temporal Lobe. ... Occipital Lobe. ... Cerebellum.
Is insula a lobe?
The insula is a lobe that has a triangular shape. It is surrounded by the anterior, superior and medial limiting sulci that are used to distinguish the three parts of the operculum: The frontal operculum.
Which of the five cerebral lobes is not visible on the surface of the brain?
The first four lobes are superficially visible. They are named for each cranial bone overlying them. There is a fifth lobe described by some, called the insula, which cannot be seen from the brain's surface. The cerebral lobes often work together in functions such as memory, speech, emotion, and vision.
What are the lobes of the brain?
The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, ...
Which lobe of the brain receives auditory information from the ears and secondary areas?
Auditory information. The temporal lobe contains the primary auditory cortex, which receives auditory information from the ears and secondary areas, and processes the information so we understand what we’re hearing (e.g. words, laughing, a baby crying).
What is the most famous case of frontal lobe dysfunction?
The most famous case of frontal lobe dysfunction is the story of railway worker Phineas Gage. In 1848, Gage was using a tamping iron to pack in gunpowder for blasting a tunnel through rock.
Which lobe is responsible for emotional regulation?
The frontal lobe is separated from the parietal lobe by a space called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by the lateral sulcus. The frontal lobe is generally where higher executive functions including emotional regulation, planning, reasoning and problem solving occur.
Which lobe is responsible for integrating sensory information?
The parietal lobe is behind the frontal lobe, separated by the central sulcus. Areas in the parietal lobe are responsible for integrating sensory information, including touch, temperature, pressure and pain.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for visual processing?
The occipital lobe is the major visual processing centre in the brain. The primary visual cortex, also known as V1, receives visual information from the eyes. This information is relayed to several secondary visual processing areas, which interpret depth, distance, location and the identity of seen objects.
What test can be used to check the parietal lobe?
Using callipers or a folded paperclip, and asking a subject to keep their eyes closed , this test can be used to check parietal lobe function. (Image: Lawrence House: Public Domain)
How many lobes are there in the brain?
Terminologia Anatomica (1998) and Terminologia Neuroanatomica (2017) divides the cerebrum into 6 lobes. Each lobe of the brain consists of different sub regions that work together to create full function within the entirety of the brain.
Which lobe of the brain contains the most dopamine neurons?
The frontal lobe contains most of the dopamine -delicate neurons in the cerebral cortex. The dopamine system is associated with reward, attention, short-term memory tasks, planning, and motivation. Dopamine tends to limit and select sensory information arriving from the thalamus to the forebrain.
What is the limbic lobe?
The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped region of cortex on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The term is ambiguous, with some authors including the paraterminal gyrus, the subcallosal area, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus and the subiculum; while the Terminologia Anatomica includes the cingulate sulcus, the cingulate gyrus, the isthmus of cingulate gyrus, the fasciolar gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the parahippocampal sulcus, the dentate gyrus, the fimbrodentate sulcus, the fimbria of hippocampus, the collateral sulcus, and the rhinal sulcus, and omits the hippocampus.
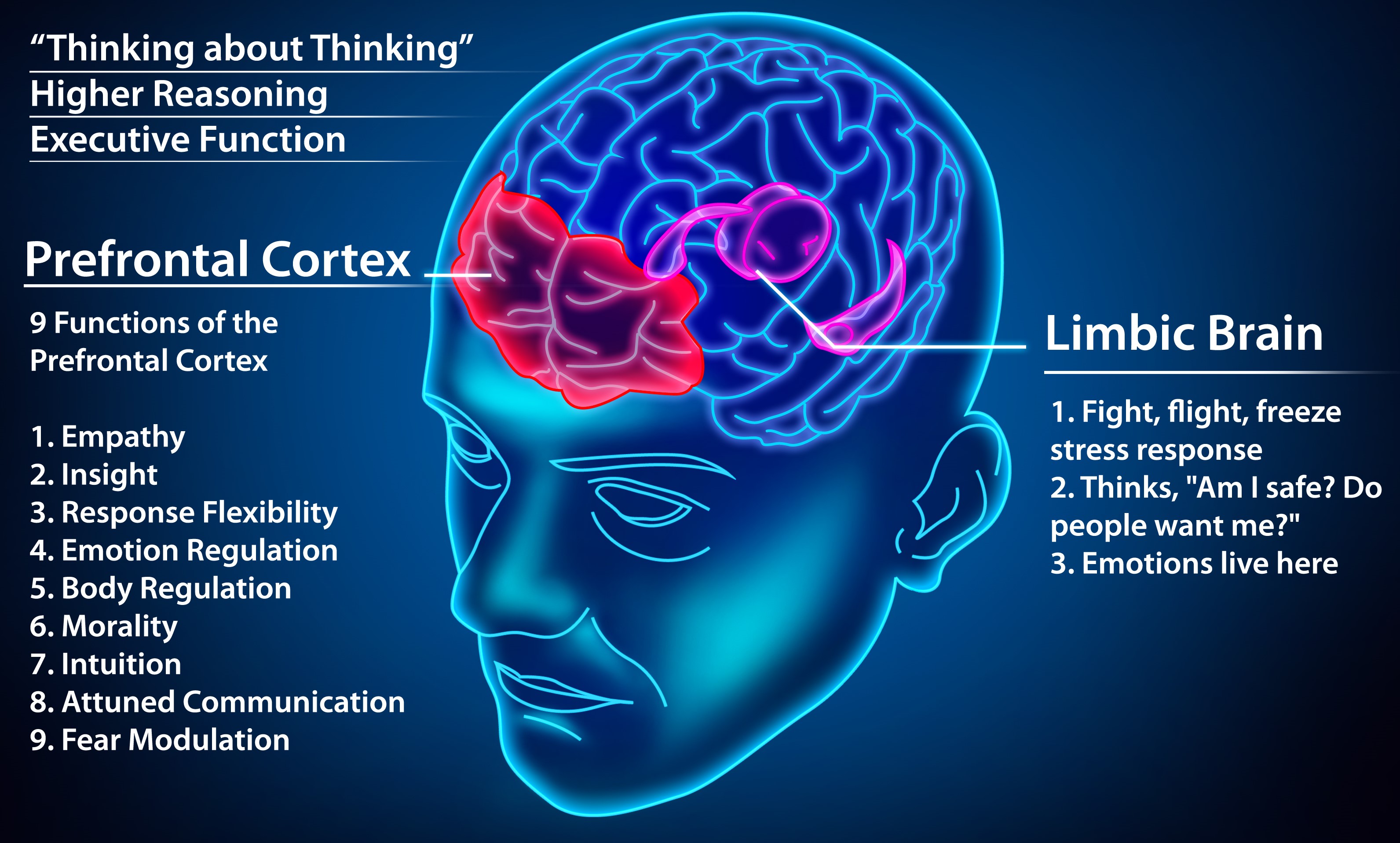
What is the effect of a gene variant that reduces dopamine activity in the prefrontal cortex?
A report from the National Institute of Mental Health says a gene variant that reduces dopamine activity in the prefrontal cortex is related to poorer performance and inefficient functioning of that brain region during working memory tasks, and to a slightly increased risk for schizophrenia.
Which lobe of the brain controls voluntary movements?
It is separated from the parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by a deep fold called the lateral sulcus also called the Sylvian fissure. The precentral gyrus, forming the posterior border of the frontal lobe , contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts. Precentral region contains Primary motor cortex (area 4) and Premotor cortex (area 6). These areas control movements, both skilled and postural.
Where is the visual cortex located?
Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the posterior pole of the occipital lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for executive control?
The frontal lobe consists of the prefrontal cortex which is located in the most anterior (farthest away) section of the frontal lobe. It is critical for one’s working memory and executive control which helps keep goals and complex tasks organized.
How many lobes are there in the brain?
5 lobes of the brain. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe and the temporal lobe, four of which have the same name as the bone above them. Deep within the lateral sulcus lies a fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil.
Which lobe of the brain is the largest?
Let us therefore see the characteristics of each brain lobe. 1. Frontal lobe. Marked in blue in the image. In humans, it is the largest of the lobes of the brain.
What part of the brain is hidden between the rest of the lobes?
Insula . The insula is a part of the cortex that is hidden between the rest of the lobes of the brain and, to see it, it is necessary to separate the temporal and parietal lobes from each other. That is why it is often not considered as just another lobe.
Which lobe of the brain controls movement?
Each side of your brain contains four lobes. The frontal lobe is important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity. The parietal lobe processes information about temperature, taste, touch and movement, while the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
Which lobe is responsible for the processing of sensory information from all areas of the body?
Parietal lobe. Marked in yellow in the image. It is situated between the frontal and occipital lobes and is primarily responsible for the processing of sensory information from all areas of the body, such as touch, temperature stimuli, pain and pressure, which can be related to the recognition of numbers.
What is the most visible part of the brain?
Each hemisphere is covered by a layer called the cerebral cortex (which is the most visible part of the brain and seems to be full ...
What is the function of the lobes of the brain?
It is characterized by its role in the processing of high-level cognitive functions such as planning, coordination, execution and control of behavior. By extension, it also enables goal setting, anticipation, articulation of language, and regulation of emotions.
What are the four lobes of the brain?
Brain Lobes and their Functions. The brain is divided into four sections, known as lobes (as shown in the image). The frontal lobe, occipital lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe have different locations and functions that support the responses and actions of the human body.
What is the smallest lobe of the brain?
The occipital lobe, the smallest of the four lobes of the brain, is located near the posterior region ...
Why is it more common to injure the frontal lobe than the other lobes of the
It is more common to injure the frontal lobe than the other lobes of the brain because the lobe is located at the front of the skull. The effects of damage to the frontal lobe often result in personality changes, difficulty controlling sexual urges, and other impulsive and risk-taking behaviors. The parietal lobe has several functions ...
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe. There are two temporal lobes located on both sides of the brain that are in close proximity to the ears. The primary function of the temporal lobes is to processing auditory sounds. Other functions of the temporal lobe include: 1 Since the hippocampus, or part of the brain responsible for transferring short-term memories into long-term memories, is located in the temporal lobe, the temporal lobe helps to form long-term memories and process new information. 2 The formation of visual and verbal memories. 3 The interpretation of smells and sounds.
What is the parietal lobe?
This lobe is responsible for processing sensory information from various parts of the body. Here are some of the functions of the parietal lobe: Sensing pain, pressure, and touch. Regulating and processing the body's five senses.
What is the temporal lobe?
Other functions of the temporal lobe include: Since the hippocampus, or part of the brain responsible for transferring short-term memories into long-term memories, is located in the temporal lobe, the temporal lobe helps to form long-term memories and process new information. The formation of visual and verbal memories.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for spatial information?
The parietal lobe processes sensory information for cognitive purposes and helps coordinate spatial relations so we can make sense of the world around us. The parietal lobe resides in the middle section of the brain behind the central sulcus, above the occipital lobe. The temporal lobe is located on the bottom of the brain below the lateral fissure.
Which lobe of the brain receives information from various lobes?
The motor cortex receives information from various lobes of the brain and utilizes this information to carry out body movements. Damage to the frontal lobe can lead to changes in sexual habits, socialization, and attention as well as increased risk-taking .
How many neurons are in the brain?
The brain is made up of billions of neurons and that it also has a number of specialized parts that are each involved in important functions. While there is still a great deal that researchers do not yet know about the brain, they have learned a great deal about the anatomy and function of the brain. Understanding these parts can help give people ...
What is the cerebral cortex?
The Cerebral Cortex. MedicalRF.com/Getty Images. The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain that makes human beings unique. Functions that originate in the cerebral cortex include: Consciousness. Higher-order thinking. Imagination. Information-processing. Language.
What are the diseases that affect the brain?
Neurogenetic diseases including Huntington's disease and muscular dystrophy. Trauma such as head injury and spinal cord injury 11. By studying the brain and learning more about its anatomy and function, researchers are able to develop new treatments and preventative strategies for conditions that affect the brain.
How many types of neurological diseases are there?
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, there are more than 600 types of neurological diseases. 11 Some of the things that can affect the brain and its function include:
What is the brain stem?
The brainstem is an area located at the base of the brain that contains structures vital for involuntary functions such as the heartbeat and breathing. The brain stem is comprised of the midbrain, pons, and medulla. 3
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for the processing of sensory information?
Parietal Lobe. The parietal lobe is located in the middle section of the brain and is associated with processing tactile sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain. A portion of the brain known as the somatosensory cortex is located in this lobe and is essential to the processing of the body's senses.
How many lobes are there in the brain?
There are in fact four lobes in each hemisphere of the brain, and the two hemisphere are connected by the corpus callosum. Each lobe is divided by the longitudinal fissure, allowing for the four lobes in each hemisphere.
What is the limbic lobe?
The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped region of cortex on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The term is ambiguous, with some authors [who?] including the paraterminal gyrus, the subcallosal area, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus and the subiculum; [8] while the Terminologia Anatomica includes the cingulate sulcus, the cingulate gyrus, the isthmus of cingulate gyrus, the fasciolar gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the parahippocampal sulcus, the dentate gyrus, the fimbrodentate sulcus, the fimbria of hippocampus, the collateral sulcus, and the rhinal sulcus, and omits the hippocampus.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for sensory inputs?
The parietal lobe is positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.#N#The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch (mechanoreception) in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe.#N#Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure — the homunculus (Latin: "little man"), in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule and inferior parietal lobule are the primary areas of body or spatial awareness. A lesion commonly in the right superior or inferior parietal lobule leads to hemineglect.
Which lobe of the brain controls the motor system?
The precentral gyrus, forming the posterior border of the frontal lobe , contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts.#N#The frontal lobe contains most of the dopamine-delicate neurons in the cerebral cortex. The dopamine system is associated with reward, attention, short-term memory tasks, planning, and motivation. Dopamine tends to limit and select sensory information arriving from the thalamus to the forebrain. A report from the National Institute of Mental Health says a gene variant that reduces dopamine activity in the prefrontal cortex is related to poorer performance and inefficient functioning of that brain region during working memory tasks, and to a slightly increased risk for schizophrenia.
Where is the temporal lobe located?
The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.#N#The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memories, language comprehension, and emotion association.
What is the visual cortex?
The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex . The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the posterior pole of the occipital lobe. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception.

Overview
The lobes of the brain are the major identifiable zones of the cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres, which are only roughly symmetrical in structure, are today considered as having six lobes each. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct to some degree…
Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned in front of the parietal lobe and above and in front of the temporal lobe. It is separated from the parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by a deep fold called the lateral sulcus also called the Sylvian fissure. The precentral gyrus, which forms the posterior border of the frontal lobe, contains the primary motor cortex (area 4 under the Brodmann area arc…
Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch (mechanoreception) in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral …
Occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the posterior pole of the occipital lobe. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the S…
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memories, language comprehension, and emotion association.
Within the temporal lobe is an area of the brain called the hippocampus which is associated with …
Limbic lobe
The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped region of cortex on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The term is ambiguous, with some authors including the paraterminal gyrus, the subcallosal area, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus and the subiculum; while the Terminologia Anatomica includes the cingulate sulcus, the cingulate gyrus, t…
Insular cortex
The insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes). The insular cortex has an important function for sending axons to the amygdala and responding to tones and somatosensory stimulation.
Berret, et al. (2019) used mice to study the fear response that is associated with perceived threa…
Model images
• Inferior view of cerebrum.
• Lateral view of left hemisphere.
• Both hemispheres. Left and right lobes are color-matched. Insular lobe
• Insular lobe.