What type of cartilage is the most springy?
Types of cartilage
- Elastic cartilage. Elastic cartilage is the most springy and supple type of cartilage. ...
- Fibrocartilage. Fibrocartilage is the toughest type of cartilage and can withstand a great deal of weight. ...
- Hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage, also known as articular cartilage, is both springy and tough. ...
How does cartilage differ from bone?
The main difference between bone and cartilage are listed below. Bones are the hard, inelastic and a tough organ that forms part of the vertebral skeleton. Cartilage is a soft, elastic and flexible connective tissue that protects the bone from rubbing against each other. Bones are of two types: compact or spongy.
What is the difference between cartilage and meniscus?
is that cartilage is (anatomy) a type of dense, non-vascular connective tissue, usually found at the end of joints, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, in the throat and between intervertebral disks while meniscus is a crescent moon, or an object shaped like it.
What type of cartilage is at the end of bones?
We have 3 types of cartilage tissue:
- Hyaline cartilage is made of collagen and has a distinctive glassy appearance. It is found inside of joints and inside the respiratory system. ...
- Elastic cartilage made of, you guessed it, elastic fibers . They can bend and snap back, like your outer ear, larynx, and epiglottis.
- Fibrocartilage is made of collagen and is in between vertebrae. ...

How many cartilage are there in the human body?
Three types of cartilage exist in the body: hyaline, fibro, and elastic cartilage.
Where are the 3 types of cartilage found?
There are three types of cartilage:Hyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone.Fibro- is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments.Elastic - is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.
What is cartilage and types of cartilage?
There are three types of cartilage: hyaline, fibrous, and elastic cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread type and resembles glass. In the embryo, bone begins as hyaline cartilage and later ossifies. Fibrous cartilage has many collagen fibers and is found in the intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis.
How many types of cartilage joints are there?
There are two types of cartilaginous joints: synchondroses and symphyses. In a synchondrosis, the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage. Synchondroses are found in the epiphyseal plates of growing bones in children.
What are the 3 functions of cartilage?
Cartilage has many functions, including the ability to resist compressive forces, enhance bone resilience, and provide support on bony areas where there is a need for flexibility. The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte, which resides within the lacunae.
What is cartilage called?
The three types of cartilage in your body are hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage.
What Colour is cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-grey in color, with a firm consistency and has a considerable amount of collagen.
What is a cartilage Class 11?
Cartilage is a soft, elastic and flexible connective tissue that protects the bone from rubbing against each other.
What is the most common type of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage. ... Elastic cartilage (like hyaline cartilage) has chondrocytes located in lacunae and the tissue is surrounded by a perichondrium . ... Fibrocartilage is intermediate in appearance between dense connective tissue and hyaline cartilage.
What is cartilage made of?
What is cartilage made of? Cartilage a strong and smooth substance made up of “chondrocytes,” or specialized cartilage cells, that produce a matrix of collagen, proteoglycans (a special type of protein) and other non-collagenous proteins.
What are the 3 cartilaginous joints?
Types of Cartilaginous JointsThe first sternocostal joint.Petrobasilar synchondrosis.Neurocentral joints of vertebrae.Spheno-occipital synchondrosis.Joints between the ends and shaft of growing long bones.
Which cartilage is strongest cartilage of the body?
White fibrous cartilageWhite fibrous cartilage is the strongest type of cartilage that is present in the spinal column in between the intervertebral discs.
Where is hyaline cartilage located?
Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread and is the type that makes up the embryonic skeleton. It persists in human adults at the ends of bones in free-moving joints as articular cartilage, at the ends of the ribs, and in the nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
Where is elastic cartilage located?
Elastic cartilage is located in the pinna of the ear, external and internal auditory tubes, epiglottis, and larynx (cuneiform cartilage). In the fresh state, owing to the presence of elastic fibers, elastic cartilage is somewhat yellow in appearance and is more opaque than hyaline cartilage (seeTable 7.1).
Where is fibrous cartilage located?
Fibrocartilage is a dense, whitish tissue with a distinct fibrous texture. It forms the intervertebral discs of the spine and menisci of the knee,as well as smaller structures such as the glenoid and acetabular labra, and the lining of bony grooves for tendons.
Where is chondrocyte found?
the cartilage tissueChondrocytes are the only specialized cell type found in the cartilage tissue. Their diameters vary in between 7 and 30 µm according to the anatomical layer. These cells form 1–2% of the tissue volume (Alford and Cole, 2005). They are responsible for functional and structural integrity of cartilage.
What Are the 3 Types of Cartilage?
Although there are areas of overlap, the 3 types of cartilage in the human body are:
What is the third most common type of cartilage?
Hyaline Cartilage. The third and most widespread type of cartilage is hyaline. Bones develop from hyaline cartilage. The supporting skeleton of a fetus is actually hyaline cartilage that later becomes ossified into bone. This ossification process ends at puberty as the cartilage turns to bone, with the exception the joints.
What is the C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber in the knee joint?
The meniscus (the C-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage that acts as a shock absorber in the knee joint), and. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) or jaw joint. The toughness, flexibility, and extra fibers of fibrous cartilage makes it ideal for certain attachment points of ligaments and tendons.
What type of collagen is found in fibrous cartilage?
Like all cartilage, fibrous cartilage contains type II collagen. However, fibrous is the only one of the 3 types of cartilage that also contains type I collagen, which is the form of collagen found primarily in bones, skin, tendons, and ligaments.
What happens to cartilage as you age?
But as we age, it’s often a different story. If you have aches, pain, and stiffness regularly —particularly if it occurs at a specific joint—you are most likely starting to experience the effects of joint cartilage degeneration, a form of arthritis. Age takes its toll on all body tissues, including cartilage, which is a type ...
Why is cartilage unique?
All cartilage is unique in that it doesn’t have a blood supply, nerve connections, or connections to the lymphatic system like other structures in the body. This lack of blood and lymph supply makes the growth and healing of cartilage slow and challenging.
Where is fibrous cartilage found?
Fibrous cartilage is found in: The intervertebral discs (the cartilage cushions between each vertebral in the spine), The capsules that surround joints, such as the joint where the pelvic bones meet in front (the pubic symphysis), The meniscus (the C-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage that acts as a shock absorber in the knee joint), and.
How many types of cartilage are there?
Types of Cartilage. There are three cartilage types in the human body. Although their components are very similar, the quantities of each component differ, providing different qualities to each type. Accordingly, each type has a particular location.
What is the most common form of cartilage?
The most common form of cartilage is hyaline cartilage. Hyalos is the Greek word for glass, which describes the appearance of this type of connective tissue – translucent, blueish-white, and shiny. Hyaline cartilage is usually only 2 – 4 mm thick (all cartilage must be thin, as there is no vascularization in this tissue type, ...
What are the main components of cartilage?
The Main Ingredients of Cartilage. Cartilage is made up of highly specialized cells called chondrocytes and chondroblasts (chondro refers to cartilage), and other extracellular material which forms the cartilage matrix. All connective tissue types within the human body are derived from the embryonal mesoderm.
Why does cartilage grow slowly in older people?
Because of this, there is little metabolic activity, and little to no new growth in cartilage tissue – one of the reasons the elderly commonly suffer from degenerative joint pain. Cartilage does continue to grow slowly, however. This can be seen in the larger ears and noses of older individuals.
What is the role of elastic cartilage?
Elastic cartilage’s role is purely structural, offering flexibility and resilience due to a mixture of elastic fibers and type II collagen fibers. It is yellow in color, and without the organized structure of fibrocartilage when viewed on a microscope slide. Types of Cartilage.
What is the role of cartilage in the body?
Cartilage is a supple tissue which allows for facial movement as well as providing a lightweight supportive structure in the external ear, and the tip and septum of the nose. In other regions it acts as a shock absorber, cushioning areas where bone meets bone and preventing abrasion and damage. A joint would also not be able to bend without ...
Which connective tissue is the last to form?
All connective tissue types within the human body are derived from the embryonal mesoderm. Bone, the strongest of the connective tissues, is the last to form and can remain in cartilage form well after birth. Increased cartilage to bone ratio enables a flexible and pliable new-born to exit the birth canal. A new-born has 300 bones, as opposed ...
What are some examples of cartilage?
Examples of tubes include the cricoid cartilage and carina of the trachea, the torus tubarius at the opening of the auditory tube, and the auricle/pinna of the ear.
What is the most abundant type of cartilage?
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in multiple areas of the body, including joints, the ear and nose, and intervertebral discs. Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant type of cartilage, plays a supportive role and assists in movement.
What is the articular cartilage of the elbow?
Articular cartilage of the elbow (sagittal view) The function of articular cartilage is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which consists mainly of proteoglycans and collagen.
Why is cartilage so slow to repair?
Moreover, cartilage has a very slow turnover and is difficult to repair due to the fact that cartilage tissue is avascular (and also aneural ). Its growth is not usually quantified by an increase in size or mass of the cartilage itself, but instead by its biomechanical properties. Chondrocytes (histological slide)
What are the cells that make up the cartilage matrix?
The chondroblasts that are caught in the matrix are called chondrocytes, and are the main type of specialized cells found in cartilage. Chondrocytes are responsible for producing large quantities of collagenous extracellular matrix and ground substance that is rich in proteoglycans and elastin fibers.
Why does cartilage breakdown occur?
Damage or injury can also happen through pathologic states, where ossification or breakdown of cartilage occurs due to dysfunction of cartilage-specific cells or synovial cells, or imbalances in the microenvironment surrounding the cartilage . Cartilage has limited reparative capacities for a number of reasons:
How does ECM affect cartilage?
Therefore, when this ECM is affected, it can lead to damage or injury. This can happen through physical mechanical forces, where excessive friction and applied forces wear down the cartilage (e.g. due to overuse or traumatic injury during athletics). Damage or injury can also happen through pathologic states, where ossification or breakdown of cartilage occurs due to dysfunction of cartilage-specific cells or synovial cells, or imbalances in the microenvironment surrounding the cartilage.
What are the different types of cartilage?
Cartilage is classified in three types, elastic cartilage, hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage, which differ in relative amounts of collagen and proteoglycan. Cartilage does not contain blood vessels (it is avascular) or nerves (it is aneural).
What is cartilage in a micrograph?
Cartilage. Light micrograph of undecalcified hyaline cartilage showing chondrocytes and organelles, lacunae and matrix. Cartilage (cartilaginous tissue) is a resilient and smooth elastic tissue, rubber-like padding that covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints and nerves, and is a structural component of the rib cage, the ear, ...
Why is cartilage repair so difficult?
Repair. Cartilage has limited repair capabilities: Because chondrocytes are bound in lacunae, they cannot migrate to damaged areas. Therefore, cartilage damage is difficult to heal. Also, because hyaline cartilage does not have a blood supply, the deposition of new matrix is slow.
What is the process of skeletal system?
In embryogenesis, the skeletal system is derived from the mesoderm germ layer. Chondrification (also known as chondrogenesis) is the process by which cartilage is formed from condensed mesenchyme tissue, which differentiates into chondroblasts and begins secreting the molecules (aggrecan and collagen type II) that form the extracellular matrix.
What is the purpose of cartilage?
Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina .
Which type of cartilage has the fewest cells?
Hyaline cartilage is found in the nose, ears, trachea, parts of the larynx, and smaller respiratory tubes. Fibrous cartilage has the fewest cells so it has the most intercellular space. Fibrous cartilage is found in the spine and the menisci.
How is biological engineering used to make cartilage?
Biological engineering techniques are being developed to generate new cartilage, using a cellular "scaffolding" material and cultured cells to grow artificial cartilage.
What are the three types of cartilage?
Cartilage: The three types of cartilage. There are three types of cartilage: Hyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone. Fibro - is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments. Elastic - is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.
Which type of cartilage is the weakest?
Hyaline cartilage has widely dispersed fine collagen fibres (type II), which strengthen it. The collagen fibres are hard to see in sections. It has a perichondrium, and it is the weakest of the three types of cartilage. Look at the eMicroscope of a section of cartilage on the left.
What is hyaline cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage. This type of cartilage has a glassy appearance when fresh, hence its name, as hyalos is greek for glassy. It looks slightly basophilic overall in H&E sections. Hyaline cartilage has widely dispersed fine collagen fibres (type II), which strengthen it. The collagen fibres are hard to see in sections.
Where are chondrocytes found?
In elastic cartilage, the chondrocytes are found in a threadlike network of elastic fibres within the matrix.
Articular Cartilage
This type of cartilage covers the end of the femur bone, where it joins the tibia at the knee. It is smooth, white, and shiny, and when a person is healthy, it allows the ends of the two bones to glide over each other without problems.
Meniscal Cartilage
There are two meniscal cartilages on each knee: one on the inside and one on the outside, and they help to absorb the shock when you walk, run, or jump. They are usually not easy to injure, so a significant shock or injury is required to cause damage.
1. Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the most abundant in our body, being the one that is present not only in the joints, but also in the nose, trachea, bronchi, larynx and the ventral ends of the ribs.
2. Elastic cartilage
The elastic cartilage stands out, in addition to its special elasticity ( something logical seeing its name), superior to that of the other two types, due to its yellowish coloration.
3. Fibrous cartilage
Finally, fibrous cartilage, also known as fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilaginous tissue present in the insertion of some tendons (the bundles of collagen-rich connective fibers that connect muscles to bones), in the articular discs, the intervertebral discs (in the spine), the pubic symphysis, which is the connection between the two parts of the pubis, the menisci of the knees, the jaw, and essentially everywhere there is an intersection between ligaments (bundles that join bone to bone) and tendons..

Overview
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater pro…
Structure
In embryogenesis, the skeletal system is derived from the mesoderm germ layer. Chondrification (also known as chondrogenesis) is the process by which cartilage is formed from condensed mesenchyme tissue, which differentiates into chondroblasts and begins secreting the molecules (aggrecan and collagen type II) that form the extracellular matrix. In all vertebrates, cartilage is the mai…
Function
The mechanical properties of articular cartilage in load-bearing joints such as the knee and hip have been studied extensively at macro, micro, and nano-scales. These mechanical properties include the response of cartilage in frictional, compressive, shear and tensile loading. Cartilage is resilient and displays viscoelastic properties.
Lubricin, a glycoprotein abundant in cartilage and synovial fluid, plays a major role in bio-lubricati…
Clinical significance
Several diseases can affect cartilage. Chondrodystrophies are a group of diseases, characterized by the disturbance of growth and subsequent ossification of cartilage. Some common diseases that affect the cartilage are listed below.
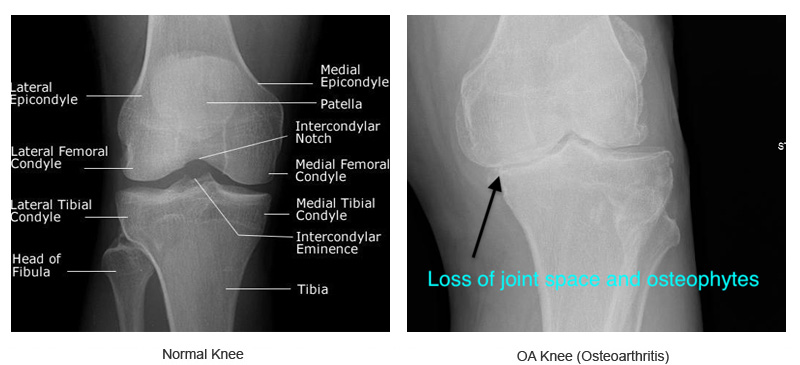
• Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is a disease of the whole joint, however, one of t…
Other animals
Cartilaginous fish (chondrichthyes) or sharks, rays and chimaeras have a skeleton composed entirely of cartilage.
Cartilage tissue can also be found among some arthropods such as horseshoe crabs, some mollusks such as marine snails and cephalopods, and some annelids like sabellid polychaetes.
The most studied cartilage in arthropods is the branchial cartilage of Limulus polyphemus. It is …
Plants and fungi
Vascular plants, particularly seeds, and the stems of some mushrooms, are sometimes called "cartilaginous", although they contain no cartilage.
Biomechanics
• Biomechanics
Further reading
• Keller-Peck C (2008). Vertebrate Histology, ZOOL 400. Boise State University.