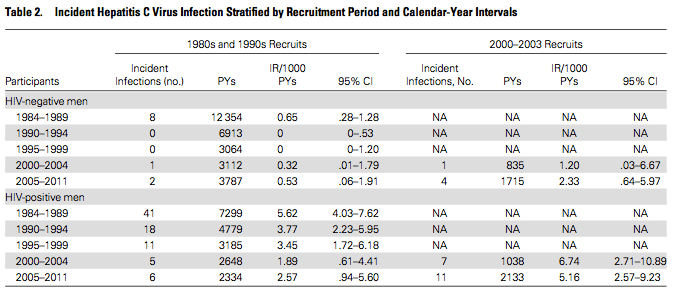
How many people are infected with hepatitis C?
Estimates from the CDC suggest that about 3.9 million people are infected with the hepatitis C virus, and that about 50% to 75% of these people (minimally, about 1.6 million people) are unaware they are infected with the virus.
What is the prevalence of chronic HCV infection in the US?
What is the prevalence of chronic HCV infection in the United States? An estimated 2.4 million people in the United States are living with hepatitis C virus infection ( 1 ). Who is at risk for HCV infection? The following people are at increased risk for HCV infection:
How many genotypes are there in hepatitis C virus (HCV)?
Smith DB, Bukh J, Kuiken C, Muerhoff AS, Rice CM, Stapleton JT, Simmonds P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology. 2014;59 (1):318-27.
How common is hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of death?
In 2017, 17,253 U.S. death certificates had HCV recorded as an underlying or contributing cause of death ( 7 ). However, this is a conservative estimate.
How many people have been infected with HCV?
2.4 million people are estimated to be living with hepatitis C in the United States. The actual number may be as high as 4.7 million or as low as 2.5 million. 850,000 people in the U.S. are estimated to be living with hepatitis B. The actual number may be as high as 2.2 million or as low as 730,000.
What percentage of the population has Hep C?
Nearly 2.4 million Americans – 1 percent of the adult population – were living with hepatitis C from 2013 through 2016, according to new CDC estimates. Half of people with hepatitis C may not know they're infected.
How do most people become infected with HCV?
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus. Today, most people become infected with HCV by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. For some people, HCV infection is a short-term or acute illness but for more than half of people who become infected with HCV, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection.
How common is hep C transmission?
Approximately 6% of infants born to infected mothers will get hepatitis C. ►Health care exposures. Although uncommon, people can become infected when health-care professionals do not follow the proper steps needed to prevent the spread of bloodborne infections. ►Sex with an infected person.
Is Hep C considered an STD?
Although not common, hepatitis C can be transmitted through sexual activity. Having a sexually transmitted infection, having sex with multiple partners, and engaging in anal sex appear to increase a person's risk for hepatitis C.
Why is there no vaccine for Hep C?
The main reason there is no vaccine for hepatitis C is because this virus has many strains, called genotypes, and many subtypes. To be effective, a vaccine must be able to protect against all or most of the genotypes and subtypes. Hepatitis C has at least 7 genotypes and more than 80 subtypes.
Can you live a normal life with hep C?
With the help of antiviral medications, you can defeat hepatitis C. Most people with hepatitis C can live a normal life as long as their liver isn't severely damaged, which can take years to occur. The sooner you get tested and diagnosed, the higher your chances of beating the virus.
How long does hep C take to damage liver?
On average it takes about twenty years for significant liver scarring to develop. The symptoms experienced and the damage done to the liver vary dramatically from person to person. Some people will have few, if any, symptoms for many years.
Who is at high risk for HCV?
Those individuals most at risk for hepatitis C infection are: People who had blood transfusions, blood products, or organ donations before June, 1992, when sensitive tests for HCV were introduced for blood screening. Health care workers who suffer needle-stick accidents.
Can you get hep C from kissing?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), hepatitis C does not spread through kissing, hugging, sharing utensils, coughing, sneezing, or sharing food or water.
Is hep C in sperm?
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is only detectable in the semen of a minority of HIV-positive gay men co-infected with both viruses, and even then at very low levels, a small study presented at the second joint BHIVA/BASHH Conference has found.
Can I get hep C from touching blood?
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person. Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection.
What group has highest rate of Hep C?
You're a baby boomer. About 75% of the people infected with hepatitis C in the U.S. were born between 1945 and 1965. If you're in this group, your chance of getting hepatitis C is at least five times greater than people of any other age.
Where is hep C most common?
Who is at risk? Hepatitis C occurs in nearly every part of the world but is most common in some countries in Asia and Africa.
How long does Hep C take to damage liver?
On average it takes about twenty years for significant liver scarring to develop. The symptoms experienced and the damage done to the liver vary dramatically from person to person. Some people will have few, if any, symptoms for many years.
How is hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C is spread through contact with blood from an infected person. Today, most people become infected with the hepatitis C virus by sharing needles or other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs.
How long does it take to get tested for hepatitis C?
Getting tested for hepatitis C is important, because treatments can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
Is hepatitis C a long term illness?
For some people, hepatitis C is a short-term illness, but for more than half of people who become infected with the hepatitis C virus, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis C can result in serious, even life-threatening health problems like cirrhosis and liver cancer. People with chronic hepatitis C can often have no symptoms ...
Is hepatitis C a risk factor?
CDC continues to recommend people with risk factors, including people who inject drugs, be tested regularly. CDC recommendations for hepatitis C screening among adults – United States, 2020. Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C is spread through contact with blood from an infected person.
AT A GLANCE: Acute Hepatitis C in 2019
Rates of acute hepatitis C increased again in 2019. The highest rates occurred in persons 20–39 years, consistent with age groups most impacted by the nation’s opioid crisis.
Hepatitis C Surveillance Data
Figure 3.1. Number of reported acute hepatitis C virus infection cases and estimated infections — United States, 2012–2019
How many people died from hepatitis in 2015?
WHO estimated that during the same year, 1.34 million people died from liver cancer, cirrhosis, and other conditions caused by chronic viral hepatitis ( 1 ).
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
All types of viral hepatitis can be controlled or prevented. Hepatitis C can be cured; a once-daily medication taken by mouth for as few as 8 weeks can cure most people who are infected with hepatitis C. Hepatitis B medications are available to help prevent liver damage and slow progression of the disease.
What is the disease that affects millions of people?
Viral hepatitis ( hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, hepatitis E) affects millions of people around the globe; hepatitis B and C result in chronic infections and disproportionately impact certain countries (see maps below). Countries most affected by hepatitis B. Countries most affected by hepatitis C.
Can hepatitis be controlled?
All types of viral hepatitis can be controlled or prevented.
How many cases of hepatitis C in 2018?
In 2018, a total of 3,621 cases of acute hepatitis C were reported to CDC ( 2 ). After adjusting for under-ascertainment and under-reporting, an estimated 50,300 acute hepatitis C cases occurred in 2018. More information on hepatitis C surveillance is available from CDC.
How rare is hepatitis C?
Now that more advanced screening tests for hepatitis C are used in blood banks, the risk of transmission to recipients of blood or blood products is considered extremely rare, at <1 case per 2 million units transfused.
Is hepatitis C screening universal?
CDC now recommends universal hepatitis C screening for all U.S. adults and all pregnant women during every pregnancy, except in setting s where the prevalence of HCV infection is <0.1% (see How should providers determine hepatitis C prevalence? ). This includes
Can hepatitis C cause liver problems?
Some people with chronic HCV infection develop medical conditions due to hepatitis C that are not limited to the liver. Such conditions can include:
Can hepatitis C cause liver enzymes to fluctuate?
Yes. It is common for patients with chronic hepatitis C to have fluctuating liver enzyme levels, with periodic returns to normal or near normal levels. Liver enzyme levels can remain normal for over a year despite chronic liver disease ( 28 ).
Can you test positive for HCV?
No. The anti-HCV test only provides information about past exposure to HCV. A negative anti-HCV result indicates that a patient has never been exposed to the virus, and therefore the anti-HCV test is only used to rule out HCV infection. If a person tests positive for HCV antibodies, hepatitis C testing is not considered complete unless the initial positive anti-HCV test is followed by a test for HCV RNA as per CDC guidelines. A positive test for HCV RNA is needed before a patient can be diagnosed with current HCV and begin receiving treatment. Ideally, positive antibody tests are “reflexed” to an HCV RNA test automatically from the same blood sample. However, reflex testing is not possible in every laboratory or clinical setting.
Can hepatitis C be transmitted between household members?
Yes; however, transmission between household members does not occur very often. If hepatitis C is spread within a household, it is most likely a result of direct (i.e., parenteral or percutaneous) exposure to the blood of an infected household member.
Which age group has the highest rate of hepatitis C?
Baby boomers (born between 1945 and 1965) account for a large portion of all chronic hepatitis C infections in the United States and currently have the highest rate of hepatitis C-related deaths. CDC recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 get a one-time test for hepatitis C, but only a small fraction have done so.
What are the risks of hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C now poses a serious health threat to three generations of Americans, all of whom need to be reached with prevention services, testing, and treatment: 1 Baby boomers (born between 1945 and 1965) account for a large portion of all chronic hepatitis C infections in the United States and currently have the highest rate of hepatitis C-related deaths. CDC recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 get a one-time test for hepatitis C, but only a small fraction have done so. 2 Adults under 40 have the highest rate of new infections, largely because of the opioid crisis. 3 Infants born to mothers with hepatitis C are a growing concern. The overall risk of an HCV-infected mother transmitting infection to her infant is approximately 4 percent to 7 percent per pregnancy. From 2011 through 2014, national laboratory data indicate that the rate of infants born to women living with hepatitis C increased by 68 percent.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
Even though new treatments can cure hepatitis C virus infections in as little as two to three months, far too many Americans have not been effectively treated. They may be unaware of their infection or they are unable to access medication because they lack healthcare coverage or have financial restrictions.
What age group has the highest rate of new infections?
Adults under 40 have the highest rate of new infections, largely because of the opioid crisis. Infants born to mothers with hepatitis C are a growing concern. The overall risk of an HCV-infected mother transmitting infection to her infant is approximately 4 percent to 7 percent per pregnancy. From 2011 through 2014, national laboratory data ...
Where is the CDC located?
CDC is headquartered in Atlanta and has experts located throughout the United States and the world.
Is hepatitis C cured?
Medications that cure hepatitis C offer the hope of eliminating the disease in the U .S., yet, today’s report suggests that millions are infected and have not benefited from these new treatment options. Expanded testing, treatment, and prevention services are urgently needed, especially in light of the surge in new infections linked to the opioid crisis.
Is the opioid crisis a threat to hepatitis C?
Opioid crisis puts new generations at risk of hepatitis C infections. Adding to the burden of those already living with hepatitis C, separate CDC surveillance data indicate that the number of new infections each year in the United States is disturbingly high and on the rise.
How many people in the US have hepatitis C?
Millions of Americans from all walks of life are living with viral hepatitis, and most don’t know they have the virus. 2.4 million people are estimated to be living with hepatitis C in the United States. The actual number may be as high as 4.7 million or as low as 2.5 million. 1.
How much did hepatitis C increase in 2010?
Acute hepatitis C infections increased 250% from 2010 to 2014.
What age group is most likely to have hepatitis C?
Millennials (most adults in their 20s and 30s) made up 36.5% of newly reported chronic hepatitis C infections. Baby boomers (most adults in their mid-50s to early 70s) made up 36.3% of newly reported chronic hepatitis C infections. Generation X (adults in their late 30s to early 50s) made up 23.1% of newly reported chronic hepatitis C infections.
How many Asian Americans have hepatitis B?
population, but they represent about half of all persons living with hepatitis B. As a result, 1 in 12 Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders are living with hepatitis B. Hepatitis C infections are increasing in the United States.
What percentage of hepatitis C is in Generation X?
Generation X (adults in their late 30s to early 50s) made up 23.1% of newly reported chronic hepatitis C infections.
What is the cause of the increase in hepatitis B?
Increases in hepatitis B infections are being fueled by the opioid and heroin use epidemics that are gripping many communities across the United States.
How is HCV spread?
HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with injection drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, needlestick injuries in healthcare, and transfusions. Using blood screening, the risk from a transfusion is less than one per two million. It may also be spread from an infected mother to her baby during birth. It is not spread by superficial contact. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.
How many people died from hepatitis C in 2016?
Deaths. 399,000 (2016) Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin occurs.
How many people died from liver cancer in 2015?
About 167,000 deaths due to liver cancer and 326,000 deaths due to cirrhosis occurred in 2015 due to hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non- A non- B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. Play media.
Why do tattoos cause hepatitis C?
This can be due to either improperly sterilized equipment or contamination of the dyes being used. Tattoos or piercings performed either before the mid-1980s, "underground", or nonprofessionally are of particular concern, since sterile techniques in such settings may be lacking. The risk also appears to be greater for larger tattoos. It is estimated that nearly half of prison inmates share unsterilized tattooing equipment. It is rare for tattoos in a licensed facility to be directly associated with HCV infection.
What is the risk of hepatitis C?
Drug use. Injection drug use (IDU) is a major risk factor for hepatitis C in many parts of the world. Of 77 countries reviewed, 25 (including the United States) were found to have a prevalence of hepatitis C of between 60% and 80% among people who use injection drugs. Twelve countries had rates greater than 80%.
How old do you have to be to get tested for HCV?
In the United States, screening for HCV infection is recommended in all adults age 18 to 79 years old.
What are the barriers to finding treatment for hepatitis C?
One barrier to finding treatments for hepatitis C is the lack of a suitable animal model. Despite moderate success, research highlights the need for pre-clinical testing in mammalian systems such as mouse, particularly for the development of vaccines in poorer communities. Chimpanzees remain the only available living system to study, yet their use has ethical concerns and regulatory restrictions. While scientists have made use of human cell culture systems such as hepatocytes, questions have been raised about their accuracy in reflecting the body's response to infection.
How many people can get HCV from injecting drugs?
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, one person with HCV who injects drugs can potentially go on to transmit the virus to 20 other people.
Why is it possible to contract HCV again?
Because your body doesn’t generate a strong immune response to HCV, it’s possible to contract the virus again. While the rate of reinfection is low, the risk may be increased in people who:
What is the cause of hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is an infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It can lead to serious liver damage, so it’s important to know all the ways it can be transmitted.
What happens if your mother has hepatitis C?
If your mother had hepatitis C when you were born, you may have a slightly higher risk of getting the virus.
How does hepatitis C get contracted?
How hepatitis C is contracted. People contract hepatitis C by coming into contact with the blood of someone who has the virus. This can happen in several different ways.
Why is it important to get tested for hepatitis C?
Additionally, hepatitis C often has no visible symptoms for many years. Because of this, it’s important to be tested if you believe you’ve been exposed to the virus.
Can HCV be spread through nonsterile medical equipment?
Nonsterile medical equipment. In rare cases, HCV can be spread through nonsterile medical equipment. This can occur due to things such as: reusing a needle or syringe that someone with hepatitis C has already used.
How Many People in the US Are Infected with the Hepatitis C Virus?
Estimates from the CDC suggest that about 3.9 million people are infected with the hepatitis C virus, and that about 50% to 75% of these people (minimally, about 1.6 million people) are unaware they are infected with the virus. Most infected are men and women aged 45–64. However, white men comprise the largest group.
How Many People Die Every Year from the Hepatitis C Virus vs. HIV Infection?
Most people, including doctors, would be crying out for help from science and the government if suddenly, a disease was found that was killing more people than HIV infections (19,659 vs 15,119 HIV deaths per year according to US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC] statistics for the US). Unfortunately, such a disease exists. It's called hepatitis C.
What Are the Largest Populations "Silently" Infected with Hepatitis C?
The largest populations of "silently" infected people are white males (and some females) between the ages of 45 and 64 as well as Blacks and Hispanics in the same age groups. These populations should be tested (screened) for infection with hepatitis C as soon as possible. Those of the highest priority to be tested are the individuals at increased risk according to the methods of spread listed above.
What is the killer virus?
We know the killer virus is hepatitis C, we know how kill it, and we have the means to detect and stop its spread. We as health-care professionals and potential victims of hepatitis C viral infection can prevent many deaths if we all act now to stop hepatitis C infections.
Why is the killer of hepatitis better understood?
Usually when their pattern of attacks are recognized and then publicized so people understand how to protect themselves from attack, or if being attacked, how to defend themselves. The killer, hepatitis C virus, is now better understood so that an initial outcry may be heard and heeded.
Can you get hepatitis C from a toothbrush?
Chronic hemodialysis. Contact with blood from someone with hepatitis C (infrequent, but may occur sharing razors or toothbrushes) Unfortunately, people with hepatitis C virus may inadvertently infect others because they may not realize they are infective as they undergo the many years of "silent" damage that can occur between initial infection ...
Can you recover from hepatitis C without medication?
Yes. About 15% to 25% of those people infected with the virus will spontaneously recover without medication. For those individuals who don't recover without medication, there are several antiviral drugs that are effective at ridding the body of the virus before enough damage has occurred to destroy the liver. Hepatitis C "cure" rates are reported to approach 100% ("cure" in this disease means no detectable virus in the person's blood).

Geographical Distribution
Transmission
Symptoms
Testing and Diagnosis
Treatment
- HCV occurs in all WHO regions. The highest burden of disease is in the Eastern Mediterranean Region and European Region, with 12 million people chronically infected in each region. In the South-East Asia Region and the Western Pacific Region, an estimated 10 million people in each r…
Prevention
- The hepatitis C virus is a bloodborne virus. It is most commonly transmitted through: 1. the reuse or inadequate sterilization of medical equipment, especially syringes and needles in healthcare settings; 2. the transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products; and 3. injecting drug use through the sharing of injection equipment. HCV can be passed from an infected mother to her …
Who Response
- The incubation period for hepatitis C ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months. Following initial infection, approximately 80% of people do not exhibit any symptoms. Those who are acutely symptomatic may exhibit fever, fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, pale faeces, joint pain and jaundice (yellowing of skin and the whites of the eyes).
Key Facts
- Because new HCV infections are usually asymptomatic, few people are diagnosed when the infection is recent. In those people who go on to develop chronic HCV infection, the infection is often undiagnosed because it remains asymptomatic until decades after infection when symptoms develop secondary to serious liver damage. HCV infection is diagnosed in 2 steps: 1. …
Progress Being Made Worldwide
- A new infection with HCV does not always require treatment, as the immune response in some people will clear the infection. However, when HCV infection becomes chronic, treatment is necessary. The goal of hepatitis C treatment is to cure the disease. WHO recommends therapy with pan-genotypic direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) for persons over the age of 12 years. DAAs ca…
Global Efforts to Eliminate Viral Hepatitis
- There is no effective vaccine against hepatitis C so prevention depends on reducing the risk of exposure to the virus in health care settings and in higher risk populations. This includes people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men, particularly those infected with HIV or those who are taking pre-exposure prophylaxis against HIV. Primary prevention interventions recomm…
Global Immunization Strategic Framework 2021-2030
- In May 2016, the World Health Assembly adopted the first Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis, 2016-2021. The strategy highlights the critical role of universal health coverage and sets targets that align with those of the Sustainable Development Goals. The strategy aims to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health problem by reducing new viral hepatitis infections by 9…
Current Status of Prevention and Treatment
Global Efforts to Improve Delivery of Hepatitis B Vaccine During Infancy
- All types of viral hepatitis can be controlled or prevented. 1. Hepatitis C can be cured; a once-daily medication taken by mouth for 8-12 weeks can cure most people who are infected with hepatitis C. In 2019, 9.4 million people were receiving treatment for chronic HCV infection, greater than a nine-fold increase since 2015 (1). 2. Medications to manage hepatitis B are available to help pre…