How many subject areas are there in the Physics GCSE?
There are eight main subject areas in the exam, spread out over two test papers: 1 Energy 2 Electricity 3 Particle model of matter 4 Atomic structure 5 Forces 6 Waves 7 Magnetism and electromagnetism 8 Space physics
What is the GCSE physics syllabus for GCSE?
GCSE Physics Syllabus: All the Topics at a Glance 1 Energy. 2 Electricity. 3 Particle Model of Matter. 4 Atomic Structure. 5 Forces. 6 Waves. 7 Magnetism and Electromagnetism. 8 Space Physics. 9 Sample Exam Questions.
What are the different types of GCSE subjects?
Although you do get to choose most your GCSE options, there are some subjects that are compulsory. These are known as core GCSE subjects and include: Welsh (if you live in Wales) Sciences (either single, double or triple science) The core science GCSE subjects are biology, physics and chemistry.
What are the 5 topics in physics?
Topics 1-4: Energy; Electricity; Particle model of matter; and Atomic structure. Multiple choice, structured, closed short answer and open response. Topics 5-8: Forces; Waves; Magnetism and electromagnetism; and Space physics.

What are the topics in GCSE physics?
The topics taught will include motion, energy, matter, force, motion, space, time and energy. Many students find physics to be a challenging subject. One of the reasons they find GCSE physics challenging is because it is very maths heavy.
What topics are in GCSE physics 2?
The second paper covers subjects 4-8: forces; waves; magnetism and electromagnetism and space physics....There are eight main subject areas in the exam, spread out over two test papers:Energy.Electricity.Particle model of matter.Atomic structure.Forces.Waves.Magnetism and electromagnetism.Space physics.
How many units are there in GCSE physics?
It is important to remember these six fundamental (or 'base') units of measurement: metre (m) - unit of length. kilograms (kg) - unit of mass. second (s) - unit of time.
How long is physics GCSE 1?
1 hour 45 minutesGCSE Physics Test Paper The first test paper covers the first four topics in the syllabus, i.e. energy, electricity, particle model of matter and atomic structure. The test will be written (rather than taken online) and lasts for 1 hour 45 minutes.
What should I revise for physics?
Know what to study.Get your basics right.Check the formulae and derivations.Look beyond numericals.Don't overlook graphical questions.Make your own notes.Look and learn.Revise and practice.
What should I revise for physics GCSE?
The GCSE Physics Exam.Prioritise Your Revision.Get to Grips with Command Words.Practise Recalling and Using Formulae.Re-Familiarise Yourself with Core Practical Work.Don't Overlook 'Working Scientifically'Small Things That Make a Big Difference.Brush Up on Your Maths.More items...
Is physics a hard GCSE?
GCSE Physics is an extremely hard GCSE, and only the brightest and best students achieve the top marks in their exams. GCSE Physics is best known for its high level of maths content, and the many equations you have to remember.
What is the pass rate for GCSE physics?
GCSE sciences: biology, chemistry and physics And in physics, grades 7/A rose by 2.3pp to 55.3 per cent, but the pass rate fell by 0.8pp to 95.3 per cent.
How many GCSE is a lot?
Most colleges like you to take a minimum of five GCSEs, including English Language and Maths at grade 4 (C) or above, while sixth forms have slightly higher entry requirements, looking for at least six GCSE examination results achieving at least a grade 4 (C).
Is physics C or 1 harder?
We all know that AP® Physics 1 is easier than AP® Physics C. We note that many of the AP® Physics C courses self-select for those motivated students or those with higher grades in Math. That is the reason for the ridiculously high rates for AP® Physics C as compared to AP® Physics 1.
How long should I be revising for GCSE?
According to The Student Room, students revise 15 to 20 hours per week for their exams, which might sound a lot until you break it down. You've probably worked it out for yourself, but the recommended time equates to three to five hours of revision per day with weekends off!
Is physics grade 12 easy?
Physics is notorious for being one of the more difficult courses in high school, and tends to be the first course that gets dropped when grade 12 rolls around.
What topics are covered in Physics 2?
Topics may include:Thermodynamic systems.Pressure, thermal equilibrium, and the Ideal Gas Law.Thermodynamics and forces.Heat and energy transfer.Thermodynamics and collisions.Probability, thermal equilibrium, and entropy.
What do you study in Physics 2?
Physics 2 explores fluid statics and dynamics, thermodynamics with kinetic theory, PV diagrams and probability, electrostatics, electrical circuits with capacitors, magnetic fields, electromagnetism, physical and geometric optics, and quantum, atomic, and nuclear physics.
What is General Physics 2 all about?
General physics 2 gives the concepts and applications of the physics concepts in sciences and engineering. This lectures presented topics of Electricity, Magnetism, Optics, and Modern Physics.
What is the difference between physics 1 and 2?
AP Physics 1 covers topics such as Newtonian mechanics, mechanical waves and the basics of electric circuits. AP Physics 2 continues with topics like electricity and magnetism, fluids and thermodynamics. They are equivalent to first-semester and second-semester college courses, respectively, in algebra-based physics.
What are the topics covered in GCSE Physics?
GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: The expanding universe. The life cycle of a star. The Solar System. Those studying this topic are expected to learn about the important elements in our Solar System, such as the Sun, the planets, the moons, the dwarf planets, asteroids and comets.
How many subjects are there in GCSE Physics?
The GCSE physics syllabus consists of eight subject areas, spread out over two test papers:
What is the particle model of matter?
Particles in gases. Temperature changes and energy. The particle model of matter is widely used to predict the behaviour of solids, liquids and gases. For this subject, the GCSE physics syllabus states that students should be able to:
Who writes GCSE packs?
All of our GCSE packs are written and developed by former GCSE physics examiners and markers. They focus on the key skills that you’ll need to do well in higher tier GCSE exams.
What are the subjects of the second paper?
The second paper covers subjects 4-8: forces; waves; magnetism and electromagnetism and space physics.
What is the syllabus for electrical circuits?
Electric circuits. Mains electricity. Static electricity. The GCSE physics syllabus states that for electric circuits, students should be able to draw and interpret circuit diagrams, including switch, lamp, fixed resistor and variable resistor. For mains electricity, you should be able to explain that a live wire may be dangerous even ...
What is the second topic of the GCSE Physics syllabus?
The second topic of the GCSE Physics Syllabus from the AQA exam board analyzes electric circuits, mains electricity and static electricity.
What subjects are taught in GCSE?
In the United Kingdom, secondary school students have a wide variety of GCSE subjects to choose from such as Architecture, Business, Biology, Engineering, English Literature, History, Maths, Religious Studies and Physics. The GCSE qualification is taken by 15 and 16-year-olds in England, Wales and Northern Ireland to mark their graduation ...
What is space physics?
Space Physics. The topic of space physics in the GCSE Physics Syllabus is of particular interest for those who love astronomy. Pupils who are studying this topic learn more about the important elements in our solar system such as the Sun, the planets, the moons, the dwarf planets, asteroids and comets.
What is the purpose of preparing for a GCSE Physics test?
Preparing for a test while having previous knowledge of what questions to expect on the examination builds confidence and increases results. Here are some of the type of questions asked on the GCSE Physics Syllabus assessments:
What are the forces in GCSE?
Students acquire essential knowledge about the most basic concepts such as gravity, contact and non-contact forces, elasticity and pressure in fluids just to name a few.
What is the last stage of GCSE?
The GCSE qualification is taken by 15 and 16-year-olds in England, Wales and Northern Ireland to mark their graduation from Key Stage 4, which is the last stage of mandatory schooling demanded by the national curriculum.
How many possible energy transfers are there?
Energy can be transferred in one of the four possible energy transfers:
Syllabus overview
Cambridge IGCSE Physics helps learners to understand the technological world in which they live, and take an informed interest in science and scientific developments. The syllabus includes the basic principles and concepts that are fundamental to the subject, some current applications of physics, and a strong emphasis on practical skills.
Resource Plus
Find out more about Resource Plus, a collection of additional teaching and learning resources which have recently been launched to support the delivery of key topics and skills in Cambridge IGCSE Physics.
Syllabuses
The syllabus year refers to the year in which the examination will be taken.
What is a GCSE in Physics?
The GCSE in Physics requires students to develop the skills, knowledge and understanding of working scientifically. Working scientifically will be assessed through examination and the completion of the eight core practicals. 1
What is GCSE science?
GCSE study in the sciences provides the foundation for understanding the material world. Scientific understanding is changing our lives and is vital to the world’s future prosperity. All students should learn essential aspects of the knowledge, methods, processes and uses of science. They should gain appreciation of how the complex and diverse phenomena of the natural world can be described in terms of a small number of key ideas that relate to the sciences and that are both inter-linked and of universal application. These key ideas include:
When was the GCSE apparatus and techniques published?
The apparatus and techniques listed in the table below are taken from the document Biology, Chemistry and Physics GCSE subject content published by the Department for Education (DfE) in June 2014.
Do you have to recall and apply equations in the exam?
Students may be asked to recall, recall and apply, or only apply these equations in the exam papers. If students are required to only apply an equation from this section the equation will be given in the question.
What subjects do you need to take for GCSE?
You also have to do foundation subjects: Computing. Physical education (PE) Citizenship. Although these are the main compulsory subjects, some schools do make other GCSE subjects compulsory, so you should double check with your school if there are any other subjects that you need to take in addition to the ones above.
What optional GCSE subjects can I take?
Optional GCSE subjects vary from school to school. Some subjects may be restricted, whereas others may not be offered at all. In some cases, if you really want to study a subject that your school doesn’t offer, you may be able to take the subject elsewhere like at college or in another school. In most cases, you’ll need to take at least one subject from the following four groups:
What are GCSEs?
GCSEs are qualifications that school children in the UK study towards when they’re 14 years old or in Year 10. GCSE stands for General Certificate of Secondary Education and chosen subjects are studied over two years with final exams taking place in Year 11. After choosing their GCSE options and completing their qualifications, school students are then able to decide whether they want to leave school education or continue studying towards A-level qualifications. Students have to stay in education or training till they're 18, although training could be an apprenticeship course taken as part of a paid job.
What GCSEs do I need to find a job?
Although every job is different, most companies will expect you to have at least 5 GCSEs including English, Maths and Science from levels A to C. In some cases, students leave secondary school with 10 GCSEs or more.
What GCSE subjects are compulsory?
Although you do get to choose most your GCSE options, there are some subjects that are compulsory. These are known as core GC SE subjects and include:
How will my GCSEs affect my future?
As a general rule, the more qualifications you gain throughout your life, the less important your GCSE options become . For example, if you end up studying at university and gaining a degree, potential employers are more likely to be interested in what you studied there, rather than what you studied when you were 16.
Why is it important to study a range of subjects?
Studying a range of subjects will provide you with a good overview of different topics and different ways of studying, which can help you identify what subjects you’re best at. Talk to your careers advisor to see if you can get a feel for what kind of career you might like to do.

Introduction
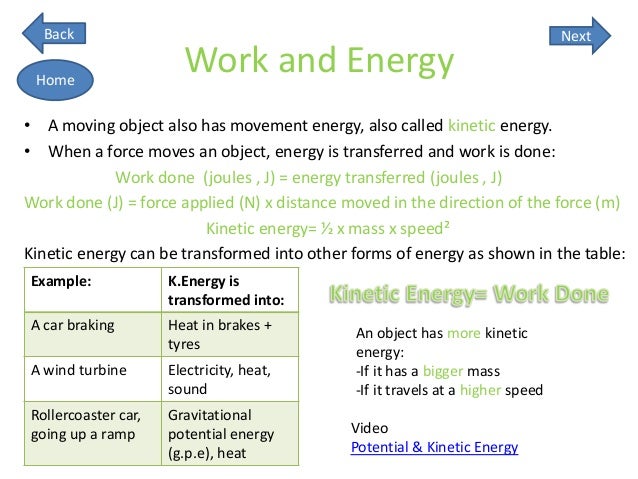
Energy
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Changes in energy stores 2. Energy and heating 3. Energy demands 4. Work, power and efficiency Students must understand energy changes in a system, and the ways energy is stored before and after such changes. You should be able to calculate the amount of energy associated with a moving object, a stretched spring and an obje…
Electricity
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Electric circuits 2. Mains electricity 3. Static electricity The GCSE physics syllabus states that for electric circuits, students should be able to draw and interpret circuit diagrams, including switch, lamp, fixed resistor and variable resistor. For mains electricity, you should be able to explain that a live wire may be dangerous even when a s…
Particle Model of Matter
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Density of materials 2. Particles in gases 3. Temperature changes and energy The particle model of matter is widely used to predict the behaviour of solids, liquids and gases. For this subject, the GCSE physics syllabus states that students should be able to: 1. Recognise/draw simple diagrams to model the difference betwee…
Atomic Structure
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Atoms, isotopes and ions 2. Models of the atom 3. Nuclear fission and fusion 4. Radioactive decay 5. Uses and dangers of radiation For this topic, the GCSE physics syllabus states that students should be able to: 1. Understand the structure of isotopes and ions 2. Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a 3. c…
Forces
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Scalar and vector quantities 2. Contact and non-contact forces 3. Gravity 4. Forces and elasticity 5. Moments, levers and gears 6. Pressure in fluids 7. Describing motion 8. Forces, acceleration and Newton’s Laws 9. Momentum The laws of gravity, elasticity, level and gears, describing motion and the pressure in fluids are all topics cov…
Waves
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Properties of waves 2. Transverse and longitudinal waves 3. Reflection and refraction 4. Sound and ultrasound (Higher Tier only) 5. Lenses 6. Black body radiation According to the GCSE physics syllabus on the subject of ‘Waves’, students should be able to: 1. Describe the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves 2. Describe evi…
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. Electromagnetic induction 2. Electromagnets 3. Magnetic fields 4. Transformers For this topic, the GCSE physics syllabus states that students should be able to: 1. Describe the attraction and repulsion between unlike and like poles for permanent magnets and explain the difference between permanent and induced magnets 2. Des…
Space Physics
- GCSE physics syllabus topics included are: 1. The expanding universe 2. The life cycle of a star 3. The Solar System Those studying this topic are expected to learn about the important elements in our Solar System, such as the Sun, the planets, the moons, the dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. The GCSE physics syllabus states that you should be able to: 1. Describe the life cycle o…
Energy
Electricity
- The second topic of the GCSE Physics Syllabus from the AQA exam board analyzes electric circuits, mains electricity and static electricity. There are various symbols that are used to identify the different components in an electric circuit. Some of the most commonly observed are: 1. Switch, 2. Lamp, 3. Fixed Resistor, 4. Variable Resistor, 5. Therm...
Particle Model of Matter
- Matter is made up of small particles called atoms and it is measured by determining its density. All matter has particles, therefore, density is used to describe how closely the particles are packed together in a solid, liquid or gas. For examples, the particles in a solid state are packed together tightly, the particles in liquids have more space to move around and in gases, they are spread ou…
Atomic Structure
- Atoms are extremely small in sizeand an atom has a nucleus containing protons and neutrons with smaller electrons that circle around the nucleus. Protons and neutrons are known for being the heaviest particles in an atom and the total number of them in an element is known as the mass number. Students also learn more about isotopes and ions.Isotopes are forms of an elem…
Forces
- The topic of forces in the GCSE Physics Syllabusis a very important and busy one. Students acquire essential knowledge about the most basic concepts such as gravity, contact and non-contact forces, elasticity and pressure in fluids just to name a few. First and foremost, pupils study the two types of physical quantities that are measured by scientists: scalar and vector. Ar…
Waves
- Waves are one of the many ways energy can be transferred between different stores. They have different parts and can be described using the following terms: 1. Rest position, 2. Displacement, 3. Peak, 4. Trough, 5. Amplitude, 6. Wavelength, 7. Time period, 8. Frequency. Wave periods and speeds are understood by applying valuable equations. There are two basic types of waves: tran…
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
- Magnetism can be contributed to the magnetic fields that surround magnets. There are two different poles on a magnet: the north pole and the south pole. The magnetic field is always stronger near the poles.It is important to note that similar poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other. There are two types of magnets: permanent and induced. Permanent magnet…
Space Physics
- The topic of space physics in the GCSE Physics Syllabusis of particular interest for those who love astronomy. Pupils who are studying this topic learn more about the important elements in our solar system such as the Sun, the planets, the moons, the dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. Information about how gravity is an important force that maintains the stable orbit of planets ar…
Sample Exam Questions
- Preparing for a test while having previous knowledge of what questions to expect on the examination builds confidence and increases results. Here are some of the type of questions asked on the GCSE Physics Syllabus assessments: 1. Multiple choice questions, 2. One and two mark questions, 3. Three and four mark questions, 4. Maths questions, 5. Practical questions, 6. …