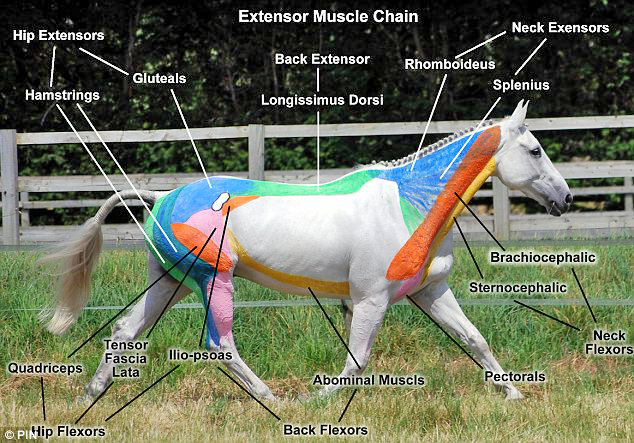
How to build muscle on a horse?
WikiHow recommended a number of exercises owners can do to strengthen their equines:
- Walk up a hill. Start small, then progress to more steep inclines with time. ...
- Trot downhill. This builds strength in the back legs. ...
- Do jumping exercises. ...
- Weave around trees to improve flexibility and all-around performance.
- Trot along riverbeds. ...
- Add extra weight to saddle bags. ...
- Walk over small logs when climbing and descending hills. ...
- Work the horse daily. ...
What is the strongest muscle in the horses body?
gluteus medius (GM) is the largest muscle of the horse, its main movement function is the extension of the hip joint. Also, how much muscle does a horse have? Your horse has a lot of muscles; 700 skeletal muscles, to be exact.
Are there more muscles in the horse than a human?
Your horse has a lot of muscles; 700 skeletal muscles, to be exact. Compare that to around 300 in the human body. Subsequently, one may also ask, how strong is a horse back? It's impossible to pin down a horse's strength exactly, but some large horse. breeds have been known to pull up to three times their own weight. That means they might pull up to 2,500 pounds or more!
What muscles help you ride a horse?
Horse riding tones our body while working both the upper and lower body muscles. The primary muscle groups that horse riding works are the core muscles: abs, back, pelvis, and thighs. An isometric sport such as horse riding requires the rider to contract their core muscles in order to keep their balance on the horse.
What muscles do horses use to spin?
How does a horse's heart rate change as he gets fitter?
How long does it take for a horse to burn ATP?
What is the difference between a horse's truck bed and a telephone pole?
Why is genetics important for horses?
Where is the semitendinosus muscle?
Does aerobic metabolism increase muscle fibers?
See 2 more
What are the 3 types of muscles in a horse?
Types of Muscles The three muscle classifications are smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. The first two are involuntary or automatic, which means they function as needed without having to be called into action for a specific need.
How muscular is a horse?
Your horse has a lot of muscles; 700 skeletal muscles, to be exact. Compare that to around 300 in the human body. Muscles are complicated: They intertwine with connective tissue and different muscle groups have different jobs.
What percentage of a horse's body is muscle?
Skeletal muscle makes up 45 percent of your horse's body weight, far more even than the bones. In addition to powering locomotion and movement, these strong, blood-rich, elastic structures protect the skeleton by distributing force and absorbing shock.
What is the largest muscle in the horse?
. gluteus mediusThe equine m. gluteus medius (GM) is the largest muscle of the horse, its main movement function is the extension of the hip joint.
What is the most muscular animal?
The strongest land animal in the world is the elephant. The typical Asian elephant has 100,000 muscles and tendons arranged along the length of the trunk, enabling it to lift almost 800 pounds. The gorilla, the strongest as well as largest primate on the planet, is at least six times stronger than the average human.
Why are horses so strong?
Their strength is part of their makeup. Horses have evolved by natural selection to have thick muscles, a large heart and powerful lungs. Yet over the centuries, people have also bred some groups of horses to be even stronger.
Why are quarter horses so muscular?
Natural genetic mutations on the myostatin gene cause a few unique breeds (Paint, Quarter Horses and some Thoroughbreds) to grow higher proportions of fast twitch muscle fibers (up to 80% more) and 12.5% more overall muscle mass.
What is the biggest bone in the horses body?
FemurFemur: the largest long bone in a horse. Proximally it forms a ball-and-socket joint with the pelvis to form the hip joint, and distally it meets the tibia and patella at the stifle joint.
Where do horses store fat?
Fat pads typically develop behind the shoulder, atop the ribcage, over the loin and croup, and around the sheath, though they may form anywhere fat naturally accumulates. The most common fat pad, and likely the largest, develops along the crest, or upper curve of the neck.
How strong is a horse's kick?
Horseback riding accidents and injuries caused by horses carry a high risk of severe trauma. In addition, a horse's kick can transfer a force of more than 10 000 Newtons to the body, causing fractures of the skull or other bones as well as devastating damage to the intestines.
How strong is a horse bite?
about 500 psiThe jaw strength (masseter muscle) of a horse is about 500 psi (pounds per square inch) Humans are usually less than 200 psi, while a Pit Bull measures 235 psi (#3 dog breed in jaw strength). Horses are prey animals who eat low protein food – grasses – all day long.
What's stronger a bull or a horse?
In general, bulls are stronger than horses. When selecting an animal for draft, farmers found that bulls (oxen) could not only pull heavier ploughs than horses, but that they could pull for longer without becoming tired.
Do horses have biceps?
The biceps brachii of horses is a complex muscle subdivided into two heads which may subserve distinct functions. The lateral head contains a large percentage of type I myofibers. This region is largely composed of short fibers (5–7 mm long) arranged in a pinnate fashion and heavily invested with connective tissue.
What is the toughest horse breed?
The strongest horses are the Belgian, Shire, Suffolk Punch, Ardennes, Percheron, and Percheron. Out of them all, Belgians are considered by most to be the strongest horse breed. All of the strongest draft horse breeds have been selectively bred over centuries to pull heavy farm equipment and industrial machinery.
How many muscles do horses have in their ears?
Using ten muscles, a horse can rotate each ear independently, up to 180 degrees, to locate, funnel, and magnify sounds. This allows the horse to position itself towards the sound that is making the noise. Horses hear sounds over a wider range of frequencies than we do.
What muscles do horses use?
Main Muscle Groups Used for Horseback RidingAbdominals. One of the most important aspects of horseback riding is core stability. ... Erector Spinae Group. ... Gluteus Maximus & Medius. ... Hip Abductors & Adductors. ... Hip Extensors. ... Iliacus. ... Obliques. ... Pectoralis Major & Minor.More items...•
What muscles do horses use to spin?
Skeletal muscles, which attach to bones via tendons, contract or shorten in length in highly coordinated ways to produce movement. These muscle contractions allow horses to spin and run with their turnout buddies, chew mouthfuls of grass, pin their ears in warning, and swish their tails at flies. By understanding how horses’ muscles contract ...
How does a horse's heart rate change as he gets fitter?
As a horse gets fitter, his cardiac muscle gets stronger, allowing it to pump more blood with every beat and maintain the same blood flow at a lower heart rate. As his fitness increases, he should be able to perform the same amount of work at a lower heart rate.
How long does it take for a horse to burn ATP?
This anaerobic muscle metabolism can provide enough ATP to let a horse exercise for about 1.5 minutes.
What is the difference between a horse's truck bed and a telephone pole?
In the horse’s body the truck bed is a bone, and the telephone poles combine to form a single muscle lying along it . That entire truckload of poles is one muscle, and each individual telephone pole represents a single muscle fiber. Now, picture hundreds to thousands of even skinnier telephone poles inside each large pole.
Why is genetics important for horses?
If the body delivers adequate levels of oxygen and nutrients, muscle will continue to contract without interruption. When things go wrong, seek your veterinarian’s help.
Where is the semitendinosus muscle?
Take the semitendinosus muscle, for example. The semitendinosus is one of the large, prominent muscles in your horse’s hamstring region. Visible to the naked eye, it runs from the pelvis along the length of the back of the femur (beside where the tail lies) and inserts onto the top region of the tibia (the long bone that stretches from the stifle to the hock). At its insertion, the muscle turns into tendon to make a firm, strong attachment to the bone. When the semitendinosus contracts (shortens, flexes) while weightbearing, the hip, stifle, and hock all extend backward, causing propulsion. When the limb is nonweightbearing, semitendinosus contraction causes stifle flexion, outward rotation of the limb, and backward motion (e.g., such as when a horse kicks).
Does aerobic metabolism increase muscle fibers?
In contrast, long duration, low- to moderate-intensity exercise—again, like endurance—relies primarily on aerobic metabolism with an increase in aerobic enzymes in the muscle fibers . Fibers that use aerobic metabolism maintain a small diameter to facilitate oxygen extraction from the blood so, rather than getting bigger, these fibers remain lean, like those of a distance runner.
How many muscles are there in a horse?
Since there are approximately 700 skeletal muscles in the horse, which produce movement, create stability and maintain the posture, it’s quite a complex territory to dive into. Especially if you also would like to include tendons, ligaments, fascia, nerves, hormones and many, many other elements that are necessary to create movement, ...
How many types of muscle contractions are there?
So there are three types of muscle contractions, all defined by the changes in the length of the muscle during contraction.
What is the term for the muscle contraction that can be done without changing the length of the muscle?
Muscles can contract without changing the length of the muscle – called isometric muscle activity : This is related to maintaining posture and it creates force which is for example required to grip but not move a heavy object (see the green person, holding the weight, but not moving it).
What is an example of eccentric muscle activity?
A horse example is bending the hind legs in piaffe by shifting the horse’s weight more back. ► 2. Muscles can contract and lengthen – called eccentric muscle activity: This is related to movement and it happens for example in the controlled lowering of the heavy weight (see the purple person: an eccentric contraction of the biceps).
Why do horses have round connected postures?
In this round, connected posture, the horse uses isometric muscle activity in the area of head and neck so his nose doesn’t get in front of the vertical.
What is multidimensional muscle training?
Multidimensional muscle training. Horse training is very multidimensional: You want to stretch and relax stiff muscles, but you also want to contract supple muscles in three different ways, while he’s shortening, lengthening and holding his muscles. By keeping our horse in between our aids, we boost the training effect, ...
What does ST mean in horse training?
Muscles of the horse. When doing Straightness Training (ST) we strive for keeping our horse in between our aids, and when working on the ground, it means in between our rein and whip aids. This way we can influence and shape the whole body of the horse, not only the head and neck. Now to get a horse in between your rein and whip aids, ...
How many muscles does a horse have?
Your horse has a lot of muscles; 700 skeletal muscles, to be exact. Compare that to around 300 in the human body. Muscles are complicated: They intertwine with connective tissue and different muscle groups have different jobs.Since your horse spends so much time using his muscles, let’s take a quick look at how they work.
What are the different types of muscles in horses?
Types of Muscles in Horses. Your horse has three muscles types: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Each muscle type has the following specific functions: 1. Skeletal. Supports and protects the skeleton and organs. Helps with joint stabilization and posture.
What type of muscle fibers are used for endurance?
Type I muscle fibers are known as "slow twitch fibers.". This means they work aerobically to use energy. Use adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for energy (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins all help produce ATP.) Used for endurance activities as muscles utilize fuel storage from nutrients.
What is a type 2 muscle?
Type II Muscles. Type II muscle fibers are known as "fast twitch fibers" and are broken down into two categories: Type II A and Type II B. Without getting too complicated, here’s what they do: Type II A: These muscles use both aerobic and anaerobic metabolisms to produce energy.
What type of fibers are in a horse's muscles?
Now that you know what kind of muscles your horse has, let’s look at what makes up those muscles. Horse muscles are made up of two different fibers: Type I and Type II. Here are the differences between the two:
How many liters of blood does a horse have?
3. Cardiac (Heart) Muscle. Strong: Circulates an average of 40 liters of blood throughout the body. Weighs about 1% of your horse’s body weight. Beats 32-36 times/minute in an average adult horse. (Some horses beat as slow as 24 beats per minute and as fast as 40 beats per minute.) Maintains blood flow.
Do horses need rest?
You already know your horse needs rest and recovery time, but greater knowledge of his muscle anatomy might help you better understand the importance of the respite. After all, we all want our horses to have the healthiest muscles possible, because healthy muscles equal better performance.
What type of muscles are needed for a horse to stand?
Distribution depending on muscles. « Postural » muscles are needed all the time in order to keep the horse in a standing position. As such, they must be rich in Type I and Type IIA fibers. These muscles are for exemple: back muscles and jaw muscles. Some of the jaw muscles are made of 100% of Type I fibers.
What muscles are needed to keep a horse standing?
As such, they must be rich in Type I and Type IIA fibers. These muscles are for exemple: back muscles and jaw muscles. Some of the jaw muscles are made of 100% of Type I fibers.
Why do two muscles work in an antagonistic way?
When we say that they work in an antagonistic way, they will oppose each other! If I tell you about it, it is because these antagonistic muscles allow several types of contractions that one must combine in order to have a well muscled horse.
How long does it take for a muscle to develop resistance?
After 4 weeks, the muscles are ready to develop more resistance and strength. We therefore move towards the next step: muscle building, which is now influencing type II fibers. We introduce gym exercises 2 to 3 times a week: collected training, lateral training, cavalettis, small obstacles, water training. All these exercises can be done on uneven terrain or terrains of varying depth.
What muscle is a quarter horse?
Let’s use the example of the middle gluteal muscle (a muscle in the buttock). For the Quarter Horse it contains on average 9% of type I fibers, against … 24% for the donkey! The Quarter Horse is as well the one breed with the most Type IIB fiber for this muscle (40%), which is why he is an excellent sprinter.
What is skeletal muscle?
To make it simple, a skeletal muscle is a grouping of muscle fibers. There are several types but three main ones. Depending on the fiber composition of the muscle, it will have different reactions to effort.
How long does it take for a horse to recover from a sandbox?
Warning! After intensive sessions or competitions, it takes at least 48-72 hours for the horse’s muscle to fully recover (24 to 48 hours at home). It is therefore important not to do too many sessions over the week.
Why is it important for horses to have strong muscles?
This improves posture, power, balance and precision, makes the horse gallop faster, jump higher and sustain pace for longer all with a reduced risk of injury.
How to make a horse more supple?
Turning the horse out where he can constantly move, roll, bite flies, scratch and stretch will enhance suppleness. Stabled horses have less opportunities to move and can be more prone to stiffness
What is a supple horse?
A supple horse like a supple person can move with ease, enjoy flexibility and a wide range of movement and be less prone to strain. This feel good factor contributes to concentration, cooperation, trainability and ‘joie de vivre’. A combination of strength, coordination and suppleness results in the horse moving with relaxation, rhythm, contact, impulsion, straightness, collection, balance and flexion. This enables him to demonstrate submission, cadence and throughness necessary for well executed dressage movements, accurate and flowing jumping and symmetrical muscle development.
How to use LSD for horses?
Long slow distance work (LSD) using aerobic respiration develops muscular endurance which enables muscles to sustain performance at sub maximal levels. This is essential for all horses in all disciplines especially for eventing and endurance horses. Time and distance must be extended gradually, moving on to the next stage only when current targets are met. This ensures progressive muscle loading without overtaxing a muscle. For a horse coming back into work, 15 minutes a day walking is a good starting point. Add 10 minutes a day gradually introducing trot and some canter work. The aim is to achieve 45 minutes of mixed gait work easily. It is important at this stage to condition all muscles equally to avoid putting strain on any particular part. LSD can take place out hacking or in an arena. Correct nutrition in the form of a balanced high energy diet is essential in supporting the muscles and the prevention of muscle disorders.
How does coordination improve dressage?
Well coordinated muscles work consistently, efficiently and accurately, improve posture and physical performance and reduce the risk of soreness and injury; dressage movements become well orchestrated and jumping more accurate. Muscle coordination and recruitment patterns are improved by repetition. This forges neural pathways which then improve muscle coordination and efficiency in an upward spiral. It is more productive to practise a new movement for 10 minutes every other day rather than for an hour once a week. Co ordination can be improved by practising cross country jumps such as a series of steps, sunken roads, banks, offset rails and ditch rail ditch on a regular basis.
What are some exercises to strengthen muscles?
General muscle strengthening is accomplished with short bursts of a varied high-intensity exercises such as:- 1 Hill work, including transitions, lateral work and rein back both up and down hill 2 Raised pole work progressively increasing height at walk and trot. 3 Performing half steps, piaffe and passage. 4 Gymnastic jumping including grids, related distances and progressively widening and heightening the obstacles. 5 Working on a loose deep surface. This must be approached gradually to reduce the risk of injury to muscles, tendons and ligaments. 6 Riding through water or long grass which encourages the horse to lift the legs clear and make the muscles work harder through the effect of drag
Why is muscle strength important?
Muscular strength is important for stability, balance, posture, weight carrying capacity, control, accuracy of movement and performance. Strengthening exercises result in joint stability, improved muscle tone and an increase in number of muscle fibres which increases muscle bulk, power and strength. Strength training should be part of a structured conditioning programme. In order to avoid fatigue and allow muscles time to recover it is important not to perform strength training sessions more than 2 or 3 times per week.
What muscle group is used in equestrians?
Hip Extensors. Hip Extensors are the muscle group located in the posterior hip and thigh. They are commonly called the “power muscles” for equestrians. Flexibility is equally as important as strength for this muscle group.
What muscle group is responsible for balance while riding?
Piriformis. The Piriformis is a muscle that connects your hip to your legs. In riding, this muscle group is highly responsible for balance while in the saddle. Because the Piriformis helps in extending and rotating the hips, imbalance in this muscle group will directly affect balance while riding.
How to improve horseback riding?
By focusing on the muscles used for horse back riding, you will be able to improve both your riding techniques and reverse any bad habits that you have developed over time. Muscle strength and flexibility promote better posture while in the saddle. It also allows you to have greater control of the horse while riding, whether through your body language or physical strength.
What muscles attach to the bottom rib?
Quadratus Lumborum attaches to the bottom rib, spinal vertebrae, and the back of your pelvis. As you can imagine, strength in this muscle is crucial for equestrians. Weakness in the quadratus lumborum will cause riders to lack control of their position in the saddle.
Why is horseback riding good for you?
Not only does horseback riding provide a fun way to improve muscle strength and overall fitness, but it also provides other health benefits !
What muscle group is used to stabilize the shoulder blades?
The Scapular Stabilizers provide stability to the shoulder blades. This group includes muscles such as the rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, serratus anterior, levator scapulae, and trapezius group. Although you may not consider this muscle group necessary for riding, it actually plays a crucial role.
How to prevent riding injuries?
Both beginner and experienced riders can greatly benefit from learning more about the muscles that allow them to do what they love. Taking care of your body by strengthening your muscle groups and practicing proper stretching is the best way to prevent unnecessary riding injuries.
How do horses see?
In general, horse vision is a little blurrier and a little less colorful than human vision. However, horses see movement very well throughout the 340° arc of their peripheral vision. This means a horse can see movement in most areas around its body, even with its head facing forward.
What are the eyes of horses?
Eye Structure and Function in Horses. The eyes of animals, including the eyes of horses, function much like your eyes. Animals also develop many of the same eye problems that people can have, including cataracts, glaucoma, and other problems. Because sight is the way in which horses get the majority of their information about their surroundings, ...
How does the retina work in horses?
The ciliary muscles relax to cause the lens to become thinner when it focuses on distant objects. In horses, the very large lens has a limited ability to change, making it hard for a horse to focus on close objects. The retinacontains the cells that sense light (photoreceptors). The most sensitive area of the retina is called the visual streakin horses. This area contains thousands of tightly packed photoreceptors that make visual images sharp. Each photoreceptor is attached to a nerve fiber. All the nerve fibers are bundled together to form the optic nerve. The photoreceptors in the retina convert the image into electrical impulses, which are carried to the brain by the optic nerve.
How to check a horse's eyes?
When examining your horse’s eyes, a veterinarian will begin by checking to see that the shape and outline of the eyes are normal and that there are no obvious abnormalities. Using light and magnification in a dar kened stall, the reflexes of the pupils and the front part of the eye will be examined. A test, called the Schirmer tear test, may be performed to ensure that the eyes are producing enough tears to keep them moist. This is a relatively simple test in which small paper strips are inserted under the eyelid to measure the amount of moisture produced. Another common test involves placing a small drop of fluorescein stain into each eye, which allows defects in the cornea of the eye to be detected.
What is the shape of the pupil in a horse?
The shape of the pupil in horses is a horizontal oval. The lens, which sits behind the iris, changes its shape to focus light onto the retina. Small muscles called ciliary muscles contract to cause the lens to become thicker, which allows the lens to focus on nearby objects.
Why are horses' eyes important?
Because sight is the way in which horses get the majority of their information about their surroundings, it is important for your horse ...
Why is it important for horses to have good eye care?
Because sight is the way in which horses get the majority of their information about their surroundings, it is important for your horse to receive good eye care to protect its sight and allow the horse to interact comfortably with its environment. In general, horse vision is a little blurrier and a little less colorful than human vision.
What muscles do horses use to spin?
Skeletal muscles, which attach to bones via tendons, contract or shorten in length in highly coordinated ways to produce movement. These muscle contractions allow horses to spin and run with their turnout buddies, chew mouthfuls of grass, pin their ears in warning, and swish their tails at flies. By understanding how horses’ muscles contract ...
How does a horse's heart rate change as he gets fitter?
As a horse gets fitter, his cardiac muscle gets stronger, allowing it to pump more blood with every beat and maintain the same blood flow at a lower heart rate. As his fitness increases, he should be able to perform the same amount of work at a lower heart rate.
How long does it take for a horse to burn ATP?
This anaerobic muscle metabolism can provide enough ATP to let a horse exercise for about 1.5 minutes.
What is the difference between a horse's truck bed and a telephone pole?
In the horse’s body the truck bed is a bone, and the telephone poles combine to form a single muscle lying along it . That entire truckload of poles is one muscle, and each individual telephone pole represents a single muscle fiber. Now, picture hundreds to thousands of even skinnier telephone poles inside each large pole.
Why is genetics important for horses?
If the body delivers adequate levels of oxygen and nutrients, muscle will continue to contract without interruption. When things go wrong, seek your veterinarian’s help.
Where is the semitendinosus muscle?
Take the semitendinosus muscle, for example. The semitendinosus is one of the large, prominent muscles in your horse’s hamstring region. Visible to the naked eye, it runs from the pelvis along the length of the back of the femur (beside where the tail lies) and inserts onto the top region of the tibia (the long bone that stretches from the stifle to the hock). At its insertion, the muscle turns into tendon to make a firm, strong attachment to the bone. When the semitendinosus contracts (shortens, flexes) while weightbearing, the hip, stifle, and hock all extend backward, causing propulsion. When the limb is nonweightbearing, semitendinosus contraction causes stifle flexion, outward rotation of the limb, and backward motion (e.g., such as when a horse kicks).
Does aerobic metabolism increase muscle fibers?
In contrast, long duration, low- to moderate-intensity exercise—again, like endurance—relies primarily on aerobic metabolism with an increase in aerobic enzymes in the muscle fibers . Fibers that use aerobic metabolism maintain a small diameter to facilitate oxygen extraction from the blood so, rather than getting bigger, these fibers remain lean, like those of a distance runner.
