
...
Point Defects
- Stoichiometric defect.
- Frenkel defect.
- Schottky defect.
What are the defects in real crystals?
Real crystals contain large numbers of defects. Defects may affect only a single point in the lattice (a point defect ), a row of lattice points (a line defect ), or a plane of atoms (a plane defect ).
What are the different types of defects in metals?
Metals can have various types of defects. A point defectA defect in a crystal that affects a single point in the lattice. is any defect that involves only a single particle (a lattice point) or sometimes a very small set of points.
What are the different types of point defects?
Crystal defect. Since all atoms occupy space, extra… Point defects include the Frenkel type, the Schottky type, and the impurity type. The Frenkel defect involves a single ion, which is displaced from its normal lattice point and shifts to a nearby interstice, or space, between atoms in the lattice.
What is the difference between Schottky and crystal defect?
Crystal defect. Point defects include the Frenkel type, the Schottky type, and the impurity type. The Frenkel defect involves a single ion, which is displaced from its normal lattice point and shifts to a nearby interstice, or space, between atoms in the lattice. In the Schottky defect, two ions of opposite sign leave the lattice.
Why is the external surface of a crystal a defect?
What is a defect in chemistry?
What type of defect is a single ion?
What is the term for a defect in the regular spacing of atoms?
What are impurity defects?
Where do surface defects occur?
Is a crystal always perfect?
See 4 more
About this website
What are the types of defects in crystals?
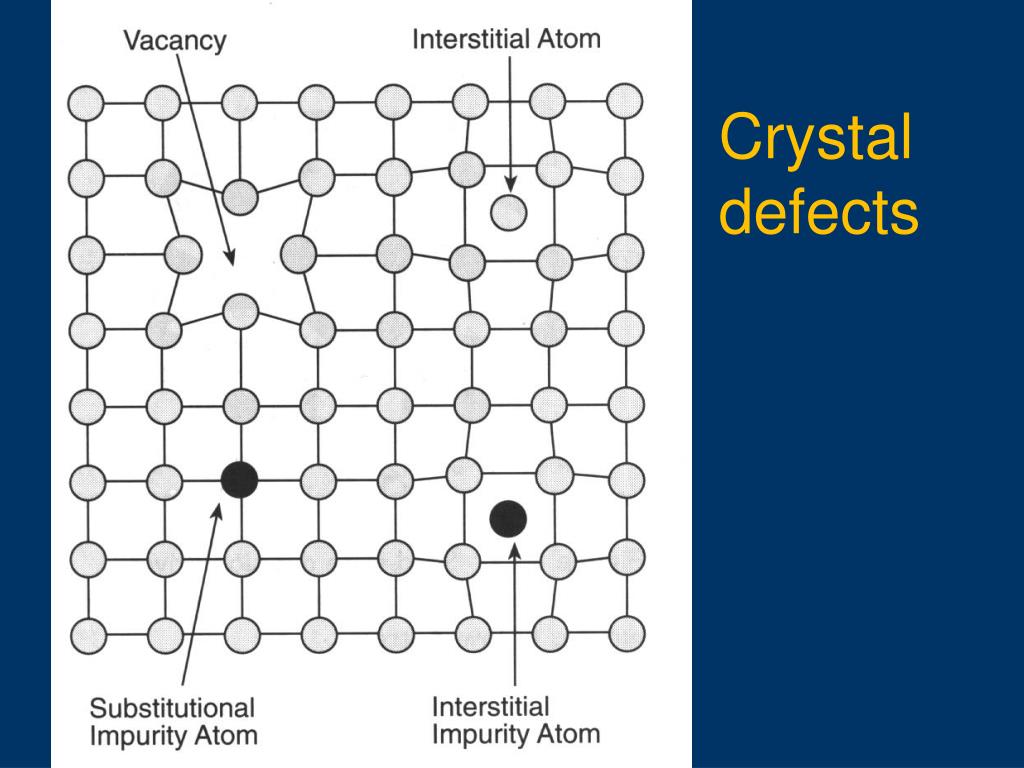
Point defects (vacancies, interstitial defects, substitution defects)Line defect (screw dislocation, edge dislocation)surface defects (material surface, grain boundaries) ... Substitutional – one atom is replaced by as different type of atom.Interstitial – extra atom is inserted into the lattice structure at a.
What are the 12 types of defects?
Table of ContentTypes of Defects in Solids.Stoichiometric Defect.Schottky Defect.Frenkel Defect.Impurity Defects.Non-stoichiometric Defects.Metal Deficiency Defect.
How many types of defects are there?
3 Types3 Types of defects every importer needs to know. Quality control professionals typically classify quality defects into three main categories: minor, major and critical. The nature and severity of a defect determines in which of the three categories it belongs.
What are crystal defects Class 12?
The irregularities or deviations from ideal arrangement around a point or an atom in a. crystalline substance. The irregularities or deviations from ideal arrangement in entire rows of lattice points are known as line defects. These irregularities are called crystal defects.
What are point defects 12th chemistry?
Solution : Point defect : The defect or imperfection produced in the arrangement of a point like constituents particle, e.g. an atom or an ion or a molecule in the crystalline structure is called point defect.
What are the 3 types of defects give examples?
There are three types of product defects: design defects, manufacturing defects, and warning/instruction defects. All three types of defects have to do with a product being faulty or inadequate in some way.
What is a defect list?
In construction management, a defect list is a list of items that need to be fixed before a project is considered complete.
What is point defect in crystal?
Point defects are the simplest defects that can be found in any crystal phase. They are localized on single sites of the crystal structure; these sites can be regularly occupied by some chemical species or else regularly unoccupied sites of the vacant interstitial sublattice.
What are the 3 types of defects give examples?
There are three types of product defects: design defects, manufacturing defects, and warning/instruction defects. All three types of defects have to do with a product being faulty or inadequate in some way.
What is the major defect?
Major Defect – A defect that is likely to result in failure; reducing the usability of the product and obvious appearance defects affecting the sale ability or shorten the life cycle of the product.
What are the defects in quality?
Product defects, also known as Quality Defects, may be defined as attributes of a medicinal product or component which may affect the quality, safety and/or efficacy of the product, and/or which are not in line with the approved Product Authorisation (PA) or Veterinary Product Authorisation (VPA) file, or other ...
What are types of defects in garments?
Different types of defects which are found in garments industry and their remedies.Seam Puckering. ... Open seam or broken seam. ... Broken Stitch. ... Drop stitch/Skipped stitch. ... Uncut/ loose thread. ... Distorted knitting. ... Seam slippage. ... Causes:
4 Main Types of Point Defects in Crystals | Metallurgy
ADVERTISEMENTS: Various types of point defects are: 1. Vacancy 2. Interstitialcy 3. Frenkel Defect 4. Impurity Atoms. A point defect is a very localised disruption in the regularity of a lattice. It is a defect of dimensions just like a point (zero dimensions). The size of the defect could be one atom, or two atomic […]
Defects in Crystal Structure: Definition, types of defects, FAQs
Line Defect. The defect is due to irregularity in a complete line, a row of lattice points of the constituent. Surface Defect. Surface defects are the boundaries or planes that separate material into regions, with each region having the same crystalline structure but different orientation.
Defects in crystal structure: sources and types of defects
Non-Stoichiometric Defects in Crystal Structure: There are many compounds in which the ratio of positive and negative ions present in the compound differs from that required by the ideal chemical formula of the compound.
Imperfections (Defects) in Crystals | Metallurgy - Engineering Notes India
ADVERTISEMENTS: The perfectly regular crystal structures that have been considered upto now are called ideal crystals in which atoms are arranged in a regular way. In actual crystals, however, imperfections or defects are always present and their nature and effects are very important in understanding the properties of crystals. These imperfections affect the properties of […]
Crystal Defect - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
M. RÜHLE, M. WILKENS, in Physical Metallurgy (Fourth Edition), 1996 4.7.1. The displacement field. Lattice defects cause displacements R(r n) ≡ Rn of the atoms from their positions rn in the defect-free reference lattice *.In general, |R n | is of the order of, or smaller than, the interatomic distances. Here we assume for simplicity that the displacements do not vary appreciably over the ...
What are the different types of defects in metals?
Metals can have various types of defects. A point defectA defect in a crystal that affects a single point in the lattice. is any defect that involves only a single particle (a lattice point) or sometimes a very small set of points. A line defectA defect in a crystal that affects a row of points in the lattice. is restricted to a row of lattice points, and a plane defectA defect in a crystal that affects a plane of points in the lattice. involves an entire plane of lattice points in a crystal. A vacancyA point defect that consists of a single atom missing from a site in a crystal. occurs where an atom is missing from the normal crystalline array; it constitutes a tiny void in the middle of a solid ( Figure 8.4.1 ). We focus primarily on point and plane defects in our discussion because they are encountered most frequently.
Which solids are susceptible to cracking when stressed?
Work-hardened metals and covalent solids such as diamonds are both susceptible to cracking when stressed. Explain how such different materials can both exhibit this property.
How to determine if an impurity is a substitutional impurity?
Using the data in Table 8.4.1 and the atomic radii in Figure 3.1.7, determine whether the impurities listed are similar in size to an iron atom. Then determine whether each impurity is chemically similar to Fe. If similar in both size and chemistry, the impurity is likely to be a substitutional impurity. If not, it is likely to be an interstitial impurity.
How to determine if a stoichiometry is incorrect?
A Identify the unit cell of the host compound. Compute the stoichiometry if 0.01% of the Na + sites are occupied by Ca 2+. If the overall charge is greater than 0, then the stoichiometry must be incorrect.
How to make a crystal if it is 100% pure?
Even if a substance were 100% pure, forming a perfect crystal would require cooling the liquid phase infinitely slowly to allow all atoms, ions, or molecules to find their proper positions . Cooling at more realistic rates usually results in one or more components being trapped in the “wrong” place in a lattice or in areas where two lattices that grew separately intersect.
Which is the second most abundant metal in the Earth's crust?
After aluminum, iron is the second most abundant metal in Earth’s crust. The silvery-white, ductile metal has a body-centered cubic (bcc) unit cell with an edge length of 286.65 pm.
Is substitution possible without disruption of the ionic packing?
Since O 2− and F − are both very similar in size, substitution is possible without disruption of the ionic packing. The difference in charge, however, requires the formation of a vacancy on another F − site to maintain charge neutrality.
What is missing from a crystal?
One or more atoms of the crystal are missing from their corresponding lattice site.
What is the Frenkel defect?
Frenkel Defect – Frenkel defect is also a point crystallographic defect which is usually observed in ionic compounds. It is named after a Soviet physicist Yakov Frenkel and is different from Schottky defect in terms of its occurrence and characteristics.
What are Point Defects?
Those defects in the crystals which occur around an atom or particle are called point defects. These defects occur only at or around a single lattice point. They do not extend in space in any dimension. That’s why they are also called zero dimensional (0-D) defects. These are the smallest possible defects in any crystalline solid material. Point defects occur when –
What is the point defect that occurs when cation and anion leave their corresponding lattice sites and?
The point defect which occurs when cation and anion leave their corresponding lattice sites and create a pair of vacancy defects is called Schottky defect. In KCl crystals Schottky defect is found. It shown below – (images will be updated soon)
What is a Schottky defect?
Schottky Defect - Schottky defect is one such point defect which is observed in various crystals. Named after a German physicist, Walter H. Schottky, this defect occurs commonly in ionic crystals where the size of cation and anion is similar. Schottky defects usually occur when heat is applied to the ionic compound crystal.
What is the point defect that occurs when an atom takes the interstitial position of the lattice structure?
It occurs due to imperfect packing during crystallization. Interstitial Defect – The point defect which occurs when an atom takes the interstitial position of the lattice structure is called interstitial defect. The atom can be of the same crystal or foreign crystal/material. If the atom is of the same crystal, ...
What are stoichiometric defects?
Stoichiometric Defects – The compounds which obey the law of definite proportions, the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass are called stoichiometric compounds. The defects in crystals which do not disturb the stoichiometry of the compound or crystal are called stoichiometric defects.
What are the different types of point defects?
Various types of point defects are: 1. Vacancy 2. Interstitialcy 3. Frenkel Defect 4. Impurity Atoms. A point defect is a very localised disruption in the regularity of a lattice. It is a defect of dimensions just like a point (zero dimensions). The size of the defect could be one atom, or two atomic diameters, which is just like a point.
What is interstitial defect?
An interstitial defect is produced if any of the small sized atoms (of B, C, H, N, O) is present in the interstitial site. The sizes of their atoms are larger than the interstitial site they occupy. Consequently, the surrounding lattice is compressed and distorted, Fig. 4.7 (c). Once these atoms are introduced in the structure (impurity such as hydrogen, or alloying addition such as carbon), the number of interstitial atoms in the structure remains nearly constant, even when the temperature is changed. Normally, the concentration of these atoms in a very pure metal is lower than the concentration of vacancies.
What is the name of the defect that forces an atom to move?
When an atom is shifted from a normal lattice site (thus creating vacancy) and is forced into interstitial position, the resulting pair of point defects (a vacancy as well as the interstitialcy) together is called a Frenkel defect, as illustrated in Fig. 4.5.
Is the number of interstitialcies in an ordinary metal negligibly small?
The number of interstitialcies in an ordinary metal is thus, negligibly small compared to the number of vacancies. Under unusual conditions, such as exposure of the metal to high energy neutrons in a nuclear reactor, or even by drastic cold working, a significant number of interstitialcies can be produced.
What is the classification of crystallographic defects?
Classification of crystallographic defects (microscopic defects) is frequently made according to the geometry or dimensionality of the defect.
What are three dimensional defects called?
Three-dimensional macroscopic defects are called bulk defects. They generally occur on a much larger scale than the microscopic defects. These macroscopic defects generally are introduced into a material during refinement from its raw state or during fabrication processes. These include cracks, pores, foreign inclusions, and other phases. The working and forging of metals can cause cracks that act as stress concentrators and weaken the material. Any welding or joining defects may also be classified as bulk defects.
What is a discontinuity of a crystal structure?
A planar defect is a discontinuity of the perfect crystal structure across a plane. Interfacial defects are boundaries that have two dimensions and normally separate regions of the materials that have different crystal structures and/or crystallographic orientations. Interfacial defects exist at an angle between any two faces of a crystal or crystal form. These imperfections are found at free surfaces, domain boundaries, grain boundaries, or interphase boundaries.
What is the discrepancy in mechanical strengths?
During the 1930s it was theorized that this discrepancy in mechanical strengths could be explained by a type of linear crystalline defect that has come to be known as a dislocation. The term ‘dislocation’ referring to a defect on the atomic scale was coined by G. I. Taylor in 1934.
What is bulk defect?
Bulk Defects. Three-dimensional macroscopic or bulk defects, such as pores, cracks, or inclusions.
What are small regions where there are no atoms?
Voids — small regions where there are no atoms, and which can be thought of as clusters of vacancies.
What is similar valency?
Similar valency a solid solution mixes with others to form a new solution
Why is the external surface of a crystal a defect?
The actual external surface of a crystal is also a surface defect because the atoms on the surface adjust their positions to accommodate for the absence of neighbouring atoms outside the surface. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
What is a defect in chemistry?
A defect is a small imperfection affecting a few atoms. The... Line defects, or dislocations, are lines along which whole rows of atoms in a solid are arranged anomalously. The resulting irregularity in spacing is most severe along a line called the line of dislocation. Line defects can weaken or strengthen solids.
What type of defect is a single ion?
Point defects include the Frenkel type, the Schottky type, and the impurity type. The Frenkel defect involves a single ion, which is displaced from its normal lattice point and shifts to a nearby interstice, or space, between atoms in the lattice. In the Schottky defect, two ions of opposite sign leave the lattice.
What is the term for a defect in the regular spacing of atoms?
Such an imperfection (crystal defect) in the regular spacing of atoms changes the electrical and optical properties of the crystal. Colour centres are vacancies that give colour to many solids. Vacancies can be created by mechanical deformation of the crystal, rapid cooling from high temperature, or the impact…
What are impurity defects?
Impurity defects are foreign atoms that replace some of the atoms making up the solid or that squeeze into the interstices; they are important in the electrical behaviour of semiconductors, which are materials used in computer chips and other electronic devices. Read More on This Topic. crystal: Crystal defects.
Where do surface defects occur?
Surface defects may arise at the boundary between two grains, or small crystals, within a larger crystal. The rows of atoms in two different grains may run in slightly different directions, leading to a mismatch across the grain boundary.
Is a crystal always perfect?
A crystal is never perfect; a variety of imperfections can mar the ordering. A defect is a small imperfection affecting a few atoms. The simplest type of defect is a missing atom and is called a vacancy. Since all atoms occupy space, extra…

Defects in Crystal Structure
Types of Crystal Defects
- The crystal defects are of four types. 1. Point Defect: It is further classified into Vacancy Defect, Interstitial Defect and Impurity Defect. 2. Line Defect. 3. Surface Defect. 4. Volume Defect.
Electrical Properties
- Elemental solids are divided into three categories namely metals, non-metals and metalloids. In the modern periodic table, non-metals are placed on the right side of the table. There are seventeen non-metals. Most of the non-metals in the periodic table are separated from metals by metalloids like boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony tellurium, polonium, astatine etc. Th…
Magnetic Properties
- While electrons are revolving around the nucleus in various orbits, they are also spinning about their own axis. A spinning charge generates a magnetic field. Hence spinning electrons act like tiny magnets. Any electron orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons. If an orbital contains only one electron then it may spin either clockwise or anticlockwise. The unbalanced s…
What Are Crystal Defects?
- An ideal crystal can be described in terms of a three-dimensionally periodic arrangement of points called lattice and an atom or group of atoms associated with it. Crystal lattice = Lattice + Motif where the lattice is a 3D periodic arrangement of points and Motif is an atom or group of atoms. Any deviations from the perfect arrangement of atoms in a crystal are called crystal defects. A cr…
Types of Crystal Defects
- Classification of crystal defects (microscopic defects) is frequently made according to the geometry or dimensionality of the defect. Other macroscopic defects that are far larger than microscopic exist in all solid materials, such as cracks, pores, foreign inclusions, and other phases. Various types of crystal defects which are studied to improve the properties are given b…
Point Defects
- Point defects (type of crystal defects) have atomic dimensions and occur only at or around a single lattice point. They are not stretched in any dimension in space. Different types of point defects in crystals are shown below - 1. Vacancy Defects 2. Interstitial Defects 3. Substitutional Defects 4. Frenkel Defects 5. Schottky Defects
Line Defects
- Line defects (type of crystal defects) typically span a large number of atoms. Dislocations are line defects that only appear in crystalline materials. A dislocation is a linear or one-dimensional imperfection in which certain atoms are misaligned. Dislocations are particularly essential in materials science because they contribute to material mechanical strength. The two fundamenta…
Planar Or Interfacial Defects
- Interfacial defects (type of crystal defects) are two-dimensional barriers that generally separate sections of materials with various crystal structures and/or crystallographic orientations. Different types of planar defects are - 1. Grain Boundaries 2. Twinning