What are the 5 different types of neurotransmitters?
Nov 14, 2021 · Neurotransmitters exist as the body’s chemical messengers that communicate with each other and with target tissues through synaptic transmission or neurotransmission. Overall, over 40 neurotransmitters exist within the human central nervous system (CNS), each having a specific and vital function for human behavior.
What is the most common neurotransmitter?
There are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; some of the most important are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, serotonin, and histamine.
What types of chemicals function as neurotransmitters?
May 09, 2021 · There are a number of neurotransmitters used by the body for different functions, including acetylcholine, glutamate, GABA, glycine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Glutamate is the principal excitatory neurotransmitter used in the brain. It is also the primary mediator of nervous system plasticity.
What are the major neurotransmitters?
Feb 22, 2022 · There are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; some of the most important are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, serotonin, and histamine.
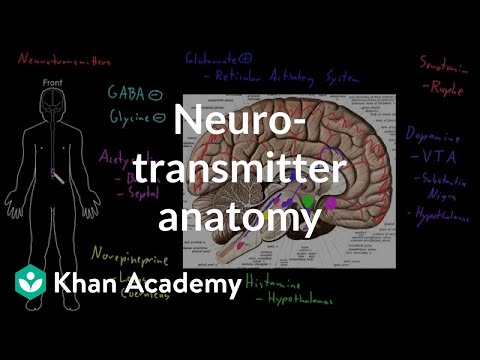
How many neurotransmitters exist in the brain?
The neuropeptides, small molecules like insulin and oxytocin, work more subtly, modulating, or adjusting, how cells communicate at the synapse. To date, scientists have identified more than 60 distinct types of neurotransmitters in the human brain, and most experts say there are more left to discover.Aug 1, 2019
What are the 4 types of neurotransmitters?
Types of NeurotransmittersAcetylcholine. Acetylcholine (Ach) was the first neurotransmitter discovered. ... Dopamine. ... Glutamate. ... Serotonin. ... Norepinephrine. ... gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) ... Other Neurotransmitters.Aug 1, 2019
What is the main neurotransmitter in the body?
Glutamate is the primary excitatory transmitter in the central nervous system. Conversely, a major inhibitory transmitter is its derivative γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), while another inhibitory neurotransmitter is the amino acid called glycine, which is mainly found in the spinal cord.Nov 9, 2017
Is there only one neurotransmitter?
Until relatively recently, it was believed that a given neuron produced only a single type of neurotransmitter. There is now convincing evidence, however, that many types of neurons contain and release two or more different neurotransmitters.
How does neurotransmission affect human behavior?
Out of these, Acetylcholine and Adrenaline act as excitatory neurotransmitters whereas Dopamine and Serotonin act as inhibitory ones. Each of this neurotransmitter is known to be responsible for the regulation of a certain aspect of the brain, thereby resulting in a more or less alteration of an individual's behavior.Aug 19, 2016
What are the 3 main neurotransmitters?
1 Answer. Acetylcholine, Glutamate and Serotonin are three examples of neurotransmitters.Oct 14, 2016
What are the 6 neurotransmitters?
Although there are several different minor and major neurotransmitters, we will focus on these major six: acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, GABA, and glutamate.May 7, 2020
Is melatonin a neurotransmitter or hormone?
Melatonin is a ubiquitous natural neurotransmitter-like compound (Figure 1) secreted by the pineal gland in the brain [1]. Melatonin has diverse functions that regulate the circadian rhythm, energy metabolism, and the immune system; it also inhibits oxidative stress and participates in the aging process [2,3].Oct 21, 2019
What are the seven neurotransmitters?
Fortunately, the seven “small molecule” neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, histamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin) do the majority of the work.
Is GABA A neurotransmitter?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the human cortex.Oct 6, 2015
Is dopamine a neurotransmitter?
Dopamine is an important endogenous catecholamine which exerts widespread effects both in neuronal (as a neurotransmitter) and non-neuronal tissues (as an autocrine or paracrine agent).
Are neurotransmitters in the brain?
Amino acids neurotransmitters These neurotransmitters are involved in most functions of your nervous system. Glutamate. This is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter of your nervous system. It's the most abundant neurotransmitter in your brain.Mar 14, 2022
Where are neurotransmitters released?
Neurotransmitters are the chemical messengers released at the nerve junctions. They are released into the junction of two neurons (synaptic cleft) and then they act on thereceptors present on the next neuron to continue the signal. Thus, they help our brain to control the functions and movements of our body organs.
How long do neurotransmitters last?
These organic substances have a short span of action. Their action lasts for a fraction of seconds at times. But some of them produce action for a long time. Based on their role in the body, they can be studied as.
Where is acetylcholine found?
Acetylcholine is a major neurotransmitter in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. It is also found in Red blood cells and other cells in the body. It is synthesized in the neurons and released at the nerve ending to pass on the nervous stimuli postsynaptically.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in the nervous system?
But it is mostly confined to the brain and spinal cord and few nerves. It affects moods like fear, anxiety and memory. It acts through receptors like D1, D2, D3. Disorders due to its deficiency or rise include depression, parkinsonism.
Where is glutamate found?
Glutamate. This is a neurotransmitter found predominantly in the brain and also as an amino-acid in the rest of the body. It acts through NMDA, AMPA receptors. It is involved in memory and learning.
What neurotransmitter is responsible for controlling nerve conduction and electric potential in the brain?
GABA is another neurotransmitter present predominantly in the brain. It acts to control nerve conduction and electric potential in the brain and also muscle tone. Its deficiency leads to epilepsy. It acts through GABA receptors.
Why are neurotransmitters important?
Due to their important role in body physiology, neurotransmitters are studies in subjects likeanatomy and physiology, pathophysiology and also in pharmacology. They are so quick in action and retraction. They can be compared with hormones as they have similar properties and modes of action.
How many neurotransmitters are there in the human body?
There are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; some of the most important are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, serotonin, and histamine. Key facts about neurotransmitters. Excitatory neurotransmitters. Glutamate (Glu)
What is the function of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are substances which neurons use to communicate with one another and with their target tissues in the process of synaptic transmission (neurotransmission). Neurotransmitters are synthetized in and released from nerve endings into the synaptic cleft. From there, neurotransmitters bind to receptor proteins in ...
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters?
Classification of neurotransmitters. Excitatory neurotransmitters function to activate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and enhance the effects of the action potential, while inhibitory neurotransmitters function to prevent an action potential.
What is the function of acetylcholine?
Regulates the sleep cycle, essential for muscle functioning. Its main function is to stimulate muscle contraction. However, the only exception to this, where acetylcholine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, is at the parasympathetic endings of the vagus nerve. These inhibit the heart muscle through the cardiac plexus.
What is the function of epinephrine?
Also known as adrenaline (Ad), epinephrine (Epi) is an excitatory neurotransmitter produced by the chromaffin cells of the adrenal gland. It prepares the body for the fight-or-flight response. That means that when a person is highly stimulated (fear, anger etc.), extra amounts of epinephrine are released into the bloodstream.
What is the function of glutamate?
Sensory neurons and cerebral cortex. Functions. Regulates central nervous system excitability, learning process, memory. Glutamate is the most common neurotransmitter in the central nervous system; it takes part in the regulation of general excitability of the central nervous system, learning processes, and memory.
What is the function of histamine in the body?
In the central nervous system, it is important for wakefulness, blood pressure, pain, and sexual behavior. In the stomach, it increases the acidity.
How many types of neurotransmitters are there in the human brain?
To date, scientists have identified more than 60 distinct types of neurotransmitters in the human brain, and most experts say there are more left to discover. These powerful neurochemicals are ...
What are the two types of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters, at the highest level, can be sorted into two types: small-molecule transmitters and neuropeptides. Small-molecule transmitters , like dopamine and glutamate, typically act directly on neighboring cells. The neuropeptides, small molecules like insulin and oxytocin, work more subtly, modulating, or adjusting, how cells communicate at the synapse. To date, scientists have identified more than 60 distinct types of neurotransmitters in the human brain, and most experts say there are more left to discover. These powerful neurochemicals are at the center of neurotransmission, and, as such, are critical to human cognition and behavior.
Why is dopamine called the pleasure chemical?
Dopamine (DA) is often referred to as the “pleasure chemical” because it is released when mammals receive a reward in response to their behavior; that reward could be food, drugs, or sex. It is one of the most extensively studied neurochemicals, mainly because it plays such diverse roles in human behavior and cognition.
How many neurons are there in the human brain?
The human brain contains an estimated 86 billion neurons. Those billions of brain cells communicate by passing chemical messages at the synapse, the small gap between cells, in a process called neurotransmission. Those chemical messages are unique molecules called neurotransmitters. There are many types of neurotransmitters in the brain, ...
Which neurotransmitter is released from the hypothalamus?
Neurochemicals like oxytocin and vasopressin are also classified as neurotransmitters. Made and released from the hypothalamus, they act directly on neurons and have been linked to pair-bond formation, monogamous behaviors, and drug addiction.
Where are neurotransmitters released?
When a cell is activated, these neurochemicals are released into the synapse from specialized pouches clustered near the cell membrane called synaptic vesicles.
What is the role of acetylcholine in the brain?
But it also has other roles in the brain, including helping direct attention and playing a key role in facilitating neuroplasticity across the cortex.
What are the different types of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters have different types of action: 1 Excitatory neurotransmitters encourage a target cell to take action. 2 Inhibitory neurotransmitters decrease the chances of the target cell taking action. In some cases, these neurotransmitters have a relaxation-like effect. 3 Modulatory neurotransmitters can send messages to many neurons at the same time. They also communicate with other neurotransmitters.
Why do we need neurotransmitters?
Many bodily functions need neurotransmitters to help communicate with the brain. Experts have identified more than 100 neurotransmitters to date. Neurotransmitters have different types of action: Excitatory neurotransmitters encourage a target cell to take action.
What are the chemical messengers in the body?
Endorphins. Epinephrine. GABA. Serotonin. Summary. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the body. Their job is to transmit signals from nerve cells to target cells. These target cells may be in muscles, glands, or other nerves. The brain needs neurotransmitters to regulate many necessary functions, including:
How do neurotransmitters communicate?
Neurotransmitters relay their messages by traveling between cells and attaching to specific receptors on target cells. Each neurotransmitter attaches to a different receptor — for example, dopamine molecules attach to dopamine receptors. When they attach, this triggers action in the target cells.
Why is dopamine important?
Dopamine is important for memory, learning, behavior, and movement coordination. Many people know dopamine as a pleasure or reward neurotransmitter. The brain releases dopamine during pleasurable activities. Dopamine is also responsible for muscle movement.
What is the function of the brain?
The brain needs neurotransmitters to regulate many necessary functions, including: The nervous system controls the body’s organs, psychological functions, and physical functions. Nerve cells, also known as neurons, and their neurotransmitters play important roles in this system. Nerve cells fire nerve impulses.
How do endorphins help with pain?
They are also the body’s natural pain relievers. One of the best-known ways to boost levels of feel-good endorphins is through aerobic exercise . A “runner’s high,” for example, is a release of endorphins. Also, research.
How many types of neurotransmitters are there?
While there are dozens of known neurotransmitters, there are seven major ones to focus on. They fall into two different types, depending on their actions. Some are excitatory neurotransmitters. This means they encourage other brain cells to fire commands. Other neurotransmitters are considered inhibitory.
How do neurotransmitters work?
Neurotransmitters do that work, sending instructions from one brain cell to the next and transferring information throughout the brain and body. The process starts where these chemical messengers are stored in tiny compartments at the end of neurons. These are called synaptic vesicles.
What is the function of oxytocin?
Your brain makes oxytocin in the hypothalamus and releases it via the pituitary gland to trigger responses all over the body. Oxytocin urges the walls of the uterus to contract when a woman delivers her baby.
Why do we need dopamine?
It encourages wakefulness. It helps your pancreas release the appropriate amount of insulin after you eat. Dopamine also coordinates your brain and your body to create voluntary movement. Writing your name, typing, and driving a car are all possible because of dopamine.
What is the gap between neurons called?
More energy means brain cells can dump chemical neurotransmitters into the space between them and the next neuron. This gap between neurons is called the synapse.
Do neurons send signals to other cells?
They allow neurons to communicate to other brain cells. That’s not it, though. Muscles receive cues from neurotransmitters, too. In fact, these chemical messengers send information throughout the body. The different types of neurotransmitters vary widely. Some manage your heart rate and blood pressure.
What is the action potential of acetylcholine?
Then the presence of acetylcholine triggers an action potential or command in the muscle fiber. But instead of sending signals to a brain cell, acetylcholine makes your muscle contract. Every time you move your muscles, acetylcholine is in play.
What is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the human body?
Important Neurotransmitters. Glutamate is the most abundant neurotransmitter in humans, used by about half of the neurons in the human brain. It is the primary excitatory transmitter in the central nervous system. One of its functions is to help form memories. Interestingly, glutamate is toxic to neurons.
What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters Definition and List. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that connect neurons, allowing signals to be sent from one part of the body to another. Science Picture Co / Getty Images. Science, Tech, Math. Chemistry. Biology. Physics.
What is the difference between dopamine and serotonin?
Low dopamine levels are associated with social anxiety and Parkinson's disease, while excess dopamine is related to schizophrenia. Serotonin is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in mood, emotion, and perception.
What is the effect of low serotonin levels on mood?
Low serotonin levels can lead to depression, suicidal tendencies, anger management issues, difficulty sleeping, migraines, and an increased craving for carbohydrates.
What are the functions of neurotransmitters?
For example, they regulate heartbeat, tell the lungs when to breathe, determine the set point for weight, stimulate thirst, affect mood, and control digestion.
What happens when a neuron fires?
If the stimulus for excitation is greater than the inhibitory effect, the neuron will "fire" and create an action potential that releases neurotransmitters to another neuron.
What are some examples of Alzheimer's disease?
Examples include botulin, curare, and hemlock. Alzheimer's disease is associated with a significant drop in acetylcholine levels. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) increases heart rate and blood pressure. It is part of the body's "fight or flight" system. Norepinephrine is also needed to form memories.
Where is the neurotransmitter released?
Generally, a neurotransmitter is released at the presynaptic terminal in response to a threshold action potential or graded electrical potential in the presynaptic neuron. However, low level 'baseline' release also occurs without electrical stimulation.
What is the only direct action of a neurotransmitter?
As explained above, the only direct action of a neurotransmitter is to activate a receptor. Therefore, the effects of a neurotransmitter system depend on the connections of the neurons that use the transmitter, and the chemical properties of the receptors that the transmitter binds to.
What is the synaptic cleft?
However, through histological examinations by Ramón y Cajal, a 20 to 40 nm gap between neurons, known today as the synaptic cleft, was discovered. The presence of such a gap suggested communication via chemical messengers traversing the synaptic cleft, and in 1921 German pharmacologist Otto Loewi confirmed that neurons can communicate by releasing chemicals. Through a series of experiments involving the vagus nerves of frogs, Loewi was able to manually slow the heart rate of frogs by controlling the amount of saline solution present around the vagus nerve. Upon completion of this experiment, Loewi asserted that sympathetic regulation of cardiac function can be mediated through changes in chemical concentrations. Furthermore, Otto Loewi is credited with discovering acetylcholine (ACh) – the first known neurotransmitter.
How do neurotransmitters affect the function of a neuron?
A neurotransmitter can influence the function of a neuron through a remarkable number of mechanisms. In its direct actions in influencing a neuron's electrical excitability, however, a neurotransmitter acts in only one of two ways: excitatory or inhibitory. A neurotransmitter influences trans-membrane ion flow either to increase (excitatory) or to decrease (inhibitory) the probability that the cell with which it comes in contact will produce an action potential. Thus, despite the wide variety of synapses, they all convey messages of only these two types, and they are labeled as such. Type I synapses are excitatory in their actions, whereas type II synapses are inhibitory. Each type has a different appearance and is located on different parts of the neurons under its influence.
Which neurotransmitter is excitatory?
The most prevalent transmitter is glutamate, which is excitatory at well over 90% of the synapses in the human brain. The next most prevalent is gamma-Aminobutyric Acid, or GABA, which is inhibitory at more than 90% of the synapses that do not use glutamate.
What is the precursor of dopamine?
L -DOPA, a precursor of dopamine that crosses the blood–brain barrier, is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. For depressed patients where low activity of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine is implicated, there is only little evidence for benefit of neurotransmitter precursor administration. L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine are both precursors for dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. These conversions require vitamin B6, vitamin C, and S-adenosylmethionine. A few studies suggest potential antidepressant effects of L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine, but there is much room for further research in this area.
What is the function of dopamine in the brain?
Dopamine has a number of important functions in the brain; this includes regulation of motor behavior, pleasures related to motivation and also emotional arousal.
